Themed collection Recent Open Access Articles

Leveraging engineered nanomaterials to support material circularity
There are numerous opportunities for nanomaterials and nanotechnology to support circular economy adoption. In this perspective, we present the important role engineered nanomaterials can play in advancing the circularity of bulk composite materials.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2885-2893
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00110A
Electrified CO2 valorization in emerging nanotechnologies: a technical analysis of gas feedstock purity and nanomaterials in electrocatalytic and bio-electrocatalytic CO2 conversion
This perspective illuminates the crucial need to consider gas feedstock purity and source when designing new electrified CO2 conversion nanomaterials.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1770-1783
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00912B
Recycling of non-product outputs containing rare elements originating in nanomaterial syntheses
Recycling of non-product outputs containing substantial amounts of rare elements originating in nanomaterial syntheses is relatively attractive as rare elements tend to be more valuable than abundant elements.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 684-687
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00795B
In vitro-based human toxicity effect factors: challenges and opportunities for nanomaterial impact assessment
Drawing the picture of the opportunities and challenges of using in vitro data to calculate effect factors in LCA.
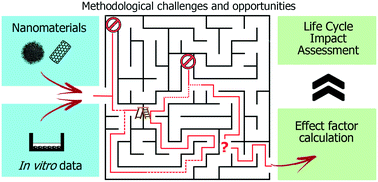
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 1913-1925
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01014J
Bioengineering applications of black phosphorus and their toxicity assessment
An overall structure of this review.
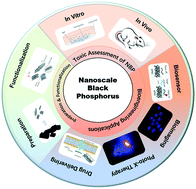
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 3452-3477
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00273B
Magnetically recyclable nanophotocatalysts in photocatalysis-involving processes for organic pollutant removal from wastewater: current status and perspectives
The critical review covers the applications, associated mechanisms, challenges, and prospects of magnetically recyclable nanophotocatalysts in photocatalysis-related processes.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1784-1816
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00906H
Graphene-based nanomaterials and microbial communities: a review of their interactions, from ecotoxicology to bioprocess engineering perspectives
This review discusses the interactions between graphene-based nanomaterials and microbial communities in different environmental compartments reconstituted in microcosms, from soil and freshwater to bioprocesses treating waste.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3725-3741
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00547F
Emerging investigator series: metal nanoparticles in freshwater: transformation, bioavailability and effects on invertebrates
MNPs may undergo different environmental transformations in aquatic systems, consequently changing their mobility, bioavailability and toxicity to freshwater invertebrates.
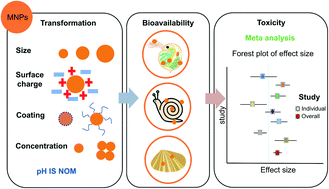
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2237-2263
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00052K
Determination of metallic nanoparticles in biological samples by single particle ICP-MS: a systematic review from sample collection to analysis
A systematic review of the use of single particle ICP-MS to analyse engineered nanomaterials in biological samples has highlighted that efforts have focused on a select few compositions and there is a lack of information for some important tissues.
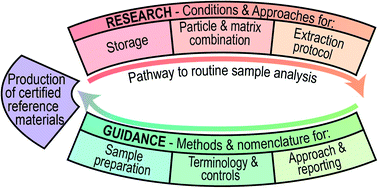
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 420-453
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00680K
Insights on toxicity, safe handling and disposal of silica aerogels and amorphous nanoparticles
The toxicity and ecotoxicity effects, handling and disposal of synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles and aerogels are reviewed and discussed.
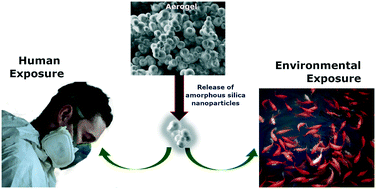
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 1177-1195
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00026H
Critical overview on the green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and their application for cancer therapy
A critical review which delves into the advantages of the use of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in nano-based cancer therapy, which includes its more positive environmental impact compared to previous systems.
