Themed collection Focus article collection

Engineering the nano-bio interface: challenges and opportunities for predicting the surface properties of monolayer-protected nanoparticles
Nanoparticle surfaces can be coated with a monolayer of functional ligands. We discuss how tuning interactions with biological systems requires careful selection of the nanoparticle core and the physicochemical properties of the ligands.

Mater. Horiz., 2025,12, 6428-6439
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5MH00310E
Beyond the four core effects: revisiting thermoelectrics with a high-entropy design
Beyond conventional design: unlocking thermoelectric potential for recuperating low-exergy industrial waste heat through high-entropy strategies and data-driven insights.

Mater. Horiz., 2025,12, 5946-5956
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5MH00356C
Light-to-matter chirality transfer in plasmonics
Introduction and review of work developing chirality in achiral plasmonic structures using only circularly polarized light to induce asymmetry, with a detailed introduction to chirality and light–matter interaction in molecules and nanostructures.

Mater. Horiz., 2025,12, 4940-4969
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5MH00179J
Superfluorescent upconversion nanoparticles as an emerging second generation quantum technology material
Ultra-fast upconverted room temperature quantum superfluorescence promises more photons per unit time. This article explores superfluorescence and how these particles can be considered as second-generation quantum technology materials.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2025,10, 1242-1249
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NH00651H
Enlightening molecular logic: basics, tools and techniques for newcomers
This paper demystifies luminescent molecular logic, detailing principles, experimental protocols, and innovative applications for sustainable, next-generation computing that transcends silicon limits and enables molecular-scale processing.

Mater. Horiz., 2025,12, 4016-4026
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5MH00192G
Unraveling the myths and mysteries of photon avalanching nanoparticles
This Focus Article dispels 19 common myths and misconceptions about photon avalanching nanoparticles to remove the shroud of mystery surrounding the mechanism, utility, and future prospects of these uniquely nonlinear optical materials.

Mater. Horiz., 2025,12, 3575-3597
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4MH01798F
Crucial role of structural design on performance of cryogel-based EMI shields: an experimental review
An experimental review of the shielding performance of graphene-based cryogels fabricated through distinct methods, with a specific focus on structural design.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2024,9, 2234-2247
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NH00210E
Towards an information-based theory of structure
Extracopularity is a local structural phenomenon characterised by the occurrence of fewer different bond angles than combinatorially possible.

Mater. Horiz., 2024,11, 5464-5469
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4MH00332B
Nanoscience and nanotechnology for water remediation: an earnest hope toward sustainability
Contextualising the promise of nanoscience and nanotechnology for water pollution remediation.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2024,9, 885-899
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NH00056K
Dual-ion conductors: from liquid to solid
This focus article primarily discusses solid dual-ion conductors, summarizes the design principles for building solid dual-ion conductors, and anticipates several potential applications based on their functional characteristics.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2024,9, 667-674
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NH00011K
Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy in drug delivery: a roadmap for correct characterization of nanoparticles and interpretation of results
In this focus article, we provide a scrutinizing analysis of transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering as the two common methods to study the sizes of nanoparticles with focus on the application in pharmaceutics and drug delivery.

