Themed collection Recent Open Access Articles

To be or not to be degraded: in defense of persistence assessment of chemicals
Characterizing the degradation behavior of chemicals in the environment is a key component of chemical hazard and risk assessment.
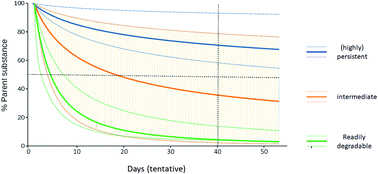
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1104-1109
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00213B
Unraveling biogeochemical complexity through better integration of experiments and modeling
A more ubiquitous use of process-based models will enhance the information gained from biogeochemical experimentation through both, a more rigorous interpretation of acquired data and the optimal design of future experiments.
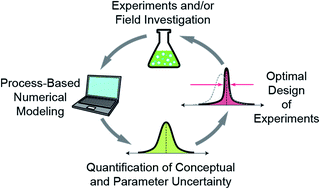
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1825-1833
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00303H
The high persistence of PFAS is sufficient for their management as a chemical class
While per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a class of synthetic organic substances with diverse structures, properties, uses, bioaccumulation potentials and toxicities, nearly all PFAS are highly persistent.
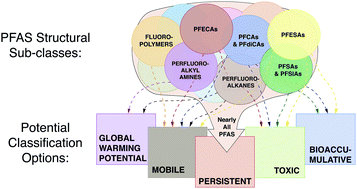
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 2307-2312
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00355G
Perspectives of genetically engineered microbes for groundwater bioremediation
Bacteria degrading 1,2,3-trichloropropane were constructed by genetic engineering and may be applicable for groundwater bioremediation, following the example of 1,2-dichloroethane.
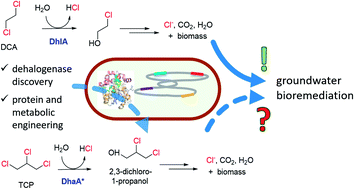
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 487-499
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00601J
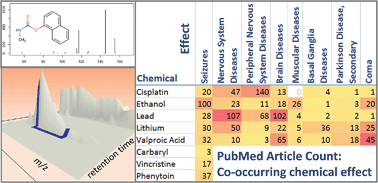
Connecting environmental exposure and neurodegeneration using cheminformatics and high resolution mass spectrometry: potential and challenges
A multi-disciplinary perspective on connecting chemistry, exposure and medical information to “neurotoxicity” for mass spectrometry-based environmental assessment, including multiple interactive resources for readers to use and explore.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 1426-1445
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00068B
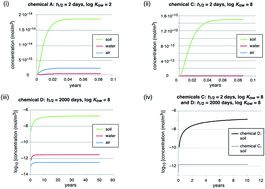
Why is high persistence alone a major cause of concern?
High persistence has important implications for chemicals regulation and management.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2019,21, 781-792
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EM00515J
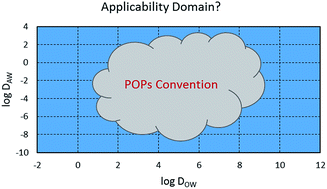
Can the Stockholm convention address the spectrum of chemicals currently under regulatory scrutiny? Advocating a more prominent role for modeling in POP screening assessment
Applying POP screening to a large chemical domain requires less reliance on individual criteria and more on integrated assessment with models.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2018,20, 32-37
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7EM00473G
A global review of long-range transported lead concentration and isotopic ratio records in snow and ice
Lead (Pb) has been used in human civilization for centuries, but the quantity and source of Pb pollution released into the environment varies spatially and temporally. Ice cores and snowpits are an excellent record of past Pb use.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 878-891
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00526K
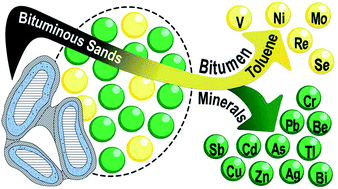
Environmental significance of trace elements in the Athabasca Bituminous Sands: facts and misconceptions
The distribution of trace elements (TEs) in the bituminous sands is dichotomous: V, Ni, Mo, Se and Re are found predominantly in the bitumen fraction, and all other TEs in the mineral fraction.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1279-1302
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00049K
Biodegradable plastics in soils: sources, degradation, and effects
Biodegradable plastic degradation in soils is highly complex. Without effective management, degradation poses potential risks to environmental and human health, soil quality, food security and safety, and environmental sustainability.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3321-3343
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00754A
Advancing the understanding of PFAS-induced reproductive toxicity in key model species
This review summarizes PFAS reproductive toxicity in five model organisms, highlighting gonadal damage, hormone disruption, and transgenerational effects, to support model selection and future research strategies.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3050-3075
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00145E
Human exposure to per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in Asia and contributing factors, with a focus on East Asia
The production and use of PFAS in some countries, coupled with uncertainties about their applications across Asia, underscore the urgent need to assess human exposure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2614-2635
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00396B
Risk assessment of tire wear in the environment – a literature review
Tire wear particle emissions in the environment have low risk prioritization. This has been estimated from data on terrestrial and aquatic exposure and hazard. The risk of tire leachables is not yet known due to inconsistency in hazard data.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2212-2232
