Themed collection Collection of articles dedicated to Professor Ken Wade, F.R.S. in celebration of his seventy-fifth birthday

Cyclic oxonium derivatives of polyhedral boron hydrides and their synthetic applications
Preparation and synthetic application of cyclic oxonium derivatives of polyhedral boron hydrides are reviewed.
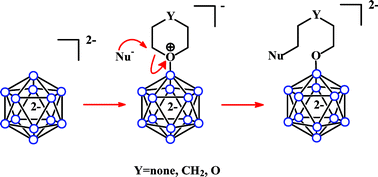
Dalton Trans., 2008, 977-992
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715363E
Platinum(II)
Schiff base as versatile phosphorescent core component in conjugated oligo(phenylene–ethynylene)s
Luminescent platinum(II) Schiff base units have been identified as an attractive signalling component in new oligo(phenylene–ethynylene) materials, which can potentially be extended to phosphorescent conjugated polymers for sensing applications.

Dalton Trans., 2008, 1412-1414
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715495J
A simple entry into nido-C2B10clusters: HCl promoted cleavage of the C–C bond in ortho-carboranyl diphosphines
Zwitterionic, nido-12-vertex carboranes with structures based on an unprecedented C2-symmetric docosahedron are remarkably easily (and reversibly) produced.
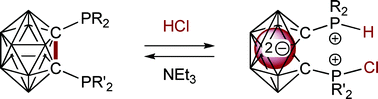
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1409-1411
https://doi.org/10.1039/B719404H
Generation of metallomesogens using common ligands functionalised with liquid-crystalline moieties
Functionalisation of 2,2′-bipyridine or acetylacetone with an alkyleneoxycyanobiphenyl group induces liquid-crystalline properties in simple metal complexes.
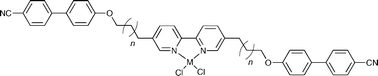
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1128-1131
https://doi.org/10.1039/B717428D
Cleavage of P–S bonds and oxygenation by a trinuclear iron carboxylate: Synthesis and structures of iron clusters containing group 15/16 anions
In the reaction of [Fe3(µ3-O)(µ2-piv)6(H2O)3](piv) (piv = tBuCOO−) with [RP(S)(µ-S)]2 (R = 4-anisyl) P–S bonds are cleaved. This reaction gave rise to the novel complex [Fe7S4(RPO2S)4(dme)4] (dme = 1,2-dimethoxyethane) and to [Fe9(µ3-O)4(RPO3)3(pic)13].
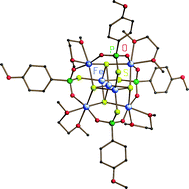
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1136-1139
https://doi.org/10.1039/B717583C
π-Bonding versus oligomerisation in the aromatic anions [C6H4N2E]−: formation of the cyclic tetrameric tetraanion [C6H4N2Sb]44−
The [C6H4N2Sb]− anion in the cyclic tetramer [C6H4N2SbLi·PMDETA]4 (1) (PMDETA = {Me2NCH2CH2}2NMe) sacrifices its formal π-aromaticity in order to adopt a donor–acceptor bonding mode unique in related main group heterocycles.
![Graphical abstract: π-Bonding versus oligomerisation in the aromatic anions [C6H4N2E]−: formation of the cyclic tetrameric tetraanion [C6H4N2Sb]44−](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B718512J&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 997-999
https://doi.org/10.1039/B718512J
Amino-closo-dodecaborate—a new ligand in coordination chemistry
For the first time coordination of amino-closo-dodecaborate is presented. The aminoborate coordinates at ruthenium with formation of a N–Ru bond and two B–H–Ru interactions.
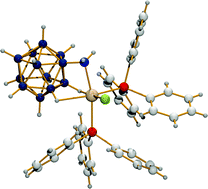
Dalton Trans., 2008, 444-446
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715305H
The preparation and characterisation of ruthenium cyanovinylidene complexes
A convenient preparative route to mono- and di-cyanovinylidene complexes is reported. Spectroelectrochemical studies and DFT calculations indicate reduction of these compounds results in population of a p-orbital at the vinylidene Cα carbon.