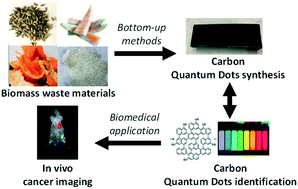
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 848-862
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00017A
Nanoscale control over water-film thickness using temperature modulation: tuning mineral carbonation reactivity
Temperature modulation was demonstrated as a novel way to control water partitioning during the reaction of silicate minerals with water-saturated supercritical carbon dioxide.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1412-1416
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00884C
Nanoparticles in bodily tissues: predicting their equilibrium distributions
We successfully predict distribution of nanoparticles (NPs) in human tissues applying surface energies for NPs, membranes, plasma and protein, considering various biochemical interactions. Phagocyte-rich and cancerous tissues accumulate NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 424-439
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00469K
Commercial photocatalyst changes the behavior of Formica pratensis and Formica polyctena
Commercial titania modified the behavior of ants by changing their cuticular hydrocarbon profile composition through photocatalytic oxidation.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 72-79
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01119G
Emerging investigator series: aramid amphiphile nanoribbons for the remediation of lead from contaminated water
Aramid amphiphiles with chelating head groups spontaneously form robust nanoribbons in water with surfaces capable of heavy metal remediation.
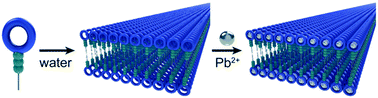
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 1536-1542
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00002K
Nanoformulations from olive pomace to enhance the efficacy of hydroxytyrosol as a natural pest control agent
Biocompatible nanoformulations made from olive pomace and egg yolk phosphatidylcholine to deliver hydroxytyrosol as an antiparasitic agent.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3625-3636
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00226A
Uptake and physiological impacts of nanoplastics in trees with divergent water use strategies
Anthropogenic contaminants can place significant stress on vegetation, especially when they are taken up into plants.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3574-3584
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00286E
Morphologic alterations across three levels of biological organization following oral exposure to silver-polymer nanocomposites in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes)
Exposure to AgNP-polymer nanocomposites and its individual component materials results in widespread but differing toxicologic effects.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3317-3334
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00368C
Fate and biological uptake of polystyrene nanoparticles in freshwater wetland ecosystems
Wetland mesocosms retained nanoplastics. Nanoplastics where taken up by freshwater invertebrates and macrophytes and mainly ended up in the sediments of the water compartment.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3475-3486
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00628J
Bioaccumulation and human risk assessment of inorganic nanoparticles in aquaculture species
Potential bioaccumulation and human oral bioavailability of TiO2 NPs and Ag NPs in aquaculture products.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2937-2947
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00167B
Quantifying mechanical abrasion of AgNP nanocomposites: influence of AgNP content on abrasion products and rate of microplastic production
Abrasion study of Ag–PETG nanocomposites helps to estimate how much AgNP microplastics are released from composite products during use or into the environment during their lifecycle.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2968-2977
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00888F
The endocrine disruptor effect of metal nanoparticles mainly depends on their capacity to release metal ions
This study compares the impact of different types of metal nanoparticles on major endocrine pathways. It shows that metal ions releasing ones such as silver nanoparticles inhibit Zn-finger dependent pathways, while rock solid nanoparticles do not.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 3192-3201
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00065J
Advanced materials earliest assessment (AMEA)
AMEA supports innovators in the earliest phases of material development. AMEA provides design rules and recommends more testing requirements and/or specific methods depending on the positioning of the material in categories.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2948-2967
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00831B
Bio-based carbon foams assembled with Fe nanoparticles for simultaneous remediation of As, Hg and PAHs in co-contaminated industrial soils
Sucrose foams are novel nanocomposites to remediate co-contaminated soils without affecting pH and EC or Fe availability in the soils.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2683-2692
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00927K
Functional silver-based nanomaterials affecting zebrafish development: the adverse outcomes in relation to the nanoparticle physical and chemical structure
The green and safe polymer HEC confers bio-interactive properties to Ag-Nps that, together with the small size and positive ζ potential, increase their biological reactivity towards zebrafish embryos.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2521-2540