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00088B
Microscopic menace: exploring the link between microplastics and cancer pathogenesis
Microplastics represent a group of emerging environmental contaminants widely recognized for their potential impacts on human health, particularly concerning the pathogenesis of cancer.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1768-1795
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00232J
Heavy metal contamination in wastewater-irrigated vegetables: assessing food safety challenges in developing Asian countries
This review analyses data on heavy metal contamination in wastewater-irrigated vegetables across four developing Asian countries, highlighting metal accumulation patterns, health impacts, regulatory gaps and calls for urgent coordinated action.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1747-1767
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00565A
Antimony mobility in soils: current understanding and future research directions
Antimony (Sb) has gained increased attention over the past few decades due to its possible detrimental effects on biota and its potential to leach and disperse from contaminated soils.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 833-848
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00743C
Microcontaminants and microplastics in water from the textile sector: a review and a database of physicochemical properties, use in the textile process, and ecotoxicity data for detected chemicals
Microcontaminants and microplastics are released at every stage of production and use and end up in wastewater treatment plants and eventually in surface waters.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 297-319
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00639A
An introduction to machine learning tools for the analysis of microplastics in complex matrices
This work introduces the reader to machine learning principles and highlights its usage in examining microplastics in soil samples.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 10-23
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00605D
Finding non-fluorinated alternatives to fluorinated gases used as refrigerants
The critical review scrutinizes some of the public statements on fluorinated gases and gives a detailed overview of the available alternatives to fluorinated gases used as refrigerants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1955-1974
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00444B
Critical review of fluorescence and absorbance measurements as surrogates for the molecular weight and aromaticity of dissolved organic matter
Optical surrogates are used to characterize dissolved organic matter composition like aromaticity and molecular weight. We both review the genesis of surrogate-composition relationships and critically evaluate additional supporting evidence.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1663-1702
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00183D
Red tides in the Galician rías: historical overview, ecological impact, and future monitoring strategies
The Galician rías (NW Iberia, Spain) are responsible for most of the national shellfish production. This is the first review of red tides in that area including an historical overview, social challenges and proposals for improving their monitoring.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 16-34
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00296A
Analytical methodologies for oxidized organic compounds in the atmosphere
Recent findings on oxidized organic compounds in the atmosphere and analytical methodologies for their detection and quantification.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1263-1287
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00163F
Lithium-ion battery recycling: a source of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to the environment?
PFAS are widely used in lithium-ion batteries, which may be problematic for the rapidly growing battery recycling industry.
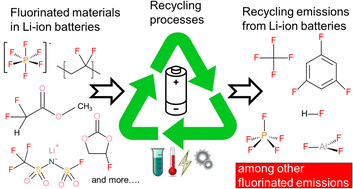
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1015-1030
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00511E
Assessing and managing environmental hazards of polymers: historical development, science advances and policy options
Approaches to regulatory assessment and management of polymers are reviewed and opportunities for improvements are highlighted based on a critical appraisal of current science on their environmental fate and effects.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 10-25
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00386D
Influences of climate change on long-term time series of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in Arctic and Antarctic biota
Time series of contaminants in the Arctic are an important instrument to detect emerging issues and to monitor the effectiveness of chemicals regulation. Climate change can affect the link between primary emissions and concentrations in Arctic wildlife.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1643-1660
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00134A
Climate change influence on the levels and trends of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and chemicals of emerging Arctic concern (CEACs) in the Arctic physical environment – a review
Direct and indirect effects of climate change influence contaminant sources, transport, re-distribution and circulation in the physical environment of the Arctic. Linkages of such observations to Arctic ecosystem exposure and effects are needed.