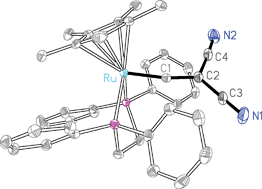
Dalton Trans., 2008, 433-436
https://doi.org/10.1039/B714274A
Synthesis of a bimetallic platinum–tungsten complex with a bridging µ-diboranyl–oxycarbyne moiety
The title compound [W{η1,µ-CO-B(NMe2)-B(NMe2)-(η5-C5H4)}(CO)2{Pt(PPh3)2}] (W–Pt), which displays a highly unusual µ-diboranyl–oxycarbyne bridge, was obtained by subsequent treatment of Li[W(η5-C5H4Li)(CO)3] with B2(NMe2)2Br2 and [Pt(η2-C2H4)(PPh3)2] via an unprecedented ansa-half-sandwich complex of tungsten.
Dalton Trans., 2008, 440-443
https://doi.org/10.1039/B714763E
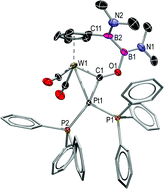
Unlocking the metallaboratrane cage: reversible B–H activation in platinaboratranes
The reaction of the new platinaboratrane salt [PtH(PTol3){B(mt)3}]Cl(Pt→B)8 (mt = methimazolyl, Tol = C6H4Me-4) with 2 equivalents of PR3 (R = Me, Et) affords, via hydride migration to boron and ligand substitution, the salts [Pt(PR3)2{κ2-S,S′-HB(mt)3}]Cl, which slowly undergo B–H reactivation, to afford, ultimately, the platinaboratrane salts [PtH(PR3){B(mt)3}]Cl(Pt→B)8.
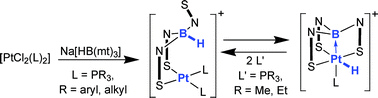
Dalton Trans., 2008, 201-203
https://doi.org/10.1039/B712058C
Zwitterionic bis(phenolate)amine lanthanide complexes for the ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic esters
Reaction of Sm{N(SiMe3)2}3 with one or two equivalents of bis(phenol)amine ligands afford bifunctional zwitterionic lanthanide catalysts that effect the ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic esters affording cyclic polyesters.
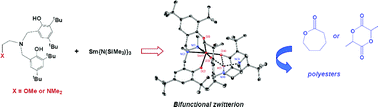
Dalton Trans., 2008, 32-35
https://doi.org/10.1039/B714583G
The oxadiazolyldiazenido(1−) ligand : a remarkably versatile platform for the synthesis of heteropolynuclear transition metal complexes
Cyclo-condensation of aroyl hydrazides with [BrW(dppe)2(N2CCl2)]+ affords neutral oxadiazolyldiazenido(1−) complexes which react readily with both transition and non-transition metal acceptors to afford a wide range of novel heteropolynuclear complexes.
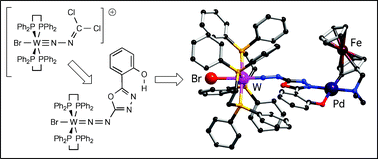
Dalton Trans., 2007, 3864-3867
https://doi.org/10.1039/B711166P
Synthesis and dehydrocoupling reactivity of iron and ruthenium phosphine–borane complexes
The phosphine–borane complexes CpM(CO)2(PPh2·BH3) (M = Fe, Ru) have been prepared and both of these species along with Fe2(CO)9 were found to catalyze the dehydrocoupling of PPh2H·BH3 in the melt at 120 °C. The Fe complexes are the first reported iron catalysts for the dehydrocoupling of phosphine–borane adducts.
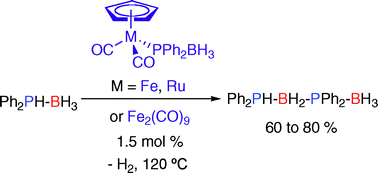
Dalton Trans., 2008, 2732-2740
https://doi.org/10.1039/B718918D
Effects of halogen substitution on the properties of eight- and nine-vertex closo-boranes
Substitution of halogens on eight- and nine-vertex polyhedral boranes impacts the cage magnetic properties. Multiple fluorine substituents lead to 3D diatropic ring currents within neutral borane cages BnFn contrasting with their paratropic BnHn analogues.
