Themed collection Soft Matter Emerging Investigators

Soft Matter Emerging Investigators 2019
This themed issue of Soft Matter highlights the work of emerging investigators in the field of soft matter. Editor-in-Chief Darrin Pochan introduces the issue.

Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1079-1086
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM90239A
Charge polarization near dielectric interfaces and the multiple-scattering formalism
Reviewing the impacts of interfacial charges on the cohesive energy, permittivity, and singular contact charge for polarizable dielectric particles.
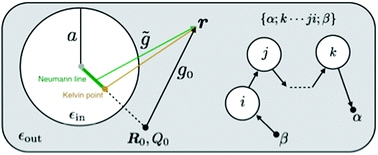
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 2125-2134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02196A
Simulations of ionization equilibria in weak polyelectrolyte solutions and gels
This article recapitulates the state of the art regarding simulations of ionization equilibria of weak polyelectrolyte solutions and gels.
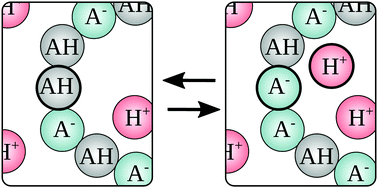
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1155-1185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02085J
Polymers on nanoparticles: structure & dynamics
Grafting polymers to nanoparticle surfaces influences properties from the conformation of the polymer chains to the dispersion and assembly of nanoparticles within a polymeric material.
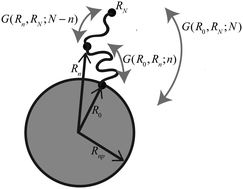
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1120-1134
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02110D
Thermodynamically driven assemblies and liquid–liquid phase separations in biology
The sustenance of life depends on the high degree of organization that prevails through different levels of living organisms, from subcellular structures such as biomolecular complexes and organelles to tissues and organs.
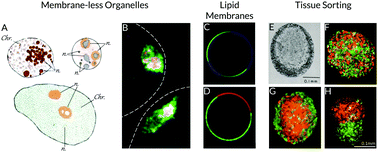
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1135-1154
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02285B
Numerical modelling of non-ionic microgels: an overview
We review numerical models of neutral microgels, going from the atomistic to the single-particle level.

Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1108-1119
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02089B
Dynamic surface antifouling: mechanism and systems
Dynamic surface antifouling (DSA) using degradable polymers with excellent antifouling performance and mechanical properties is an effective and promising strategy.
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1087-1107
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01853G
Colloidal particles at fluid interfaces: behaviour of isolated particles
We review the adsorption of colloidal particles at fluid interfaces, highlighting the effects of particle shape and chemistry.
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1186-1199
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02048E
Transition rates for slip-avalanches in soft athermal disks under quasi-static simple shear deformations
Restructuring of force-chains in yielding amorphous solids is analyzed by transition rates that link the microstructure to the macroscopic avalanche-size distributions.
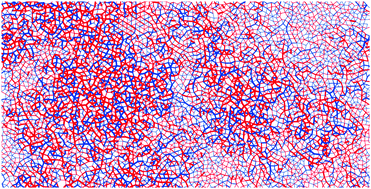
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 3487-3492
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01966E
Curved boundaries and chiral instabilities – two sources of twist in homeotropic nematic tori
In a recent series of experiments, we have shown that 5CB confined to tori and bent cylindrical capillaries with homeotropic boundary conditions also adopts a twisted escaped radial texture resulting from the curved nature of the confining boundaries. As the torus becomes more curved, the ideal location for the escaped core approaches the inner radius of the torus.
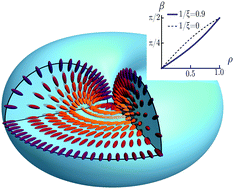
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1210-1214
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02055H
Bridging the spatiotemporal scales of macromolecular transport in crowded biomimetic systems
We combine single-molecule conformational tracking with digital Fourier microscopy to couple crowding-induced conformations and trajectories of single molecules with ensemble-averaged transport properties across an unprecedented spatiotemporal range to elucidate the complex dynamics of large DNA crowded by custom-designed networks of actin and microtubules.
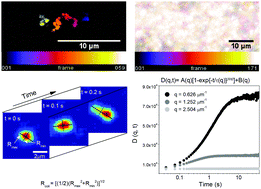
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1200-1209
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02023J
Image-based analysis of uniaxial ring test for mechanical characterization of soft materials and biological tissues
We propose a simple image-based analysis approach to accurately estimate the mechanical properties of ring-shaped materials.