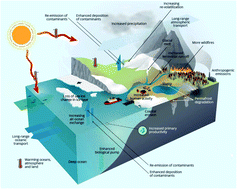
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1577-1615
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00485A
The influence of global climate change on accumulation and toxicity of persistent organic pollutants and chemicals of emerging concern in Arctic food webs
Global climate change-driven shifts in physical and ecological processes may alter POPs concentrations in Arctic food webs.
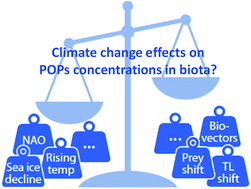
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1544-1576
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00469G
Influence of climate change on persistent organic pollutants and chemicals of emerging concern in the Arctic: state of knowledge and recommendations for future research
Future climate change in the Arctic will lead to loss of ice, snow and permafrost, increasing human activity and development, and changes in wind and ocean circulation patterns, that could alter the pathways, distribution and fate of contaminants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1530-1543
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00531F
A review of simulation experiment techniques used to analyze wildfire effects on water quality and supply
This review covers 40 laboratory- and plot-scale wildfire and rainfall simulation experiments which focus on wildfire hydrologic and water quality effects, guiding future researchers in the optimal design of their own simulation experiments.
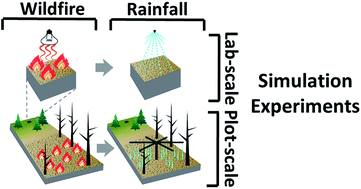
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1110-1132
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00045H
Critical review of antibiotic resistance genes in the atmosphere
Our critical review compares ARG profiles in the atmosphere across different locations and discusses characterization methods, atmospheric transport, and future research questions.
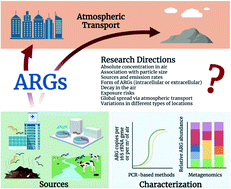
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 870-883
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00091A
A review of microplastic fibres: generation, transport, and vectors for metal(loid)s in terrestrial environments
Synthetic fibre release is an important source of microplastics to agricultural soils, through the application of sewage sludge. Microplastics are potential vectors for the transport of sorbed metal(loid)s from wastewater to soils and organisms.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 504-524
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00541C
Occurrence, human exposure, and risk of microplastics in the indoor environment
Pathways of human exposure to MPs and associated risks.
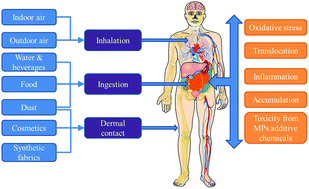
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 17-31
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00301A
Review of ecotoxicological studies of widely used polystyrene nanoparticles
With polystyrene nanoparticles being widely used in various applications, there is a great need for deeper knowledge on the safety, fate and biological effects of these particles on both individual living organisms and the whole ecosystems.
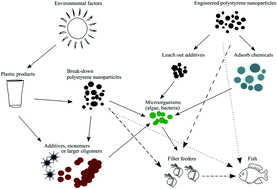
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 8-16
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00375E
Battling the known unknowns: a synoptic review of aquatic plastics research from Australia, the United Kingdom and China
A synoptic review of aquatic plastics research from Australia, the United Kingdom and China is presented, highlighting (a) key research and management challenges, and (b) a need to converge on standardised methods and bioindicator species to make global comparisons more reliable.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1663-1680
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00175B
Finding essentiality feasible: common questions and misinterpretations concerning the “essential-use” concept
The essential-use concept is a tool that can guide the phase-out of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and potentially other harmful substances of concern.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1079-1087
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00180A
The fate of plastic in the ocean environment – a minireview
The fate of plastic in the ocean is influenced by physical, chemical and biological stressors. These cause fragemntation and the formation of micro and nanoplastics but also degradation of plastics.