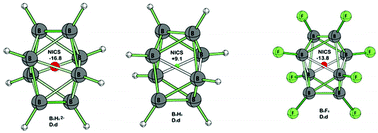
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1745-1751
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716323A
A new series of dinuclear Au(I) complexes linked by diethynylpyridine groups
A series of novel digold complexes incorporating ethynyl pyridine derivatives as a spacer unit, [(R3P)Au(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C)X(C
C)X(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C)Au(PR3)] (X = pyridine or bipyridine), have been prepared and characterised. Only the complexes with short spacer groups show aurophilic interactions in the solid state and in solution the absorption and emission spectra are dominated by ligand-based transitions.
C)Au(PR3)] (X = pyridine or bipyridine), have been prepared and characterised. Only the complexes with short spacer groups show aurophilic interactions in the solid state and in solution the absorption and emission spectra are dominated by ligand-based transitions.
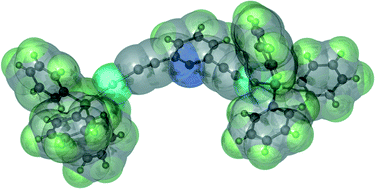
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1635-1646
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716664H
Borane reaction chemistry. Alkyne insertion reactions into boron -containing clusters . Products from the thermolysis of [6,9-(2-HC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C5H4N)2-arachno-B10H12]
C–C5H4N)2-arachno-B10H12]
The identification of by-products from the thermolysis of [6,9-(2-HC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–C5H4N)2-arachno-B10H12 adds to the knowledge of the mechanism of closo-dicarbadodecaborane synthesis.
C–C5H4N)2-arachno-B10H12 adds to the knowledge of the mechanism of closo-dicarbadodecaborane synthesis.
![Graphical abstract: Borane reaction chemistry. Alkyne insertion reactions into boron-containing clusters. Products from the thermolysis of [6,9-(2-HC [[triple bond, length as m-dash]] C–C5H4N)2-arachno-B10H12]](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B715845A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1552-1563
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715845A
Synthesis of nickel complexes with bidentate N,O-type ligands and application in the catalytic oligomerization of ethylene
The dinuclear complexes 14 and 16 have been synthesized in high yields and used as precatalysts in ethylene oligomerization. Complex 16 in the presence of 6 equiv. of AlEtCl2 gave TOF values up to 187 500 C2H4 (mol Ni h)−1 under 10 bar of ethylene and with 200 equiv. of MAO TOF values up to 104 300 C2H4 (mol Ni h)−1 under 30 bar of ethylene. The selectivity of 16 for C4 olefins was up to 94% with only 50 equiv. of MAO.

Dalton Trans., 2008, 1564-1573
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716111E
Structural chemistry of (PPh4)2M(WS4)2 materials
We discuss the synthesis and structural chemistry of (PPh4)2M(WS4)2 materials for M = Co, Ni and Zn; new polymorphs and the origin of diffuse scatter in the M = Zn phase are reported.
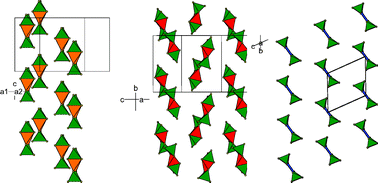
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1597-1601
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716407F
Amidinate–carboxylate complexes of dimolybdenum and ditungsten: M2(O2CR)2((NiPr)2CR′)2. Preparations, molecular and electronic structures and reactions
Reactions between M2(O2CMe)4 compounds (M = Mo or W) and lithium amidinates Li(PriN)2CR yield the MM quadruply bonded complexes trans-M2(O2CMe)2((PriN)2CR)2 where R = Me, CCPh, CCBut and 1-ferrocenyl.
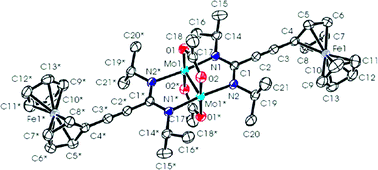
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1615-1624
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715258B
Porphyrin complexes containing coordinated BOB groups: synthesis, chemical reactivity and the structure of [BOB(tpClpp)]2+
The reactions of boron halides with porphyrins under conditions where partial hydrolysis occurs give products in which B–O–B groups are coordinated to the porphyrin in a surprising range of structural types.
