Probing the dynamic self-assembly behaviour of photoswitchable wormlike micelles in real-time†
Abstract
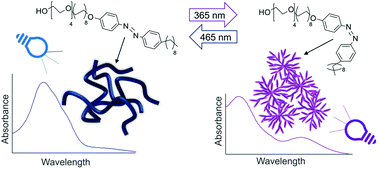
Understanding the dynamic self-assembly behaviour of azobenzene photosurfactants (AzoPS) is crucial to advance their use in controlled release applications such as drug delivery and micellar catalysis. Currently, their behaviour in the equilibrium cis- and trans-photostationary states is more widely understood than during the photoisomerisation process itself. Here, we investigate the time-dependent self-assembly of the different photoisomers of a model neutral AzoPS, tetraethylene glycol mono(4′,4-octyloxy,octyl-azobenzene) (C8AzoOC8E4) using small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). We show that the incorporation of in situ UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy with SANS allows the scattering profile, and hence micelle shape, to be correlated with the extent of photoisomerisation in real-time. It was observed that C8AzoOC8E4 could switch between wormlike micelles (trans native state) and fractal aggregates (under UV light), with changes in the self-assembled structure arising concurrently with changes in the absorption spectrum. Wormlike micelles could be recovered within 60 seconds of blue light illumination. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time the degree of AzoPS photoisomerisation has been tracked in situ through combined UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy-SANS measurements. This technique could be widely used to gain mechanistic and kinetic insights into light-dependent processes that are reliant on self-assembly.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft Matter Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...