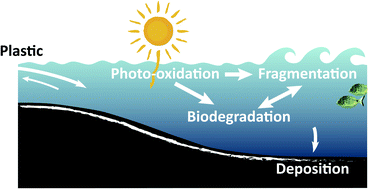
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 198-212
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00446D
Influence of microplastic colour on photodegradation of sorbed contaminants
The presence of pigments in microplastics alters the photodegradation kinetics of sorbed anthracene, which warrants consideration of microplastic colour in future environmental assessment studies of microplastic-contaminant systems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3076-3082
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00529A
Effects of urban particulate matter on the secondary structure of albumin
The changes in the secondary structure of albumin after incubation with particulate matter (PM) fractions of different compositions were studied, revealing a significant increase of the β-sheets in the presence of the metallic PM.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 892-900
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00766B
PFAS occurrence and distribution in yard waste compost indicate potential volatile loss, downward migration, and transformation
This novel investigation revealed substantial PFAS contamination and plastic-PFAS co-occurrence in yard waste compost. Insights gained from the distribution of PFAS in compost are valuable for improving its management and application.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 657-666
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00538K
Can determination of extractable organofluorine (EOF) be standardized? First interlaboratory comparisons of EOF and fluorine mass balance in sludge and water matrices
The first step towards the urgently needed standardization of EOF methods for PFAS-total assessment is presented in this interlaboratory study.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1458-1465
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00224D
Emerging investigator series: unpacking PET: comparative analysis of leachable and extractable contaminants from virgin and recycled polyethylene terephthalate bottles and textiles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) used as food contact materials, textiles, and toys, leaches a variety of plastic additives.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3431-3439
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00615E
Optimal lime materials for mitigating global warming potential with and without straw application in acidic upland soil
CaO and Ca(OH)2 are the optimal choice of lime materials for addressing acidification and mitigating GHG emissions compared with CaCO3.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3420-3430
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00494B
Profiles of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in firefighter turnout gear and their impact on exposure assessment
PFAS concentrations in firefighter turnout gear exhibited distinct layer trends and compositional differences across classes, influenced by sampling location, gear use, and aging.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3586-3594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00621J
Chemical fingerprints of cooking emissions and their impact on indoor air quality
Real-time measurements of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) reveal the chemical fingerprints of cooking chili, curry and stir fry, offering insights into emission dynamics and their impact on indoor air quality.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3665-3682
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00385G
Size-resolved analyses of trace elements in snow from an open-pit bitumen mining and upgrading region
Most trace elements in the filterable fraction of snow are predominantly <300 Da, but their concentrations are extremely low.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3403-3419
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00334B
Carbonate-hosted sphalerite weathering regulates cadmium mobilization in soils
This study unravels the fate of Cd during the weathering of Cd-bearing sphalerite in acidic and alkaline soils, providing insight into the mobility of Cd in soils affected by mining activities around carbonate-hosted Zn-sulfide ore deposits.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3652-3664
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00405E
An annular cylindrical oxidation flow reactor: hydrodynamic characterization and validation for gas-particle processing studies
Improved residence time distribution, high transmission efficiency for gases and particles and tunable oxidant exposure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3641-3651
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00412H
Environmental aging of tire and road wear particles and tire additives: a long-term field study
A 17–20 months aging of TRWP by sunlight and in a sedimentation pond shows pronounced loss of extractable chemicals and changes in composition, from parent compounds to transformation products. But considerable residues of extractables remained.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3498-3505
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00444F
Quantifying uncertainty in predicted chemical partition ratios required for chemical assessments
Models have different merits and limitations, and partition ratio predictions frequently differ >5 orders of magnitude. In general, to address uncertainty reliable experimental data are required for PFAS, ionizable, and large complex chemicals.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3457-3470
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00357A
Quantum chemical calculations for predicting the partitioning of drug molecules in the environment
The partition coefficients and vapor pressures of 23 drug molecules are calculated using advanced quantum mechanical methods to better assess their behavior in environmental compartments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3534-3550
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00524H
A first run-of-river hydropower plant development in a permafrost-rich subarctic Canadian region: short-term fate of mercury and carbon
Minimal research exists on the environmental impact of hydroelectricity in permafrost areas. This study reports increases in methylmercury in flooded soils, surface waters and first trophic levels following impoundment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3572-3585
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00171D
Distribution of semi-volatile organic compounds, metals, and biological activities in two industrialized cities in Ontario, Canada using passive air sampling
Passive air sampling enabled targeted characterization of semi-volatile pollutants and endocrine disrupting activities impacting two industrialized cities in Ontario, Canada.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3595-3611
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00493D
Critical biotransformation half-lives of chemicals in air-breathing wildlife to assess food-chain bioaccumulation and biomagnification
This study reveals species-specific variations, across chemical partition space, in the required critical biotransformation half-life to avoid biomagnification and presents a weight-of-evidence approach with a focus on biotransformation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3482-3497