![Graphical abstract: Porphyrin complexes containing coordinated BOB groups: synthesis, chemical reactivity and the structure of [BOB(tpClpp)]2+](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B716189A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1602-1614
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716189A
Macropolyhedral boron-containing cluster chemistry. The reversible disassembly and reassembly of the hexagonal pyramidal {B7} feature in the [S2B18H19]− anion
DFT calculations define that protonation of the [S2B18H19]− anion 1 to give [S2B18H20] 4 disassembles its rare hexagonal pyramidal {B7} feature, and that deprotonation of 4 gives a fluxional [S2B18H19]− isomer 5, from which 1 reassembles.
![Graphical abstract: Macropolyhedral boron-containing cluster chemistry. The reversible disassembly and reassembly of the hexagonal pyramidal {B7} feature in the [S2B18H19]− anion](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B715915C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1625-1634
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715915C
Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of Group 4 metallacycles incorporating a Me2C-linked cyclopentadienyl-carboranyl ligand
The insertion of unsaturated molecules into the M–N bonds of metallacycles is a useful and effective method for the construction of very large ring systems.
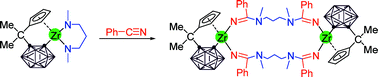
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1454-1464
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716929A
Robust chiral zirconium alkoxide initiators for the room-temperature stereoselective ring-opening polymerisation of rac-lactide
Chiral Schiff bases complexes of Ti and Zr are active initiators for the ring-opening polymerisation of rac-lactide. Zirconium initiators give heterotactic polylactide in solution at room temperature, in the melt, and in the presence of protic impurities.
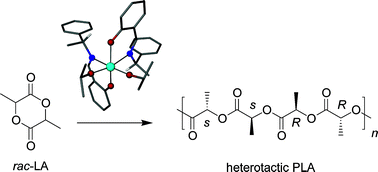
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1437-1443
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716304E
Influence of the solvent and R groups on the structure of (carboranyl)R2PI2 compounds in solution. Crystal structure of the first iodophosphonium salt incorporating the anion [7,8-nido-C2B9H10]−
The influence of the R groups on P and the solvent on the solution molecular geometry of adducts (carboranyl)R2PI2, generated by the reaction of carboranylphosphanes with I2 in 1 : 1 ratio, has been studied.
![Graphical abstract: Influence of the solvent and R groups on the structure of (carboranyl)R2PI2 compounds in solution. Crystal structure of the first iodophosphonium salt incorporating the anion [7,8-nido-C2B9H10]−](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B716217K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1471-1480
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716217K
Synthesis and characterisation of new bimetallic alkali metal –magnesium mixed diisopropylamide-acetylides : structural variations in bimetallic lithium- and sodium-heteroleptic magnesiates
Reactions of mixed alkali metal–magnesium tris(diisopropylamides) with phenylacetylene produce an acetylido-rich Na⋯Mg⋯Mg⋯Na chain structure or an amido-rich (LiNMgN)22+(C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)2− inverse crown.
CPh)2− inverse crown.
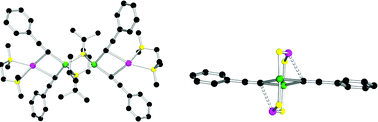
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1481-1486
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716215D
Synthesis of aluminium borate –boron oxide and binary titanium–boron and zirconium–boron oxides from metal alkoxides and (MeO)3B3O3 in non-aqueous solvents
Metal alkoxides M(OR)4 (M = Ti, Zr; R = organyl) or Al(OiPr)3 react with (MeO)3B3O3 in dry propan-2-one to give gels which when calcined in air for 24 h at 500–1000 °C afforded bi-phased mixed-oxide materials.
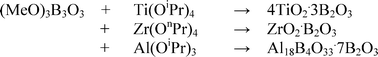
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1503-1506
https://doi.org/10.1039/B717379B
Synthesis and structural elucidation of solvent -free and solvated lithium dimethyl (HMDS) zincates
Reaction of the unsolvated lithium HMDS zincate [LiZn(HMDS)Me2] with PMDETA affords the solvate [(PMDETA)Li(µ-Me)Zn(Me)(HMDS)] where the amide (circled blue) occupies an unusual terminal position exclusively bonded to Zn.