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00813D
Green chemistry: advancing planetary phosphorus sustainability through the synergy of graphene oxide modified with magnetic nanoparticles (M@GO) for extracting tertiary effluent phosphorus in sewage treatment plants
The M@GO sorbent is easily separated from wastewater by a magnetic field.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2607-2619
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00859B
Impact of CeO2 nanoparticles on the microbiota of the S. flos-cuculi L. (Caryophyllaceae) rhizosphere
Influence of cerium oxide nanoparticles (nCeO2) on root bacterial composition and the associated substrate (root zone soil) of Silene flos-cuculi (L.) by metabarcoding.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2157-2172
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00479A
Biowaste valorization: multifunctional hybrid lignin/TiO2 nanostructures for bacterial-biocide disinfection and dye removal
Hybrid lignin TiO2 nanoparticles: red-ox activity enables biocide disinfection and dye removal.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2127-2144
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EN00091A
Plasmonic-based Raman sensor for ultra-sensitive detection of pharmaceutical waste
Pharmaceutical waste and contaminants pose a significant global concern for water and food safety.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 2083-2090
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00821E
AF4-MALS-SP ICP-ToF-MS analysis gives insight into nature of HgSe nanoparticles formed by cetaceans
Hg : Se atomic ratios in NPs formed in whales were constant with increasing particle size. The NPs also incorporated other metals (Cd, Sn) indicating that this process may not act exclusively as a MeHg detoxification process.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1883-1890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00886J
The effects of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots on autofluorescence properties and growth of algae Desmodesmus communis: dependence on cultivation medium
The cultivation media markedly influence the quantum dot induced effects on photosynthesis properties and growth of green freshwater microalgae.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1701-1712
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00955F
Influence of time and ageing conditions on the properties of ferrihydrite
Storage conditions affect the initial tetrahedral iron and hydroxyl populations of ferrihydrite, both are correlated and decrease over time as function of ageing.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1682-1692
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00828B
Selective metal recovery by mucin: turning gold from wastewater into a peroxymonosulfate-activated catalyst
This study explores mucin's ability to selectively recover gold (Au) from metal wastewater. The Au, in the form of a nanoparticle, was utilized in peroxymonosulfate activation for the degradation of bisphenol A.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1487-1498
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00699A
Toward environmentally favorable nano-sensing by production of reusable gold nanoparticles from gold nano-waste: life cycle and nanocircular economy implications
This study aids in the identification of environmentally friendly and sustainable applications of gold nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1499-1507
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00505D
Particles in a box: novel design and evaluation of an adaptable engineering control enclosure for a common split tube furnace to eliminate occupational exposure to refractory ceramic insulation fibers
Split tube furnaces routinely used in nanotechnology laboratories to generate C-based nanomaterials rely on refractory ceramic insulation fibers, which can pose an inhalation risk to operators.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 889-899
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00041A
Gold and titania nanoparticles accumulated in the body induce late toxic effects and alterations in transcriptional and miRNA landscape
Conventional toxicological methods and integrated transcriptomic analysis were used to comprehensively assess the potential health hazard of residual metal nanoparticles accumulated in the body due to poor solubility.
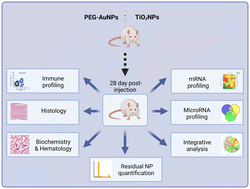
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1296-1313
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00954H
Super stable evaporators based on upcycled self-healing adsorbents for wastewater regeneration
Establishing a self-healing platform for the removal and resource recovery of heavy metals, enabling heavy metal-free drinking water.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1271-1282
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00829K
Similarity of multicomponent nanomaterials in a safer-by-design context: the case of core–shell quantum dots
Concepts of similarity applied to complex multicomponent advanced materials for an informed balance of performance and hazard.
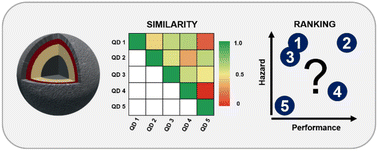
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 924-941
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00338H
Multifunctional halloysite nanotube–polydopamine agro-carriers for controlling bacterial soft rot disease
Halloysite nanotube-polydopamine core–shell nano-carriers loaded with thymol offer a sustainable alternative to existing pesticide formulations while providing enhanced efficacy, stability, and crop safety.
