Themed collection Carbon Dioxide utilisation

Modified Cu–Zn–Al mixed oxide dual function materials enable reactive carbon capture to methanol
A novel RCC process using modified CZA DFMs to produce renewable MeOH is presented. K/CZA provides exceptionally high productivity of MeOH compared to previously reported attempts of RCC to MeOH.

EES. Catal., 2024,2, 253-261
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00254C
In situ solvothermal reduction engineering enables delicate control over surface-rich oxygen vacancies on Bi2WO6 for highly efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction
An in situ solvothermal reduction strategy is proposed to precisely regulate the oxygen vacancy distribution of Bi2WO6 in a refined control manner over programmable temperature, which shows a prominent photocatalytic CO evolution rate.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 495-503
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00019B
Revealing the activity and selectivity of ppm level copper in gas diffusion electrodes towards CO and CO2 electroreduction
Cu is a unique metal that catalyzes carbon monoxide/carbon dioxide (CO/CO2) to form high-order hydrocarbons and oxygenates through the CO/CO2 reduction reaction (CO/CO2RR) at decent selectivity and productivity.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 117-124
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00071G
Ultra-high-rate CO2 reduction reactions to multicarbon products with a current density of 1.7 A cm−2 in neutral electrolytes
The optimized cupric oxide nanoparticles on gas diffusion electrodes exhibited ultra-high-rate CO2 reduction reactions to multicarbon products with a current density of 1.7 A cm−2 in neutral electrolytes.
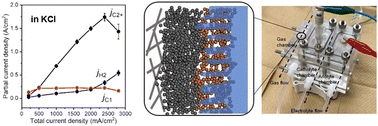
EES. Catal., 2023,1, 9-16
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00035K
Electrochemically decoupled reduction of CO2 to formate over a dispersed heterogeneous bismuth catalyst enabled via redox mediators
Electrochemical CO2 reduction is a topic of major interest in contemporary research as an approach to use renewably-derived electricity to synthesise useful hydrocarbons from waste CO2.
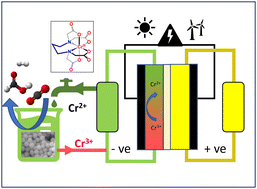
EES. Catal., 2024,2, 379-388
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00271C
Operando insights into correlating CO coverage and Cu–Au alloying with the selectivity of Au NP-decorated Cu2O nanocubes during the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction
Adding small amounts of Au Nanoparticles on Cu2O Nanocubes boost the selectivity of C2+ products during electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction.

EES. Catal., 2024,2, 311-323
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00162H
Highly selective Ag foam gas diffusion electrodes for CO2 electroreduction by pulsed hydrogen bubble templation
The manuscript presents a novel approach for polymer-based Ag-DHBT-GDE fabrication, enabling highly efficient CO2 electrolysis to CO with remarkable performance and selectivity.

EES. Catal., 2024,2, 286-299
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00220A
Enhancing C≥2 product selectivity in electrochemical CO2 reduction by controlling the microstructure of gas diffusion electrodes
Cu gas diffusion electrodes based on hydrophobic polymer substrates show an enhanced selectivity towards C2H4 and C≥2 products during the electrochemical reduction of CO2 upon decreasing substrate pore size.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 1009-1016
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00140G
Full-spectrum utilization of solar energy for simultaneous CO2 reduction and seawater desalination
To address the underutilization of infrared light in photocatalysis, a synergistic CO2 photoreduction and seawater desalination system was developed, which exhibited a good bifunctional performance.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 755-764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00098B
Identification of non-metal single atomic phosphorus active sites for the CO2 reduction reaction
Due to intrinsic difference between non-metal atoms and metal atoms, SACs with non-metal centers will also have unique characteristics, which would cause changes in the adsorption configuration of reaction intermediates, thereby regulating the reaction path.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 774-783
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00156C
Pathways to enhance electrochemical CO2 reduction identified through direct pore-level modeling
CO2 reduction in gas diffusion electrodes is modeled using direct numerical simulation, with species transport resolved in 2D throughout the catalyst layer, including steric effects. Modeling yields numerous ways to optimize GDE performance.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 704-719
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00122A
Microwave-assisted carbon-confined iron nanoparticles for steering CO2 hydrogenation to heavy hydrocarbons
The key to efficient thermocatalytic conversion of CO2 lies in the rational design of catalysts.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 516-528
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00071K
Unlocking nanotubular bismuth oxyiodide toward carbon-neutral electrosynthesis
Defective ultrathin Bi5O7I nanotubes are designed by the combination of structure and defect engineering strategies to achieve highly active, selective, and stable performance for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formate.

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 290-300
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EY00034F
Structural ordering enhances highly selective production of acetic acid from CO2 at ultra-low potential
The production of acetic acid from CO2 is tuned by the atomic ordering and optimized chemical bonding in ternary chalcogenides.
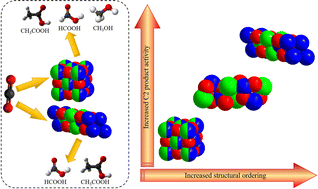
EES. Catal., 2023,1, 162-170
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00081D
Non-conventional low-temperature reverse water–gas shift reaction over highly dispersed Ru catalysts in an electric field
Selective CO2 hydrogenation to CO at low temperature (473 K or lower).

EES. Catal., 2023,1, 125-133
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00004K
Direct carbonate electrolysis into pure syngas
In a direct carbonate electrolysis system, a CO2 diffusion layer enabled the production of CO-rich syngas.
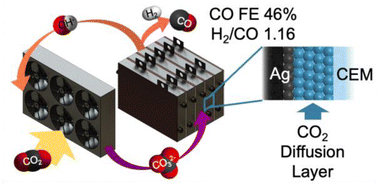
EES. Catal., 2023,1, 54-61
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00046F
Pit-embellished low-valent metal active sites customize CO2 photoreduction to methanol
Controllable adjustment of low-valent metal active sites near the pits can promote the WO3−x surface charge delocalization, which dominates the formation of *CHO intermediates, thus customizing a unique reaction pathway for CO2 reduction to CH3OH.
EES. Catal., 2023,1, 36-44
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EY00029F
About this collection
EES Catalysis is the home of innovative catalytic technologies. Please find here the topic collection for carbon dioxide utilisation, including a wide range of materials, to meet net zero targets and potentially form important products for energy applications.