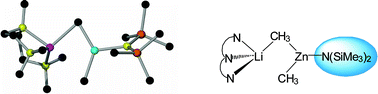
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1323-1330
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716494G
Synthetic and structural investigations of alkali metal diamine bis(phenolate) complexes
Three alkali metal diamine bis(phenolate) complexes have been prepared and structurally characterised—all adopt very different structural arrangements.
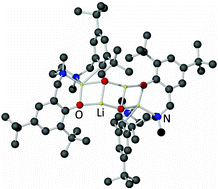
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1295-1301
https://doi.org/10.1039/B718186H
Alkyl and aryl dicationic derivatives of cyclic triphosphenium ions
Several new alkyl and aryl dicationic derivatives of cyclic triphosphenium ions have been synthesised in solution via two alternative routes; five of these ions have been structurally characterised by X-ray diffraction at 120 K.
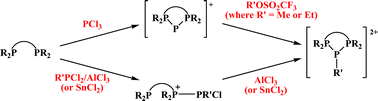
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1144-1149
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716027E
Rhodium catalysed dehydrogenative borylation of alkenes : Vinylboronates via C–H activation
Alkenes can be converted to useful vinylboronate esters using B2pin2, B2neop2, or HBpin and trans-[RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2] as the catalyst precursor via conventional or microwave heating.

Dalton Trans., 2008, 1055-1064
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715584K
N-Phosphino-amidines and -guanidines: synthesis, structure and P,N-chelate chemistry
A readily prepared family of tuneable N-phosphino-amidines and -guanidines is reported, whose dynamic behaviour, donor characteristics and versatile κ2-P,N-chelate ability have been explored.
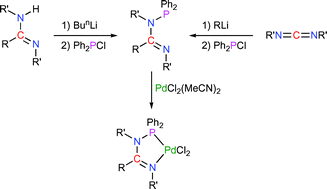
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1043-1054
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715736C
Halogen-containing tetrametallic aluminium alkoxides
New halogen-containing tetrametallic aluminium alkoxides of formula [Al{(µ-OEt)2AlMeCl}3] (2-cis; 2-trans), and [Al{(µ-OEt)2AlBr2}3] (4), have been synthesized by combining Al(OEt)3 and Me2AlCl (for 2) or EtAlBr2 (for 4). The structure of 4 is shown.
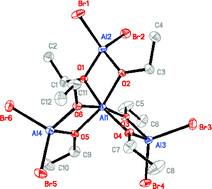
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1037-1042
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716812H
Synthesis and structures of some new types of lithium β-diketiminates
Novel lithium salts: the binucleating β-diketiminates (2, 3, 6, 7), the mixed β-diketiminate/1,3-diazaallyl (9), the enamide (1) and the isoindolinide (5) are reported.
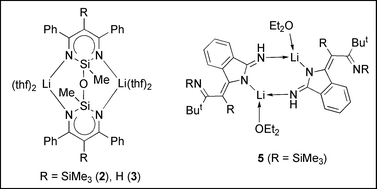
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1073-1080
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716888H
New 13-vertex metallacarborane sandwich compounds; synthetic and structural studies
[4,4′-M-(1,10-closo-C2B10H12)2]n− anions are reported. With [K(18-crown-6)]+ B–H⋯K+ interactions help prevent crystallographic disorder. The relative conformations of the two MC2B10 cages are rationalised in terms of the metal valence electron count.
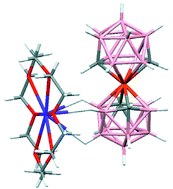
Dalton Trans., 2008, 1009-1017
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716169G
Coordination chemistry of a new P,Te-centred ligand : synthesis, NMR spectra and X-ray structures of M(TePPri2NPPri2)2 (M = Zn, Cd, Hg)
The lithium salt of an anionic P,Te-chelating ligand was prepared from TePri2PNP(H)Pri2 and BunLi and reacted in situ with group 12 metal chlorides to generate homoleptic coordination complexes.
