Will surface effects dominate in quasi-two-dimensional gallium oxide for electronic and photonic devices?
Abstract
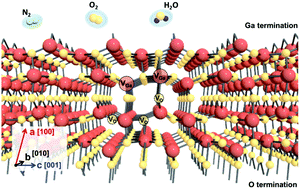
There is currently great interest in ultra-wide bandgap semiconductors for their applicability in power switching electronics with improved efficiency compared to current technologies and also to solar-blind UV detection. One of the most promising materials is Ga2O3, available in large area bulk crystals and as exfoliated nano-layers (nanobelts, nanomembranes, and nanosheets). One aspect of this material that has not been widely recognized is the sensitivity of its surface to environment. The goal of this brief focus article is to provide some insight into the mechanisms and defects that underlie this effect and explain inconsistencies in the literature.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Focus article collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