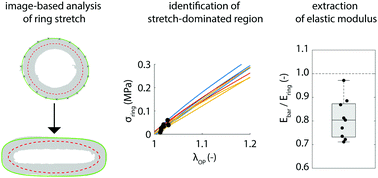
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 3353-3361
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02343C
Design rules for encapsulating proteins into complex coacervates
We explore using two-polymer coacervation to encapsulate model proteins and present design rules to guide encapsulation of novel targets.
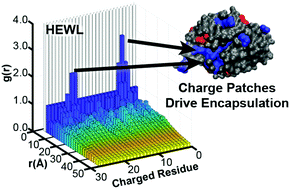
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 3089-3103
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SM00372J
In vivo adhesion force measurements of Chlamydomonas on model substrates
A universal adhesion mechanism allows Chlamydomonas to effectively colonize abiotic surfaces, as evidenced by in vivo adhesion force measurements.
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 3027-3035
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02236D
Lipid bilayer disruption induced by amphiphilic Janus nanoparticles: the non-monotonic effect of charged lipids
In this study, we report the complex effects of charged lipids on the interaction between amphiphilic Janus nanoparticles and lipid bilayers.
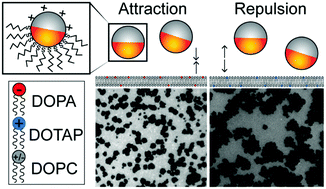
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 2373-2380
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02525H
Adsorption of amino acids on graphene: assessment of current force fields
We thoroughly investigate the differences in free energy of adsorption and the structures of the amino acids adsorbed on graphene with force fields.
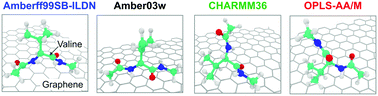
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 2359-2372
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02621A
3D printing with 2D colloids: designing rheology protocols to predict ‘printability’ of soft-materials
Delving into the ‘printability’ of soft matter using bespoke rheological protocols on suspensions and gels of 2D colloids.

Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1444-1456
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01936C
The fingerprint of a flow: wrinkle patterns in nonuniform coatings on pre-stretched soft foundations
We study the wrinkle patterns obtained when applying a thin polymeric film on a uniaxially prestretched soft foundation.
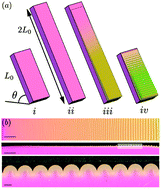
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1405-1412
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02057D
A stirring system using suspended magnetically-actuated pillars for controlled cell clustering
We develop a simple, scalable stirring system that can be used for controlled clustering of particles and cells.
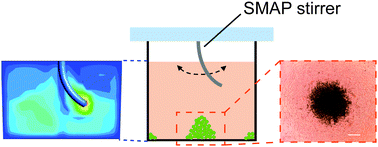
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1435-1443
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01957F
An experimental rheological phase diagram of a tri-block co-polymer in water validated against dissipative particle dynamics simulations
A rheological phase diagram of aqueous solutions based on Pluronic L64 was experimentally evaluated and validated via DPD simulations.
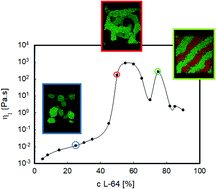
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1396-1404
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01959B
Microfluidic fabrication of vesicles with hybrid lipid/nanoparticle bilayer membranes
Water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion drops, fabricated using capillary microfluidics, enable the formation of vesicles with hybrid lipid/nanoparticle membranes.
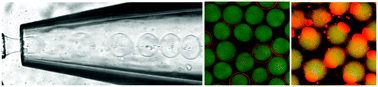
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1388-1395
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02050G
Double stimuli-responsive polysaccharide block copolymers as green macrosurfactants for near-infrared photodynamic therapy
The NIR absorbing photosensitizer phthalocyanine zinc (PC(Zn)) was stabilized in aqueous media as water-dispersible nanoparticles with a reduction- and pH-responsive full polysaccharide block copolymer.
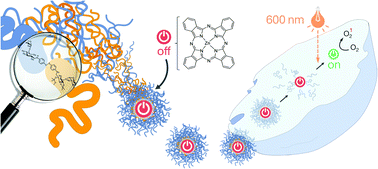
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1423-1434
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02204F
Tuning the interfacial and energetic interactions between a photoexcited conjugated polymer and open-shell small molecules
Photoexcited conjugated polymers are capable of exchanging energy with open-shell small molecules through a Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) mechanism.