Mater. Horiz., 2023,10, 5354-5370
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MH00717K
Bimetallic core–shell nanocrystals: opportunities and challenges
We present an overview of the opportunities provided by bimetallic core–shell nanocrystals, followed by a discussion of the challenges and promising solutions regarding the elucidation of the true surface composition and its dynamics.
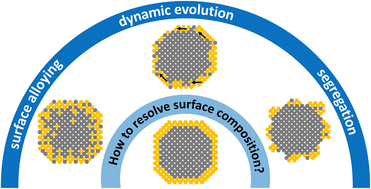
Nanoscale Horiz., 2023,8, 1194-1204
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NH00098B
Ionic and electronic energy diagrams for hybrid perovskite solar cells
Generalized energy diagrams facilitate the understanding of the ionic and electronic charge carrier equilibrium in the bulk and at interfaces of devices based on mixed conductors, such as hybrid perovskite solar cells.
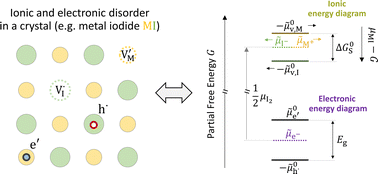
Mater. Horiz., 2023,10, 1641-1650
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2MH01569B
Organic building blocks at inorganic nanomaterial interfaces
Inorganic–organic interfaces: a tutorial on using organic functional groups to enhance the performances and/or enable new functionality of inorganic nanomaterials.
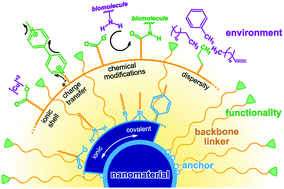
Mater. Horiz., 2022,9, 61-87
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH01294K
Engineering of flat bands and Dirac bands in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (COFs): relationships among molecular orbital symmetry, lattice symmetry, and electronic-structure characteristics
An effective framework for the band engineering in 2D covalent organic frameworks is revealed by describing the fundamental relationships among the electronic structures, the lattice symmetries, and the frontier molecular orbitals of building units.
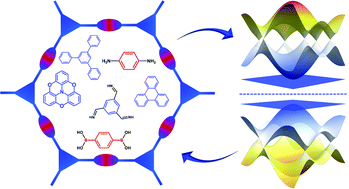
Mater. Horiz., 2022,9, 88-98
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH00935D
Scattering techniques for mixed donor–acceptor characterization in organic photovoltaics
The effects of mixing in organic photovoltaics are unclear partly due to challenges in characterization. X-Ray and neutron scattering techniques have been successful in quantifying mixing but meet new challenges with emerging non-fullerene systems.
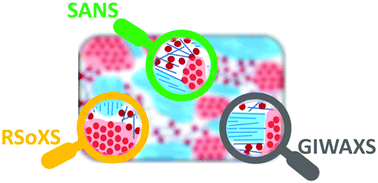
Mater. Horiz., 2022,9, 43-60
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH01219C
Plasmons: untangling the classical, experimental, and quantum mechanical definitions
Plasmons have been widely studied over the past several decades because of their ability to strongly absorb light and localize its electric field on the nanoscale, leading to applications in spectroscopy, biosensing, and solar energy storage.
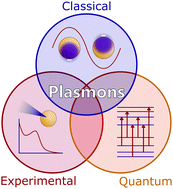
Mater. Horiz., 2022,9, 25-42
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH01163D
Electronic properties of metal halide perovskites and their interfaces: the basics
Metal halide perovskites exhibit complex electronic properties. The presently identified fundamental concepts and phenomena governing the electronic behavior of this material class are addressed in this article.
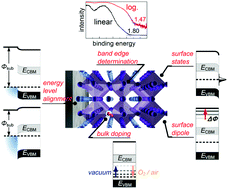
Mater. Horiz., 2022,9, 17-24
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH01106E
Structural complexity in Prussian blue analogues
We survey the most important kinds of structural complexity in Prussian blue analogues and their implications for materials function. In particular, we explore the challenges for K2Mn[Fe(CN)6], the leading cathode material for K-ion batteries.
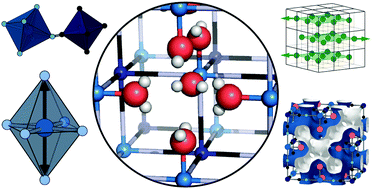
Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 3178-3186
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH01124C
Atomic vibration as an indicator of the propensity for configurational rearrangements in metallic glasses
Vibrational parameters fare better in correlating with local properties than purely static structural parameters.
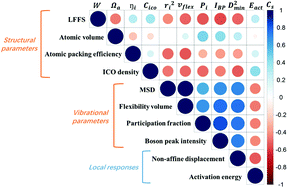
Mater. Horiz., 2021,8, 2359-2372
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MH00491C
Nanoarchitectonics: what's coming next after nanotechnology?
The nanoarchitectonics concept has the ability to bridge nanoscale science and visual size materials. The final goal of nanoarchitectonics approaches is the creation of living-creature-like functional material systems from simple nanoscale objects.
