The structure–property relationship in LAPONITE® materials: from Wigner glasses to strong self-healing hydrogels formed by non-covalent interactions†
Abstract
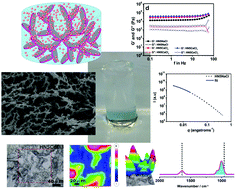
Rheology, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis, zeta potential measurement, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and micro-FTIR and absorbance spectroscopy were used to enlighten the controversial literature about LAPONITE® materials. Our data suggest that pristine LAPONITE® in water does not form hydrogels induced by the so-called “house of cards” assembly, but rather forms Wigner glasses governed by repulsive forces. Ionic interactions between anisotropic LAPONITE® nanodiscs, sodium polyacrylate and inorganic salts afforded hydrogels that were transparent, self-standing, moldable, strong, and biocompatible with shear-thinning and self-healing behavior. An extensive study on the role of salts in the gelification process dictates a trend that relates the valence of cations with the viscoelastic properties of the bulk material (G′ values follow the trend, monovalent < divalent < trivalent). These hydrogels present G′ values up to 5.1 × 104 Pa, which are considered high values for non-covalent hydrogels. Hydrogels crosslinked with sodium phosphate salts are biocompatible, and might be valid candidates for injectable drug delivery systems due to their shear-thinning behavior with rapid self-healing after injection.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry and Soft Matter Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...