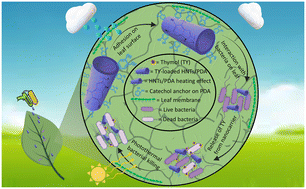
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1114-1128
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00934C
Photocatalytic and surface properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in soil solutions
Effet of chemical compounds in soil solution to the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1204-1216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00622K
Precursor- and waste-free synthesis of spark-ablated nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity and stability towards airborne organic pollutant degradation
Environmentally friendly and waste-free production of photocatalytic filters involving spark ablation and calcination processes for enhanced and durable photocatalytic performance.
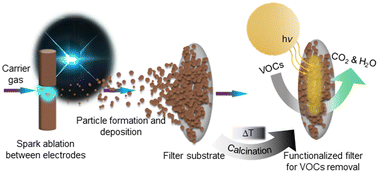
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1023-1043
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00348E
Europium-doped layered double hydroxide with spectral conversion property for enhanced photosynthesis
The europium doped layered double hydroxides (Eu-LDH) architecture has been designed via a co-precipitation method. It has been demonstrated photo-responsive property to enhance photosynthetic efficiency on Nicotiana benthamiana in greenhouse.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 812-818
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00394A
Submicron- and nanoplastic detection at low micro- to nanogram concentrations using gold nanostar-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates
This study focuses on using gold nanostar-based SERS substrates to detect 4 different types of plastic (6 particle sizes within the submicron- and nano-regimes). Substrates could be used to detect concentrations of plastics as low as 625 ng mL−1.
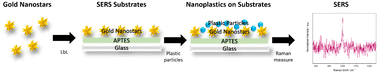
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 1000-1011
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00401E
Predicting the phytotoxic mechanism of action of LiCoO2 nanomaterials using a novel multiplexed algal cytological imaging (MACI) assay and machine learning
This work uses novel high-throughput phenotypic profiling techniques to elucidate the most probable phytotoxic mechanism of action of LiCoO2 nanosheets.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 507-517
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00629H
A versatile test system to determine nanomaterial heteroagglomeration attachment efficiency
Test system to determine nanomaterial heteroagglomeration attachment efficiency for fate models and risk assessment.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 588-600
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00161J
Depth-dependent transformation of ZnO and Ag nanoparticles in sulfate-reducing sediments tracked using scanning transmission electron microscopy
The transformation of Ag and ZnO nanoparticles was investigated along pore water depth gradients in sulfate-reducing sediments. This work highlights the benefits of tailored experimental strategies to study nanoparticle environmental transformations.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 136-148
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00550J
Clearance of nanoparticles from blood: effects of hydrodynamic size and surface coatings
The clearance pathways of nanoparticles from blood following pore penetration and phagocytosis (take the liver and kidney as examples).
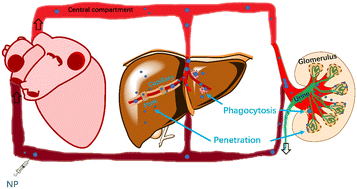
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 406-417
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00812F
Unveiling the origin of the efficient photocatalytic degradation of nitazoxanide over bismuth (oxy)iodide crystalline phases
The effect of the phase transition from bismuth iodide to bismuth oxyiodides on the photodegradation efficiency of nitazoxanide is explored.
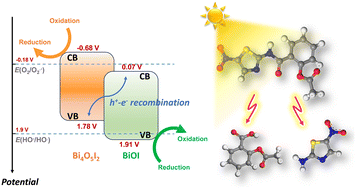
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 336-350
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00548H
Sub-100 nm nanoplastics: potent carriers of tributyltin in marine water
This study demonstrates that sub-100 nm nanoplastics have a significantly greater capacity for tributyltin adsorption, raising concerns that small nanoplastics may remobilise existing TBT pollution, rendering it more available to marine organisms.