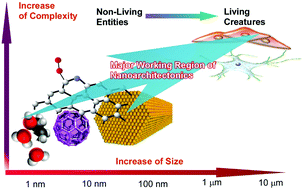
Nanoscale Horiz., 2021,6, 364-378
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00680G
Technology progress on quantum dot light-emitting diodes for next-generation displays
This article focuses on state-of-the-art technologies used in the research on materials, devices and processes to achieve high-performance QD-LEDs.
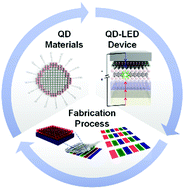
Nanoscale Horiz., 2021,6, 68-77
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00556H
Are two-dimensional materials radiation tolerant?
Due to their low weight, small size and low power consumption, two-dimensional materials are expected to be used in space applications. This brings about the issue of their radiation hardness, which is briefly discussed in this article.
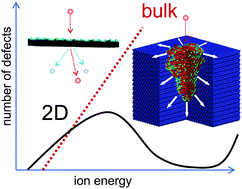
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 1447-1452
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00465K
A structural chemistry look at composites recycling
Composite materials, especially carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, are a class of structural materials now commonly used in aircraft, marine, and other applications, with emerging large-scale use in the automotive and civil engineering applications.
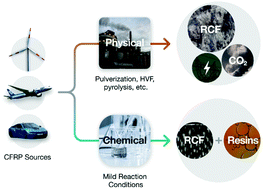
Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 2479-2486
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH01085E
Ultrasmall Au nanoclusters for bioanalytical and biomedical applications: the undisclosed and neglected roles of ligands in determining the nanoclusters' catalytic activities
The structure and biocatalytic activities of Au NCs are discussed from the perspective of the ligands, with particular emphasis on the exploration of the undisclosed and neglected roles of shell ligands in the biocatalytic activities of Au NCs.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 1355-1367
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00207K
Hollow multishelled structures revive high energy density batteries
This Focus article clarifies that hollow multishelled structure-based electrode is indispensable to realize practically high energy density of rechargeable batteries.
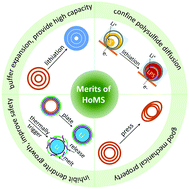
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 1287-1292
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00311E
Good or evil: what is the role of water in crystallization of organometal halide perovskites?
Water modulates the nucleation, growth and stability of halide perovskites, which can be rationally controlled.
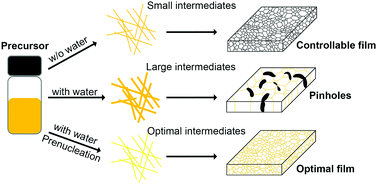
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 1147-1154
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00270D
Alloy scattering of phonons
Solid-solution alloy scattering of phonons is a demonstrated mechanism to reduce the lattice thermal conductivity.
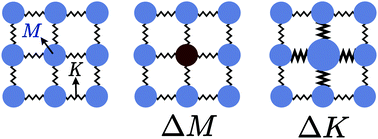
Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1452-1456
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01990A
Thermally assisted delayed fluorescence (TADF): fluorescence delayed is fluorescence denied
Thermally assisted delayed fluorescence (TADF) allows for efficient collection of both singlet and triplet excitons with both emitting through the singlet channel. TADF opens the door to photo- and electroluminescence efficiencies close to 100%.
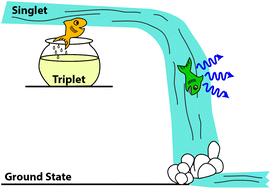
Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 1210-1217
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MH00276C
Single atom catalysts: a surface heterocompound perspective
Evolution of heterogeneous catalysts with steady down-sizing: from small particles, clusters, dots to single atoms, and now the “surface heterocompound”.
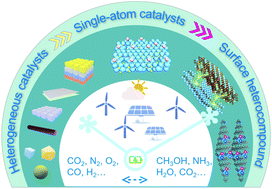
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 757-764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NH00088D
Materials science based on synthetic polysaccharides
Automated Glycan Assembly produces well-defined oligosaccharides for detailed structural characterization. These glycans can assemble into supramolecular materials with different morphologies.