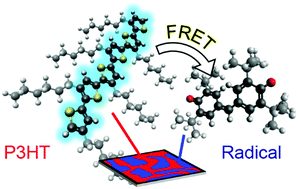
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1413-1422
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01930D
Colloid supported lipid bilayers for self-assembly
Careful tuning of the experimental parameters involved in preparing colloid supported lipid bilayers enables the self-assembly of flexible structures.
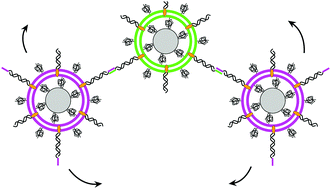
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1345-1360
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01661E
Laser sintering of polymer particle pairs studied by in situ visualization
The effects of sintering conditions on laser sintering of polymer particle doublets are unraveled by in situ visualization.
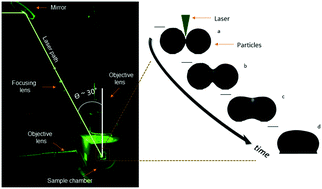
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1373-1387
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02081G
Universal localization transition accompanying glass formation: insights from efficient molecular dynamics simulations of diverse supercooled liquids
High-throughput simulations reveal a universal onset of particle localization in diverse glass-forming liquids.

Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1223-1242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02051E
Triggered disassembly and reassembly of actin networks induces rigidity phase transitions
We couple time-resolved optical tweezers microrheology with diffusion-controlled microfluidics and mathematical modeling to elucidate the time-dependent mechanics of entangled and crosslinked actin networks during dynamic depolymerization and repolymerization of actin filaments.
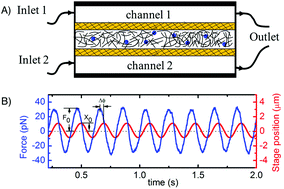
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1335-1344
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01912F
Using machine learning to discover shape descriptors for predicting emulsion stability in a microfluidic channel
A novel shape descriptor identified by machine learning captures diverse droplet shapes and achieves high prediction accuracy of droplet instability.
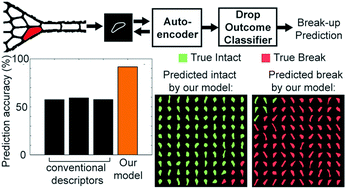
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1361-1372
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02054J
Mechanical unfolding of alpha- and beta-helical protein motifs
Alpha-helices and beta-sheets are the two most common secondary motifs in proteins. Beta-helices combine features of both motifs to perform a wide variety of functions. Possessing a larger width to height ratio, beta-helices resist unfolding by rotating to larger angles with respect to the loading direction, resulting in hydrogen bonds being ruptured in shear or out of plane peeling rather than in-plane peeling. This allows beta-helices to achieve greater energy dissipation per residue than alpha-helices.
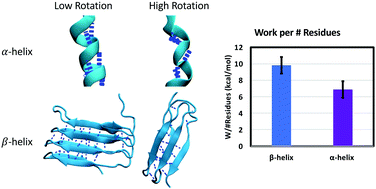
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1243-1252
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02046A
Buckling of geometrically confined shells
Moderately thick shells constrained in the radial and transverse directions buckle to a wavenumber set by a single geometric parameter.
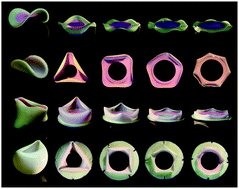
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1215-1222
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02035C
Effect of anisotropic diffusion on spinodal decomposition
Phase transition dynamics of a fluid system are very sensitive to the diffusion tensor.
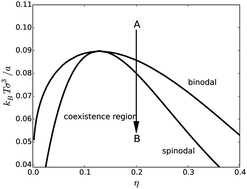
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1319-1326
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02017E
Singular dynamics in the failure of soft adhesive contacts
We observe that soft gels recoil with singular dynamics after adhesive detachment, driven by surface stress and slowed by viscous flow through the gel's porous, elastic network.
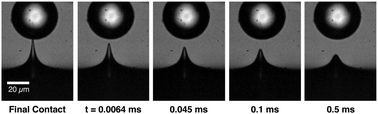
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1327-1334
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02075B
Phase behavior and morphology of multicomponent liquid mixtures
Cahn–Hilliard and Flory–Huggins theories are employed to investigate emergence of nested morphologies in phase separated multicomponent systems.