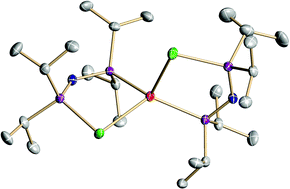
Dalton Trans., 2008, 957-962
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715789D
Boron trihalide mediated haloallylation of aryl aldehydes: reaction and mechanistic insight
The reaction of aryl aldehydes with allylsilanes in the presence of boron trihalides produces haloallylated products. Mechanistic details are presented.
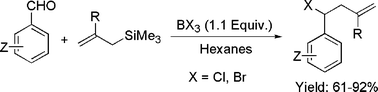
Dalton Trans., 2008, 776-778
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715395C
Cyanide ion complexation by a cationic borane
The cationic borane [1-(Mes2B)-8-(Me3NCH2)-C10H6]+ ([2]+) complexes cyanide to form [1-(Mes2(NC)B)-8-(Me3NCH2)-C10H6] (2-CN). This reaction also occurs under biphasic conditions and may serve to transport cyanide in organic phases.

Dalton Trans., 2008, 814-817
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715534D
Quenched gas-phase reactions of tetraborane(10), B4H10, with substituted alkynes : new nido-dicarbapentaboranes and arachno-monocarbapentaboranes
New derivatives of the nido-dicarbapentaborane, 1,2-C2B3H7, are formed in gas-phase reactions of B4H10 with substituted ethynes RC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CR′ (R = Me, Et, nPr, tBu or Me3Si, R′ = H; R = Me or Et, R′ = Me).
CR′ (R = Me, Et, nPr, tBu or Me3Si, R′ = H; R = Me or Et, R′ = Me).
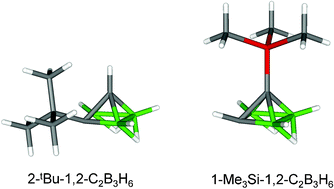
Dalton Trans., 2008, 676-684
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715105E
A re-evaluation of the two-step spin crossover in the trinuclear cation [Co3(dipyridylamido)4Cl2]+
Density functional theory reveals the remarkable diradical character of the extended metal atom chain [Co3(dpa)4Cl2]+ (dpa = the anion of 2-dipyridylamine).
![Graphical abstract: A re-evaluation of the two-step spin crossover in the trinuclear cation [Co3(dipyridylamido)4Cl2]+](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B715021K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 608-614
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715021K
Gallium oxide thin films from the AACVD of [Ga(NMe2)3]2 and donor functionalised alcohols
Thin films of Ga2O3 have been produced from [Ga(NMe2)3]2 and ROH (R = CH2CH2NMe2, CH(CH2NMe2)2, CH(CH3)CH2NMe2, CH2CH2OMe, HOC(CH3)2CH2OMe) by aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition on glass.
![Graphical abstract: Gallium oxide thin films from the AACVD of [Ga(NMe2)3]2 and donor functionalised alcohols](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B713804K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 591-595
https://doi.org/10.1039/B713804K
Multinuclear NMR studies of the products resulting from the reaction of pyridine or 2,2′-bipyridine with [Rh4(CO)12]
Addition of py or bipy to [Rh4(CO)12] results in immediate disproportionation to give anionic Rh5-clusters, which have been structurally characterized in solution using both 1D and 2D NMR methods; their geometries are all structurally related but subtly different.
![Graphical abstract: Multinuclear NMR studies of the products resulting from the reaction of pyridine or 2,2′-bipyridine with [Rh4(CO)12]](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B715139J&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2008)
Dalton Trans., 2008, 685-690
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715139J
Protonated tert-pentyl dication (C5H122+, isopentane dication)
Structures of protonated tert-pentyl dication (C5H122+, isopentane dication) were calculated at the MP2/cc-pvtz level.
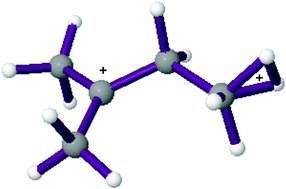
Dalton Trans., 2008, 521-526
https://doi.org/10.1039/B713188G
Bulky aryl functionalized carbazolyl ligands: amido alternatives to the 2,6-diarylphenyl ligand class?
Sterically encumbered amido ligands based on a 1,8-diarylcarbazol-9-yl backbone have been investigated as electronically distinct alternatives to the widely-used terphenyl ligand class in the stabilization of low-coordinate metal complexes, and structurally characterized for the first time (see Figure).