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00220F
Mercury transfer and transformation from mine soil to river sediments: the potential role of amorphous iron oxides in methylation processes in southern Burkina Faso
Artisanal gold mining in Burkina Faso contaminates soil with mercury (Hg). Once eroded into rivers, Hg bound to amorphous iron oxides is likely to undergo methylation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3246-3260
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00426H
Molecular docking for screening chemicals of environmental health concern: insight from a case study on bisphenols
Molecular docking for high throughput screening binding of chemicals to functional protein related to health impact.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3192-3207
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00084J
Ferrihydrite level in paddy soil affects inorganic arsenic species in rice grains
Synthetic 2-line ferrihydrite amendment reduces arsenic uptake and accumulation in two varieties of rice grown in flooded paddy soils.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3107-3118
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00475F
Hydroxyl radical-initiated degradation kinetics of organic pollutants in surfactant-rich environments
This study quantifies how surfactant-rich environments can alter the degradation kinetics of organic pollutants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3119-3131
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00203F
Rainfall-induced lateral and vertical microplastic transport of varying sizes in agricultural fields
Agricultural soils, particularly those utilizing plastic products for crop production, are increasingly recognized as sources of microplastics (MPs) to aquatic ecosystems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2968-2981
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00304K
Dissolved trivalent manganese in forest soils – interactions of natural organic ligands with manganese oxides
Natural organic ligand-induced dissolution of Mn oxides contributes to the pH- and time dependent formation of organically complexed, dissolved trivalent Mn in forest soils, and thus terrestrial environments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2875-2893
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00388A
Chemical proteomics reveals human liver fatty acid binding protein as a predominant and selective target of triphenyl phosphate
Triphenyl phosphate (TPHP) forms covalent protein adducts, with the binding being protein and structure selective, making this a likely mechanism of toxicity.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2865-2874
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00327J
Extended pesticide soil monitoring in Cuban potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) production: residue co-occurrence, dissipation rates, ecological risks, and implications
While our extended pesticide soil monitoring under potato cultivation confirms generally shorter half-lives under tropical conditions, the corresponding residues might still pose a risk to terrestrial ecosystems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2685-2697
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00119F
Overcoming the challenge of quantifying aged microplastic by qNMR spectroscopy
Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) spectroscopy holds strong potential for environmental microplastic analysis, contingent on addressing the challenge of quantifying aged synthetic microplastics.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2821-2834
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00393H
Controls on the apparent quantum yield for photomineralization of dissolved organic matter in arctic freshwaters
Sunlight breaks down dissolved organic matter (DOM) in lakes and streams to produce carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas). The efficiency of this process depends on light exposure, the aromatic content of DOM (i.e., Ar–C), and dissolved iron (Fe).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2755-2769
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00293A
Emerging investigator series: release and phototransformation of benzophenone additives from polystyrene plastics exposed to sunlight
There are increasing concerns about the human and environmental health impacts of plastic exposure, which includes the risks associated with plastic additives.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2673-2684
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00292C
Selective ultra-trace atmospheric passive sampling of gaseous perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids
Nylon membrane filters are chemically selective sorbents for passive sampling atmospheric acids, such as perfluorinated carboxylic acids.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2785-2797
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00297D
Drivers and riverine fluxes of rare earth elements to coastal ecosystems across temperate, boreal, and subarctic ecoregions in Eastern Canada
REE fluxes from rivers into the Hudson Bay and Atlantic Ocean in Quebec reveal regional contrasts, with fluxes to the Atlantic 2.7 times higher, partly due to erosion. REE levels were influenced by dissolved organic carbon, iron, pH and temperature.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2740-2754
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00391A
Environmental stability characteristics of the immobilization effect of sulfhydryl grafted palygorskite on soil-available cadmium
The immobilization effect of sulfhydryl-grafted palygorskite on soil-available Cd demonstrated environmental stability, confirmed by chemical exposure and sorption, simulated acid rain leaching, thermal variation, and two-year field validation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2698-2712
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00262A
Characterization of commercial eco-glitters derived from modified regenerated cellulose after laboratory exposure in two aquatic media
Total degradation of commercial biodegradable glitter in purified and seawater was not achieved after 96 days.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2329-2340
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00105F
The interaction of Pu(IV) with low index ferrihydrite surfaces: a periodic boundary condition DFT study
The complexation of Pu(IV) to hydrated ferrihydrite surfaces was studied using the DFT+U approach. Results show that Pu(IV) binds strongly via the formation of multiple partially covalent Pu–O bonds, in good agreement with experimental findings.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2318-2328
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00076A
Analysis of indoor secondary organic aerosol formation near occupants in a classroom using computational fluid dynamics simulations
This research integrates the volatility basis-set model with CFD to improve understanding of secondary organic aerosol formation near indoor occupants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2538-2549
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00036J
About this collection
Please see below for recent Open Access papers published in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts.