Themed collection Designing Nanoparticle Systems for Catalysis

List of participants
Poster list
Perspectives on the design of nanoparticle systems for catalysis
An overview of the Faraday Discussion, “Designing Nanoparticle Systems for Catalysis”, is presented.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 595-607
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00124C
Supported cluster catalysts synthesized to be small, simple, selective, and stable
Molecular metal complexes on supports have drawn wide attention as catalysts offering new properties and opportunities for precise synthesis to make uniform catalytic species that can be understood in depth.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 9-33
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00076J
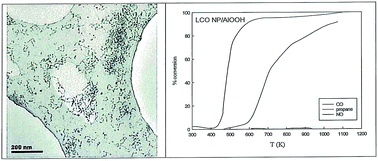
Nanoengineering ABO3 active sites from low-energy routes (TX100-stabilised water-in-oil microemulsions, surface segregation and surface complexation on colloidal AlOOH/sol–gel Al2O3 surfaces) for pollution control catalysis
LaCoO3 nanoparticles are active in CO and propane oxidation when adsorbed on AlOOH.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 537-553
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00006A
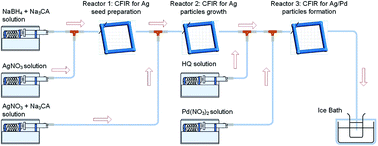
Continuous synthesis of hollow silver–palladium nanoparticles for catalytic applications
Hollow bimetallic nanoparticles exhibit unique surface plasmonic properties, enhanced catalytic activities and high photo-thermal conversion efficiencies amongst other properties, however, their research and further deployment are currently limited by their complicated multi-step syntheses.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 427-441
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00001H
Effects of heat treatment atmosphere on the structure and activity of Pt3Sn nanoparticle electrocatalysts: a characterisation case study
In this work, a variation in heat treatment atmosphere approach is taken to provide a series of related PtSn catalysts with the same nominal composition of Pt3Sn, but with different surface compositions.
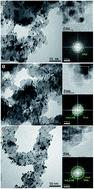
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 555-573
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00221A
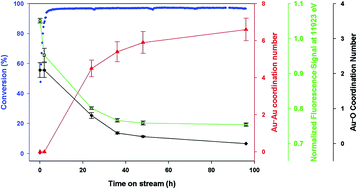
CO oxidation over supported gold nanoparticles as revealed by operando grazing incidence X-ray scattering analysis
Operando GISAXS/GIXD studies revealed that supported Au nanoparticles on a flat SiO2/Si(111) support undergo shape and phase transformations during CO oxidation.
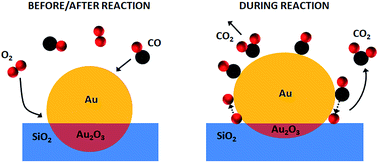
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 243-254
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00007G
One pot microwave synthesis of highly stable AuPd@Pd supported core–shell nanoparticles
A series of 1 wt% supported Au, Pd and AuPd nanoalloy catalysts were prepared via microwave assisted reduction of PdCl2 and HAuCl4 in a facile, one pot process.
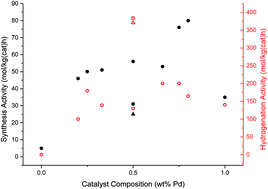
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 409-425
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00004B
Supported metal nanoparticles with tailored catalytic properties through sol-immobilisation: applications for the hydrogenation of nitrophenols
Nanoparticle property control, and excellent catalytic capabilities, has been demonstrated using Pd/TiO2 prepared by sol-immobilisation with solvent and temperature control.
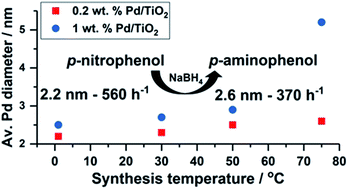
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 443-454
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00216E
Advancing semiconductor–electrocatalyst systems: application of surface transformation films and nanosphere lithography
We demonstrate that shadow nanosphere lithography (SNL) is an auspicious tool to systematically create three-dimensional electrocatalyst nanostructures on the semiconductor photoelectrode through controlling their morphology and optical properties.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 523-535
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00003D
Gold as a modifier of metal nanoparticles: effect on structure and catalysis
Bimetallic gold based catalysts have been prepared using a sol immobilisation technique. Depending on the second metal different structure have been obtained.
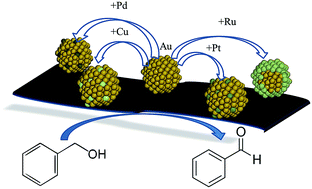
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 395-407
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00223H
Stability and mobility of supported Nin (n = 1–10) clusters on ZrO2(111) and YSZ(111) surfaces: a density functional theory study
We have used spin polarized density functional theory (DFT) to evaluate the geometrical resilience of Ni clusters on ZrO2(111) and YSZ(111).
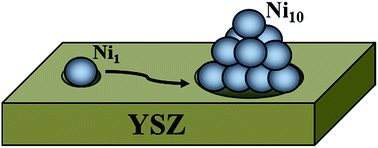
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 87-104
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00217C
Structural behaviour of copper chloride catalysts during the chlorination of CO to phosgene
An attapulgite-supported Cu(II)Cl2 catalyst has been studied with XANES and DFT approaches to follow the chlorination reaction of CO to phosgene.
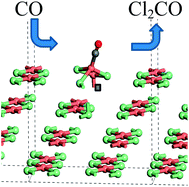
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 67-85
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00005K
The deposition of metal nanoparticles on carbon surfaces: the role of specific functional groups
The influence of hydroxyl and carbonyl groups on the deposition of gold from solution onto graphite surfaces was explored: OH gives Au0 whereas C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O results in Au3+.
O results in Au3+.
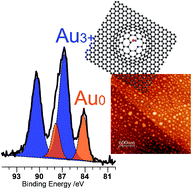
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 455-470
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00210F
The electronic properties of Au clusters on CeO2 (110) surface with and without O-defects
We use density functional theory with Hubbard corrections (DFT+U) to understand the local electronic properties of Au adatom and Au2 dimer adsorption on the CeO2 (110) surface with and without O-defects.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 123-145
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00002F
In situ formation of the active sites in Pd–Au bimetallic nanocatalysts for CO oxidation: NAP (near ambient pressure) XPS and MS study
Transformation of the surface structure of HOPG-supported bimetallic Pd–Au particles in the course of CO oxidation has been demonstrated using NAP XPS and MS techniques.
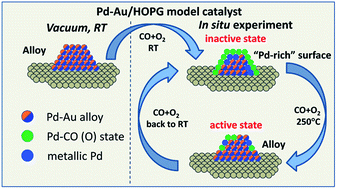
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 255-268
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00219J
CO adsorption and oxygen activation on group 11 nanoparticles – a combined DFT and high level CCSD(T) study about size effects and activation processes
The focus of this study lies in the activation of molecular oxygen and reaction with CO within density functional theory (DFT) and high level CCSD(T) calculations.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 105-121
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00225D
Operando study of palladium nanoparticles inside UiO-67 MOF for catalytic hydrogenation of hydrocarbons
Formation of Pd nanoparticles inside UiO-67 MOF was monitored by in situ X-ray absorption and diffraction.
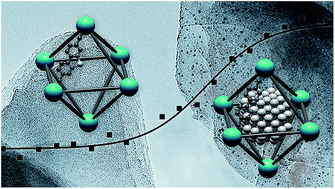
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 287-306
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00224F
Modelling free and oxide-supported nanoalloy catalysts: comparison of bulk-immiscible Pd–Ir and Au–Rh systems and influence of a TiO2 support
DFT calculations on free and TiO2-supported Pd–Ir and Au–Rh nanoalloys reveal that Janus and core–shell configurations compete on oxide supports.
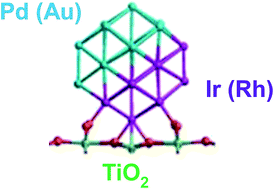
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 53-66
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00213K
Correlating structural dynamics and catalytic activity of AgAu nanoparticles with ultrafast spectroscopy and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations
Electron–phonon coupling times, equilibrium structures and surface segregation as a function of hollow core–shell AgAu nanoparticle composition.
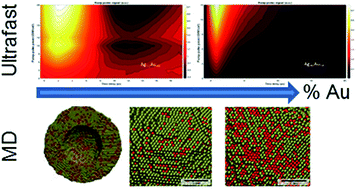
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 269-286
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00220C
The challenge of catalyst prediction
New insights and successful use of computational catalysis is highlighted.