Mater. Horiz., 2020,7, 963-969
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH01936G
Thickness of elemental and binary single atomic monolayers
The thickness of monolayers is a fundamental property of two-dimensional (2D) materials that has not found the necessary attention. Since the boundary is not well-defined and it changes its value with the surrounding, the thickness is difficult to grasp.
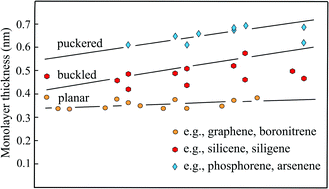
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 385-399
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00658C
Small-angle X-ray scattering of nanoporous materials
Schematic of the general process of small-angle X-ray scattering acquisition, fitting, and modeling to determine material parameters of nanoporous materials.
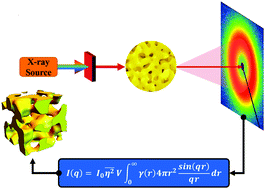
Nanoscale Horiz., 2020,5, 12-24
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00347A
Will surface effects dominate in quasi-two-dimensional gallium oxide for electronic and photonic devices?
The ultra-wide band gap semiconductor Ga2O3 has advantages for power electronics applications in the automotive industry, data center power management and industrial systems but attention must be paid to its surface sensitivity to the environment.
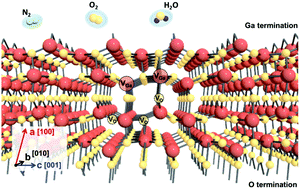
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 1251-1255
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00273A
The impact of nanoparticle shape on cellular internalisation and transport: what do the different analysis methods tell us?
This focus article looks at how nanoparticle shape affects cellular internalisation of nanoparticles and what different analysis methods can tell us.
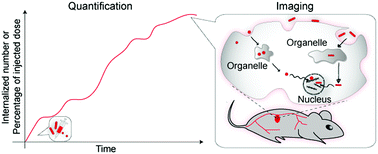
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 1538-1547
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH00664H
Quantum-confined superfluid
The quantum-confined superfluid concept is introduced, and its applications in chemistry and biology are summarized.
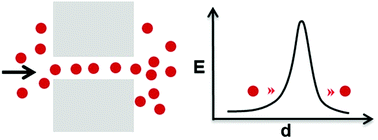
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 1029-1036
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00214F
When defects become ‘dynamic’: halide perovskites: a new window on materials?
If defects in materials cost more (energy) than decomposing them, defect densities will be low and thermodynamically controlled, with the right kinetics, as for halide perovskites.
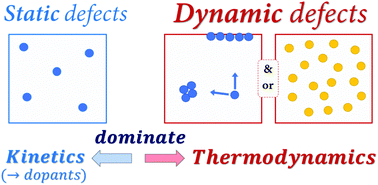
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 1297-1305
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH00606K
Nanomechanics of low-dimensional materials for functional applications
When materials’ characteristic dimensions are reduced to the nanoscale regime, their mechanical properties will vary significantly to that of their bulk counterparts.
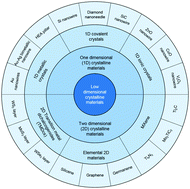
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 781-788
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00118B
Aggregation-induced emission: fundamental understanding and future developments
In-depth discussion on recent progress of fundamental understanding of AIE mechanisms, identifying the existing challenges and opportunities for future developments.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 428-433
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01331D
How to quantify isotropic negative thermal expansion: magnitude, range, or both?
Negative thermal expansion (NTE) is the counterintuitive material property of volume contraction on heating. We compare different systems with contrasting mechanisms for isotropic NTE using the metric of NTE capacity.
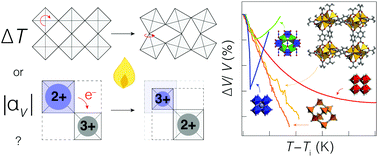
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 211-218
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01065J
Physical magnification of objects
For hundreds of years, scientists have magnified images of objects to reveal their detailed composition and structure. Now, scientists are beginning to physically magnify objects themselves.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 11-13
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00931G
An introduction to ratchets in chemistry and biology
This article describes the functions and mechanisms of particle and electron ratchets, and the interplay between theory and experiment in this field of non-equilibrium transport.

Mater. Horiz., 2017,4, 310-318
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH00062F
Engineering dendrimers to produce dendrimer dipole excitation based terahertz radiation sources suitable for spectrometry, molecular and biomedical imaging
Systematic engineering of PAMAM dendrimer CNDPs (i.e., surface chemistry and interior compositions) produced hyperpolarizable substrates that generated terahertz radiation when exposed to a pump laser.
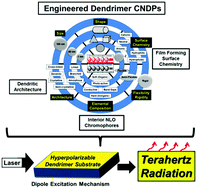
Nanoscale Horiz., 2017,2, 127-134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NH00010C
Thermoresponsive polymers with lower critical solution temperature: from fundamental aspects and measuring techniques to recommended turbidimetry conditions
This focus article addresses fundamental and practical aspects of investigating polymers with lower critical solution temperature behavior.
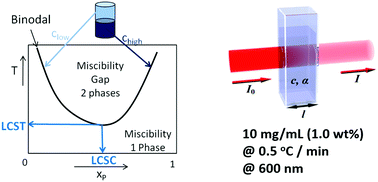
Mater. Horiz., 2017,4, 109-116
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH00016B
Doping two-dimensional materials: ultra-sensitive sensors, band gap tuning and ferromagnetic monolayers
Well-designed defects can lead to unprecedented properties and interesting applications. For example, heteroatom-doped graphene exhibits enhanced Raman scattering for ultrasensitive detection of certain molecules.
Nanoscale Horiz., 2017,2, 72-80
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NH00192K
The living dead – common misconceptions about reversible deactivation radical polymerization
We illustrate common misconceptions and errors when interpreting polymerization data from ‘Living/controlled’ radical polymerization, preferably termed ‘reversible deactivation radical polymerization’ (RDRP). Avoiding the discussed errors leads to better defined materials for soft matter materials applications.
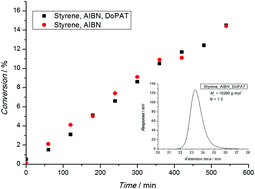
Mater. Horiz., 2016,3, 471-477
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MH00265J
Spraying functional fibres by electrospinning
This brief focus article shows you how to prepare functional fibers with controllable morphology, alignment and composition via an electrospinning technique.
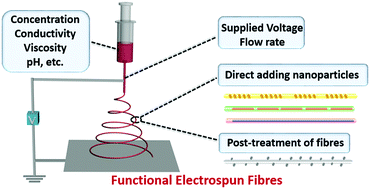
Mater. Horiz., 2016,3, 266-269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MH00045B
Principles and implementations of electrolysis systems for water splitting
Efforts to develop renewable sources of carbon-neutral fuels have brought a renewed focus to research and development of sunlight-driven water-splitting systems.
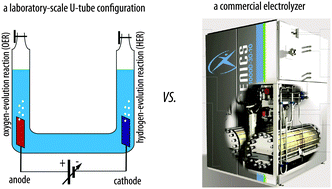
Mater. Horiz., 2016,3, 169-173
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MH00016A
Statistics, damned statistics and nanoscience – using data science to meet the challenge of nanomaterial complexity
Combining advances in digital technology and modern methods in statistics with a detailed understanding of nano-structure/property relationships can pave the way for more realistic predictions of nanomaterials performance.
Nanoscale Horiz., 2016,1, 89-95
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NH00126A
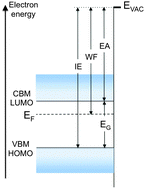
Fermi level, work function and vacuum level
Electronic levels and energies of a solid, such as Fermi level, vacuum level, work function, ionization energy or electron affinity, are of paramount importance for the control of device behavior, charge carrier injection and transport.
Mater. Horiz., 2016,3, 7-10
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5MH00160A
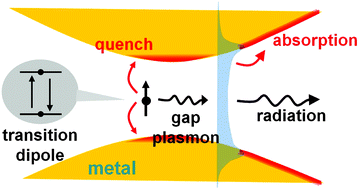
Light emission in nanogaps: overcoming quenching
Tiny metal nanogaps may offer a unique platform for achieving extremely larger spontaneous decay rate with high quantum yield.
Nanoscale Horiz., 2016,1, 11-13
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NH00059A
A gentle introduction to the noble art of flow chemistry
The authors provide a simple tutorial-style introduction to do-it-yourself flow chemistry, emphasising the advantages of well designed, self-built kit over expensive off-the-shelf commercial equipment.

Mater. Horiz., 2014,1, 373-378
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MH00054D
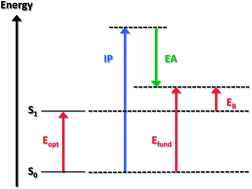
Mind the gap!
The energy gap is a critical material parameter. Here, we illustrate the concepts behind the various flavors of energy gaps relevant for organic materials and call for a more consistent use of appropriate terminologies and procedures.
Mater. Horiz., 2014,1, 17-19
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3MH00098B
About this collection
This themed collection contains Focus articles published in Materials Horizons and Nanoscale Horizons.
These articles are free to access upon publication.
Focus articles are educational articles that can take the form of either an editorial or review article. They are designed to address topic areas that are often misunderstood or require greater explanation.