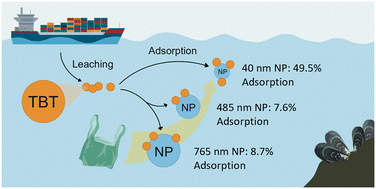
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2024,11, 241-252
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00659J
Development of single-cell ICP-TOFMS to measure nanoplastics association with human cells
Nanoplastics, solid polymer particles smaller than 1 μm, are suspected to be widely present in the environment, food and air, and may pose a potential threat to human health.
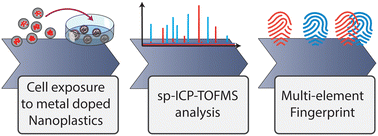
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3439-3449
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00681F
Reduction in insect attachment ability by biogenic and non-biogenic ZnO nanoparticles
ZnO-nanoparticles reduce the attachment ability of the green stinkbug Nezara viridula, a major pest worldwide, by aggregating on insect attachment devices. These findings can help to develop nontoxic pest-control methods that can be alternatives to insecticides.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3062-3071
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00545C
Porous calcium copper titanate electrodes for paracetamol degradation by electro-oxidation via CuO-induced peroxymonosulfate activation
Pharmaceutical-induced water pollution threatens health and ecosystems. Advanced oxidation, like electrocatalysis with peroxymonosulfate and calcium copper titanate as a key catalyst, shows promise for removing trace pollutants.
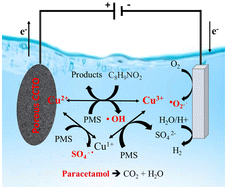
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3156-3170
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00317E
Investigation of magnetite–Co interactions: from environmentally relevant trace Co levels to core–shell Fe3O4@Co(OH)2 nanoparticles with magnetic applications
Three different Co(II) species are identified at the surface of stoichiometric magnetite (Fe(II)/Fe(III) = 0.5) by experiments, modeling, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. This affects the fate of Co, and the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles.
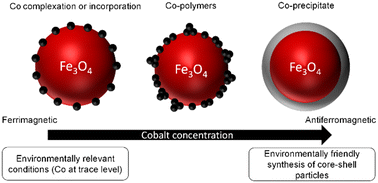
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3051-3061
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00379E
Synergistic and non-synergistic impact of HAP-based nano fertilizer and PGPR for improved nutrient utilization and metabolite variation in hemp crops
Nanofertilizer prepared with urea-hydroxyapatite amalgamation along with PGPR promotes urea availability over longer period of plant growth and reduces wasteful urea expense in soil, curtailing environmental pollution.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3101-3110
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00380A
Matrix-driven environmental fate and effects of silver nanowires during printed paper electronics end of life
The fate and impact of silver nanowires incorporated in a paper-based nano-enabled product (NEP) was investigated in freshwater mesocosms.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 3039-3050
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00263B
Green synthesis of a magnetite/graphitic carbon nitride 2D nanocomposite for efficient Hg2+ remediation
Green synthesis of a magnetite/graphitic carbon nitride 2D nanocomposite for efficient Hg2+ remediation in different aqueous matrices utilising a thermal assist sonication method.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2658-2671
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00367A
pH-responsive copper-doped ZIF-8 MOF nanoparticles for enhancing the delivery and translocation of pesticides in wheat plants
Copper-doped ZIF-8 nanoparticles loaded with fludioxonil enhanced pesticide translocation in plants compared with use of free fludioxonil, providing insight into the use of stimuli-responsive metal-doped MOF nanocarriers as pesticide-delivery systems in sustainable agriculture.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2578-2590
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00300K
Transformations, interactions, and acute biological responses of nanoplastics on mixotrophic microalgae Poterioochromonas malhamensis
Biological responses of nanoplastics (NPLs) to microalgae P. malhamensis were concentration, size and medium-dependent. The aggregation behavior is the most influential factor controlling the biological effects of NPLs in culture medium and environmental natural waters.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2459-2472
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00324H
Graphene oxide degradation by a white-rot fungus occurs in spite of lignin peroxidase inhibition
Graphene oxide can be degraded by ubiquitous fungal enzymes alternative to lignin peroxidase, inhibited by the nanomaterial.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2286-2298
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00072A
Antifungal activity and mechanisms of AgNPs and their combination with azoxystrobin against Magnaporthe oryzae
AgNPs not only disrupt activation of the Pmk1-mediated intracellular signaling pathway and conidial autophagy, but also display enhanced fungitoxicity to azoxystrobin-sensitive/resistant strains of M. oryzae when co-applied with azoxystrobin.