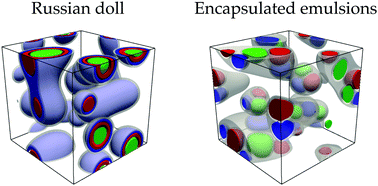
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1297-1311
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02045K
Polarization-dependent deformation in light responsive polymers doped by dichroic dyes
A polarization-dependence of the deformation in light-responsive materials can be induced through optimizing the dye dopant alignment.
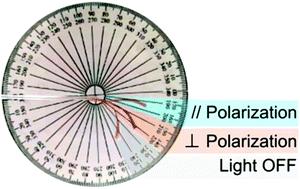
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1312-1318
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01954A
Mechano-responsive microcapsules with uniform thin shells
We introduce micrometer-sized capsules whose shells occupy as little 2% of their volumes. We demonstrate that these capsules are mechanically stable and have a low permeability even towards small encapsulants during storage.
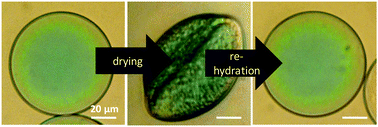
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1290-1296
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02047G
The stabilization of primitive bicontinuous cubic phases with tunable swelling over a wide composition range
Phase behavior of GMO/DOTAP/DOPE-PEG with bicontinuous cubic phases of different symmetry present in a wide composition range.
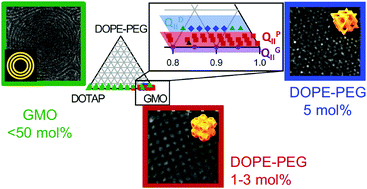
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1269-1277
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02059K
Probing the dynamic self-assembly behaviour of photoswitchable wormlike micelles in real-time
UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy is combined with small-angle neutron scattering to monitor the dynamic self-assembly of an azobenzene photosurfactant from worm-like micelles to fractals during photoisomerization.
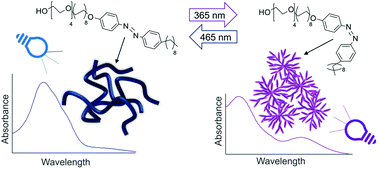
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1253-1259
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01948G
Influence of polymer flexibility on nanoparticle dynamics in semidilute solutions
The effects of polymer stiffness on nanoparticle dynamics in solution are probed using multi-particle collision dynamics simulations and mode-coupling theory.
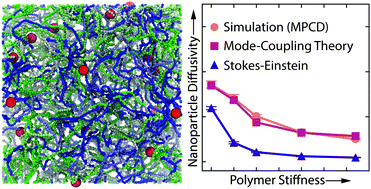
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1260-1268
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01834K
The structure–property relationship in LAPONITE® materials: from Wigner glasses to strong self-healing hydrogels formed by non-covalent interactions
Rheology, SAXS, and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis, zeta potential measurement, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and micro-FTIR and absorbance spectroscopy were used to enlighten the controversial literature about LAPONITE® materials.
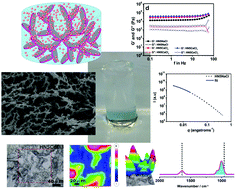
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 1278-1289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM01965G
The interplay between activity and filament flexibility determines the emergent properties of active nematics
Simulations of active nematics show that energy input at the particle scale preferentially dissipates into bend modes, leading to a softening of the apparent bend modulus with increasing activity. Thus, the nature of the energy cascade from the particle to macroscales in active materials can be controlled by particle internal degrees of freedom.
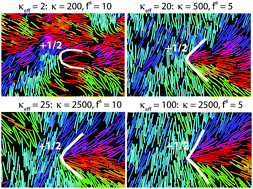
Soft Matter, 2019,15, 94-101
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02202J
About this collection
Soft Matter is proud to present this 2019 Emerging Investigators collection. This collection gathers the very best work from soft matter scientists in the early stages of their independent careers. The 2019 Soft Matter Emerging Investigators were individually nominated by members of the journal Editorial and Advisory Boards, and previous Emerging Investigators, in recognition of their potential to influence future directions in the field of soft matter.
Accompanying this collection is the Emerging Investigators special issue, in which these articles will be formally published. This issue is scheduled for publication in early 2019.