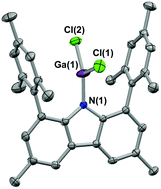
Dalton Trans., 2008, 332-337
https://doi.org/10.1039/B716674E
Synthesis, reactivity and complexation studies of N,S exo-heterodisubstituted o-carborane ligands . Carborane as a platform to produce the uncommon bidentate chelating (pyridine)N-C-C-C-S(H) motif
The species 1-(2′-pyridyl)-2-SR-1,2-closo-C2B10H10 and [7-(2′-pyridyl)-8-SR-7,8-nido-C2B9H10]– have been prepared and their enantiomers isolated. [PdCl(1-(2'-pyridyl)-2-S-1,2-closo-C2B10H10)(PPh3)2] is one of the two examples of a rigid bidentate chelating (pyridine)N-C-C-C-S(H) motif having been structurally characterized.
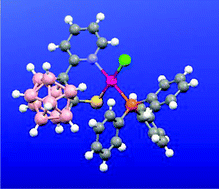
Dalton Trans., 2008, 345-354
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715362G
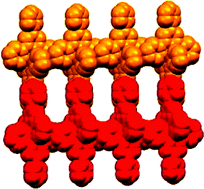
Vectorial property dependence in bis{4′-(n-pyridyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine}iron(II) and ruthenium(II) complexes with n = 2, 3 and 4
Structural and spectroscopic studies of [M(L)2]2+, (M = Fe or Ru; L = 4′-(2-pyridyl)-, 4′-(3-pyridyl)- and 4′-(4-pyridyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine) are reported. The complexes undergo mono- and bis-N-methylation with changes in the absorption spectra and electrochemical properties.
Dalton Trans., 2008, 386-396
https://doi.org/10.1039/B714970K
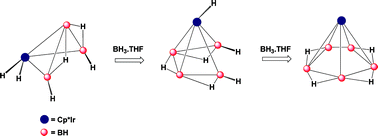
Expansion of iridaborane clusters by addition of monoborane. Novel metallaboranes and mechanistic detail
Cluster expansion of arachno-1-{η5-C5Me5IrH2}B3H7 with BH3·THF results in the formation of three nido clusters, 1-(η5-C5Me5Ir)B5H9, 3-(η5-C5Me5Ir)B9H13and 3,4-(η5-C5Me5Ir)2B8H12 along with the isolation of an exopolyhedral cluster, nido-3,4-(η5-C5Me5Ir)2B8H13(µ-BH2).
Dalton Trans., 2008, 371-378
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715040G
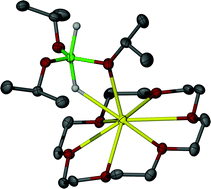
Hypervalent hydridosilicates: synthesis, structure and hydride bridging
A range of hydridosilicate and fluorosilicate anions adopt a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with axial hydride and fluoride ligands engaging in Si–H⋯K+ and Si–F⋯K+ bridges to crown ether complexed potassium counter-ions.
Dalton Trans., 2008, 271-282
https://doi.org/10.1039/B713427D
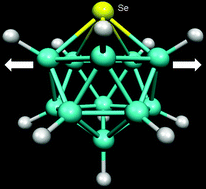
The gas-phase structure of 1-selena-closo-dodecaborane(11), 1-SeB11H11, determined by the concerted use of electron diffraction and computational methods
The molecular structure of 1-SeB11H11 has been determined, showing that it is distorted from a regular icosahedron through the expansion of the pentagon of boron atoms adjacent to selenium.
Dalton Trans., 2008, 96-100
https://doi.org/10.1039/B714457A
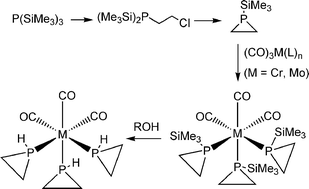
1-Trimethylsilylphosphirane as a ligand and as a stable masked reagent for phosphirane
Thermally stable trimethylsilylphosphirane is readily prepared in good yield from tris-trimethylsilylphosphine. The silyl phosphirane is a convenient source of phosphirane by protonolysis in the free state or whilst coordinated.