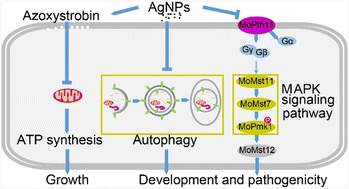
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2412-2426
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00168G
Metallic functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles enhances the selective removal of glyphosate, AMPA, and glufosinate from surface water
Functionalizing nanomaterials with polydopamine and different metals allows selective adsorption of target compounds, like emerging contaminants. Obtained materials are stable, efficient, and faster than bare or other nanoparticles.
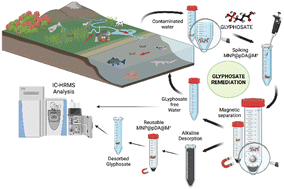
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2399-2411
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00129F
Polystyrene nanoplastics target lysosomes interfering with lipid metabolism through the PPAR system and affecting macrophage functionalization
Nanoplastics (NPs) are currently a main concern for environmental, animal and human health due to their potential to accumulate in different environmental compartments and provoke effects in living organisms.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 2245-2258
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01077A
Metabolomics-based analysis in Daphnia magna after exposure to low environmental concentrations of polystyrene nanoparticles
Particles used in the study: 53 nm PS-NH2 and 62 nm PS-COOH. Significant metabolic responses at: 3.2 μg L−1 PS NPs.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1858-1866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00142C
Nanoscale heterogeneity of arsenic and selenium species in coal fly ash particles: analysis using enhanced spectroscopic imaging and speciation techniques
Arsenic and selenium in coal fly ash are heterogeneously distributed at the nanoscale, explaining why the leaching of these elements is not readily predicted by bulk- or micron-scale element speciation methods.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1768-1777
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01056A
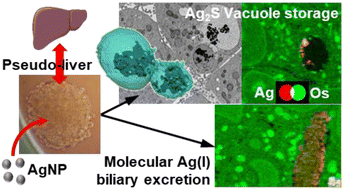
Deciphering silver nanoparticle fate in liver up to biliary excretion using HepG2/C3A spheroids in scenarios mimicking different exposure pathways
This study probes the exposure route-dependent fate of silver nanoparticles by using a 3D cell model mimicking the liver. It reveals the cellular trafficking and transformation of silver species, up to their storage in vacuoles or biliary excretion.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1842-1857
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00177F
Magnetic few-layer graphene nanocomposites for the highly efficient removal of benzo(a)pyrene from water
Magnetic graphene-based composite nanomaterials were developed to capture benzo(a)pyrene from water media. The synthesized nanomaterials couple very easy magnetic separation after adsorption with highly efficient removal of ∼99.9%.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1660-1675
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00047H
Interactions between cerium dioxide nanoparticles and arsenite change their biological fate in the gastrointestinal tract of mice
The large-scale production of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs), such as cerium dioxide nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs), raises concerns towards their impact on human health.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1585-1598
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00109A
Does the doping strategy of ferrite nanoparticles create a correlation between reactivity and toxicity?
The doping strategy of ferrite nanoparticles induced a correlation between their reactivity and toxicity. The evidence showed the induction of biological responses as a factor of their dissolution and suspension properties of ferrite nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1553-1569
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EN00076A
Chemical composition, coordination, and stability of Ca–organic associations in the presence of dissolving calcite
Aqueous Ca-(bi)carbonate organic associations with increased thermal stability.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1504-1517
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN01143C
Polycarbonate nanoplastics and the in vitro assessment of their toxicological impact on liver functionality
Polycarbonate photodegradation products, namely nanoplastics and molecular by-products, are formed in a single step. Studying their effects in a suitable hepatic model proves that both components induce toxicity toward hepatocellular functions.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2023,10, 1413-1427
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00963C
About this collection
Please see below for recent Open Access papers published in Environmental Science: Nano.