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 35-52
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00208D
Time-resolved operando studies of carbon supported Pd nanoparticles under hydrogenation reactions by X-ray diffraction and absorption
We present a comprehensive study of a 5 wt% Pd/C catalyst in various environments by using in situ and operando X-ray absorption and diffraction.
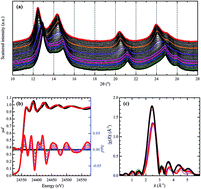
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 187-205
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00211D
Step edge structures on the anatase TiO2 (001) surface studied by atomic-resolution TEM and STM
Atomic arrangements in oxide surfaces can be uncovered by combining side view imaging using transmission electron microscopy and top view imaging using scanning tunnelling microscopy.
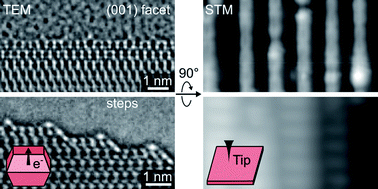
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 325-338
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00222J
Looking for the active hydrogen species in a 5 wt% Pt/C catalyst: a challenge for inelastic neutron scattering
We looked at the active hydrogen species in a highly dispersed and very homogeneous 5 wt% Pt/C industrial catalyst (Pt particle mean diameter of 2.0 ± 0.5 nm) for hydrogenation reactions, by coupling H2 adsorption measurements with Inelastic Neutron Scattering (INS).

Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 227-242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00214A
DFT calculation of oxygen adsorption on platinum nanoparticles: coverage and size effects
DFT calculations are used to simultaneously explore the effects of nanoparticle size and coverage for O adsorption on Pt nanoparticles.
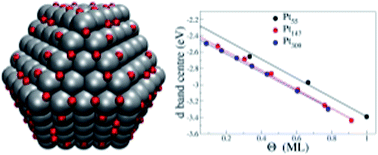
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 497-522
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00218A
Insights into structure and dynamics of (Mn,Fe)Ox-promoted Rh nanoparticles
The mutual interaction between Rh nanoparticles and manganese/iron oxide promoters in silica-supported Rh catalysts for the hydrogenation of CO to higher alcohols was analyzed by applying a combination of spectroscopy and microscopy.
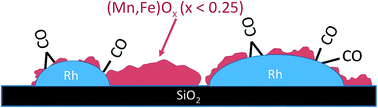
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 207-225
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00215G
Model systems in heterogeneous catalysis: towards the design and understanding of structure and electronic properties
We discuss in this paper two case studies related to nano-particle catalyst systems: one concerns a model system for the Cr/SiO2 Phillips catalyst for ethylene polymerization and the other provides additional information on Au nano-particles supported on ultrathin MgO(100)/Ag(100) films.
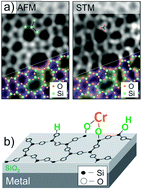
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 307-323
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FD00209B
The challenges of characterising nanoparticulate catalysts: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 339-394
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90014K
Theory as a driving force to understand reactions on nanoparticles: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 147-185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90013B
Control of catalytic nanoparticle synthesis: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 471-495
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90015A
Application of new nanoparticle structures as catalysts: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,208, 575-593
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90016G
About this collection
We are delighted to share with you a selection of the papers presented at our Faraday Discussion on Designing Nanoparticle Synthesis for Catalysis which took place in London, UK in May 2018. The final versions of all the articles presented and record of the live discussions are now available in the published Faraday Discussions volume 208.
Heterogeneous catalysis is a core area of contemporary physical chemistry posing major fundamental and conceptual challenges, and nanoparticles are pivotal components of many successful heterogeneous catalysts. For example, commercial Fischer–Tropsch catalysts require supported cobalt nanoparticles that are 6 nm in diameter for optimal performance. Nanoparticles are ubiquitous in many heterogeneous catalysts and this Faraday Discussion has explored the modern methods being used to design, synthesise and characterize nanoparticles, and how these bridge across the disciplines of physical science and chemical engineering. The core aim of the discussion was to develop a fundamental understanding of these crucial aspects of catalytic science, especially relating to nanoparticle synthesis and its use in catalytic reactions, knowledge of which is essential for the design of new catalysts.
Want to get a flavour of the meeting? Read the conference report here.