Dalton Trans., 2008, 47-53
https://doi.org/10.1039/B715327A
Syntheses, structures and redox properties of some complexes containing the Os(dppe)Cp* fragment, including [{Os(dppe)Cp*}2(μ-C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC
CC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C)]
C)]
The [{Os(dppe)Cp*}2(μ-C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC
CC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C)]n+ complexes have electronic structures comparable with those of the Ru and, to a lesser extent, Fe analogues.
C)]n+ complexes have electronic structures comparable with those of the Ru and, to a lesser extent, Fe analogues.
![Graphical abstract: Syntheses, structures and redox properties of some complexes containing the Os(dppe)Cp* fragment, including [{Os(dppe)Cp*}2(μ-C [[triple bond, length as m-dash]] CC [[triple bond, length as m-dash]] C)]](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B712104K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2007)
Dalton Trans., 2007, 5387-5399
https://doi.org/10.1039/B712104K
Cationic rhodium mono-phosphine fragments partnered with carborane monoanions [closo-CB11H6X6]− (X = H, Br). Synthesis, structures and reactivity with alkenes
Mono-phosphine rhodium fragments partnered with the carborane anions [closo-CB11H12]− and [closo-CB11H6Br6]− have been prepared and their reactivity with alkenes investigated.
![Graphical abstract: Cationic rhodium mono-phosphine fragments partnered with carborane monoanions [closo-CB11H6X6]− (X = H, Br). Synthesis, structures and reactivity with alkenes](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=B711468K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2007)
Dalton Trans., 2007, 4829-4844
https://doi.org/10.1039/B711468K
A ligand influence on the stability of heterobimetallic complexes containing the Ti(µ-O)Al skeleton. Transformation of heterometallic systems to the homometallic Ti(IV) and Al(III) complexes
Heterobimetallic complexes, supported by the bulky NacNac ligand and containing the Ti(µ-O)Al skeleton transformed to the homometallic Ti(IV) and Al(III) complexes LAlMe2 and LTiMe(µ-O)2TiMeL or LAlMeCl and LTiCl(µ-O)2TiClL.

Dalton Trans., 2007, 4149-4159
https://doi.org/10.1039/B710470G
About this collection
It is a pleasure to write the preface to this 'special collection of articles' of Dalton Transactions dedicated to Ken Wade. Ken's name is, of course, familiar to every student and practicing inorganic chemist from his pioneering work concerned with the relationship between structure and electron count in polyhedral cluster systems, and indeed, his early proposals regarding what are now known generally as 'isolobal relationships'. True to the nature of the man, Ken's lectures and discussions on the subject are mostly conducted with reference to "Bloggs' Rules." Others will perhaps be more familiar with the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory under alternative names!
Throughout his career, Ken's contributions to main group and inorganic chemistry have extended well beyond his insights into electron-counting and bonding. He has carried out many important studies on the synthesis and structures of main group compounds. His Ph.D. research, with Norman Greenwood at Nottingham University, focussed on conductivity of molten adducts. His postdoctoral studies, carried out at Cambridge with Harry Emeléus, were on reactions of diborane, and those at Cornell with Albert Laubengayer, were on organonitrogen-aluminium chemistry. Ken became a lecturer at Durham in 1961, where he continued to be extremely active in the area of synthetic main group chemistry. He has been a key contributor to the areas of azomethine, lithium amide and organolithium chemistry, in addition to publishing seminal papers on electron-counting rules. Ken was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 1989, in recognition of his contributions to chemistry and was elected President of Dalton Division of The Royal Society of Chemistry in 1996.
From a personal perspective, Ken has had a major impact on all of our lives, taking us under his wing in one role or another during the formative stages of our academic careers. Even though he formally retired 10 years ago, Ken maintains a tireless enthusiasm for chemistry, writing books and original papers, reviewing articles, attending chemistry meetings, and giving invited lectures around the world. Many chemists agreed without hesitation to contribute their work to this special collection of Dalton Transactions articles. We are delighted to pay tribute to Ken for his friendship, his role as a teacher and mentor, and his important and extensive contributions to chemistry. This collection is a token of our appreciation of a truly outstanding chemist, Professor Ken Wade, F.R.S.