Themed collection Special Issue: Frontiers of Hydrogen Energy and Fuel Cells

Ammonia as a carbon-free hydrogen carrier for fuel cells: a perspective
The potential of utilizing ammonia as a hydrogen carrier for on-site power generation via ammonia decomposition is systematically discussed.
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 332-342
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00036B
Recent progress in high-loading single-atom catalysts and their applications
Achieving single-atom dispersion of metal active components remains daunting. Here, we summarized several key synthesis methods and applications of high-loading SACs, hoping to highlight important research areas for future development.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 486-500
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00062A
Cutting-edge methods for amplifying the oxygen evolution reaction during seawater electrolysis: a brief synopsis
Three approaches for enhancing OER activity and selectivity for hydrogen production in seawater electrolysis.
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 475-485
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00071K
Designing active and stable Ir-based catalysts for the acidic oxygen evolution reaction
Various strategies for optimization of Ir-based OER catalysts are summarized, including elemental doping, surface engineering, atomic utilization and support engineering.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 299-311
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00070B
Core–shell nanostructured magnesium-based hydrogen storage materials: a critical review
This minireview focuses on the synthesis of core–shell nanostructured magnesium-based materials to achieve hydrogen storage performances and analyses the mechanistic effects of this unique structure.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 282-298
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00061C
Recent progress of antipoisoning catalytic materials for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells doped with phosphoric acid
The current challenges and opportunities faced by HT-PEMFCs are discussed, as well as possible future solutions. This review can provide guidance for the future development of high-performance HT-PEMFC catalysts.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2024,2, 173-190
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00101F
Recent progress of manganese dioxide based electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
This review discusses the OER reaction mechanism (AEM and LOM) and the research progress of MnO2-based OER catalysts. The optimization strategy of MnO2-based catalysts was summarized.
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 312-331
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00034F
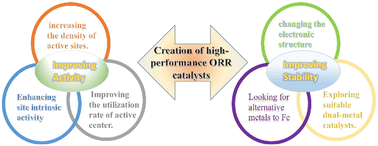
Non-noble metals as activity sites for ORR catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs)
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have great potential to become the next generation green energy technique, but its application is limited by the slow kinetics of the cathode oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in acidic medium.
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 388-409
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00002H
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of PEM fuel cells at low hydrogen partial pressures: efficient cell tests for mass production
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of PEM fuel cells under varying hydrogen concentrations reveals the origins of the correlation between hydrogen partial pressure and fuel cell performance.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2024,2, 132-140
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00075C
Electrochemical recovery of Pt/C electrocatalyst: optimization of the potential range on the leaching process and application to an aged MEA
An optimized potential window for efficient platinum electrodissolution, the first step of a Pt recycling process, is proposed.
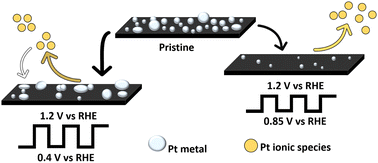
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2024,2, 118-131
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00085K
Effect of the calcination temperature on the characteristics of Ni/Fe-oxide electrocatalysts for application in anion exchange membrane electrolysers
Ni–Fe oxides were prepared by the oxalate pathway and heat-treated at three different temperatures. An outstanding performance was achieved in AEMWE by NiFeOx 450-anode-based MEA.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 553-562
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00065F
Unveiling the particle size effect and surface reactivity of Pt/C nanoparticles for ammonia electrooxidation using in situ infrared spectroscopy
In situ PM-IRRAS provides information about the reaction products of ammonia electrooxidation on the surface of Pt/C nanoparticles and in the bulk of electrolyte.
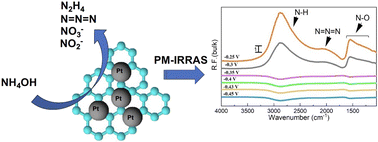
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 542-552
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00063J
Highly active ZIF-8@CNT composite catalysts as cathode materials for anion exchange membrane fuel cells
This study investigates the oxygen reduction reaction activity of transition-metal-doped ZIF-8 and carbon-nanotube-based composite catalysts in alkaline media and their performance in anion-exchange membrane fuel cells using an Aemion+® 15 μm AEM.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 526-541
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00081H
The effect of grafted alkyl side chains on the properties of poly(terphenyl piperidinium) based high temperature proton exchange membranes
New high-performance high temperature proton exchange membranes have been developed for fuel cell applications.
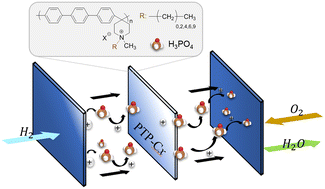
Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 516-525
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00064H
Does the platinum-loading in proton-exchange membrane fuel cell cathodes influence the durability of the membrane-electrode assembly?
MEAs with various cathode Pt loadings were elaborated and aged using a multiple-stressor accelerated stress test (AST) in a segmented PEMFC.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 501-515
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00059A
Investigation on electrocatalytic performance and material degradation of an N-doped graphene-MOF nanocatalyst in emulated electrochemical environments
This study presents electrochemical performance loss and correlated material degradation of an electrocatalyst, nitrogen-doped graphene integrated with a metal–organic framework (N-G/MOF), by the effect of H2O2-derived oxidative species.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 360-375
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00044C
Mono-, bi- and tri-metallic platinum group metal-free electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction following a facile synthetic route
HER electrocatalysts were synthesized starting from metal-phthalocyanine. The higher pyrolysis temperature is beneficial and associated with the formation of nanoparticles. The addition of the second and third metal is also beneficial for HER.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 343-359
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00058C
Polyaniline-derived carbon nanofibers with a high graphitization degree loading ordered PtNi intermetallic nanoparticles for oxygen reduction reaction
A three-dimensional carbon nanofiber (CNF) with a high graphitization degree was fabricated via high temperature treatment of polyaniline network. The CNF-1200 used as platinum-based catalyst ORR support exhibited excellent corrosion resistance.

Ind. Chem. Mater., 2023,1, 458-464
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3IM00056G
About this collection
As the most promising clean energy carrier in the 21st century, hydrogen represents the centerpiece in the transformation of energy and environmental technology. Moving toward a hydrogen-based society is crucial for humanity to address global sustainability issues and meet carbon neutrality targets, of which hydrogen production and storage, and hydrogen energy conversion (through fuel cells) are key technologies.
It is becoming increasingly clear that the development of these technologies is accelerating and interdependent. At present, demands for low-cost and at-scale chemistries and materials exist in every segment linking the hydrogen energy chain. This special issue aims to collect the inputs from the leading experts on the status, directions, and recent research breakthroughs in building future hydrogen energy ecosystem.
- Hydrogen storage materials
- Hydrogen production and generation
- Fuel cell materials from membranes to electrodes
- Fuel cell catalysts
This collection is guest edited by Prof. Lior Elbaz (Bar-Ilan University, Israel), Prof. Minhua Shao (The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, China), Prof. Jianglan Shui (Beihang University,China), Prof. Carlo Santoro (University of Milano-Bicocca, Italy,)