Themed collection 2023 Chemical Science Covers

A breath of sunshine: oxygenic photosynthesis by functional molecular architectures
Water oxidation liberating dioxygen under visible light irradiation poses a formidable challenge to natural and artificial photosystems. The quest for the “green shift” represents a major goal to enhance the overall photosynthetic performance by tailoring molecular architectures.
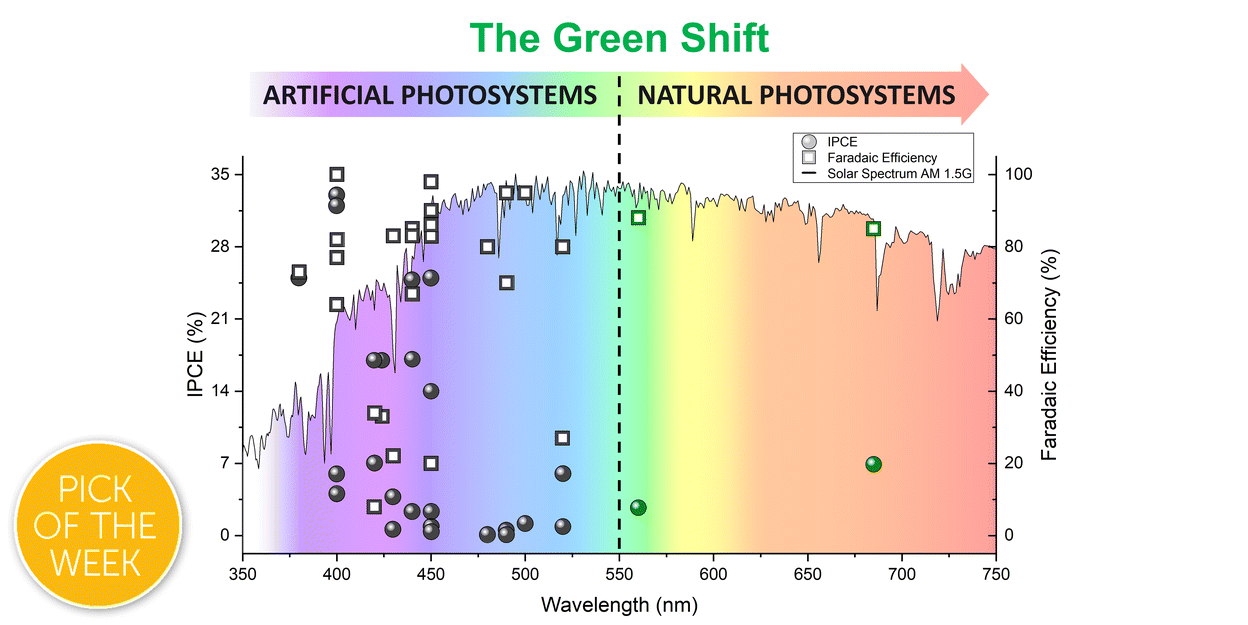
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12402-12429
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03780K
Quantum chemical calculations for reaction prediction in the development of synthetic methodologies
This perspective showcases how quantum chemical calculations drive predictive strategies to explore unknown reactions, catalysts, and synthetic routes toward complex molecules in synthetic methodology development.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11601-11616
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03319H
Chemical complexity for targeted function in heterometallic titanium–organic frameworks
Heterometallic cluster chemistry to control the function of titanium–organic frameworks.
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6826-6840
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01550E
Back to the future of organolanthanide chemistry
By taking inspiration from the structures and reactivities of its past, organolanthanide chemistry has managed to reinvent itself for the challenges of today and the future.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 443-457
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC05976B
Polyoxometalate–peptide hybrid materials: from structure–property relationships to applications
Organo-functionalisation of polyoxometalates with peptide moieties is an effective approach to obtain diverse arrays of functional hybrid materials, where each component influences the resulting change, surface chemistry, polarity, and redox properties.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10-28
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC05105B
Imprinting of nanoparticles in thin films: Quo Vadis?
The combination of molecular imprinting approaches and nanomaterials has recently emerged in new approaches for the imprinting of nanomaterials. This review summarizes the latest studies and the potential implications and applications of this field.
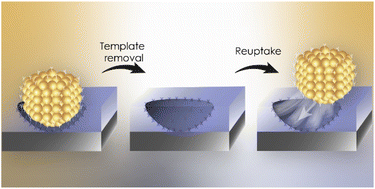
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9630-9650
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02178E
Circularity in polymers: addressing performance and sustainability challenges using dynamic covalent chemistries
This review provides a multidisciplinary overview of the challenges and opportunities for dynamic covalent chemistry-based macromolecules towards the design of new, sustainable, and recyclable materials for a circular economy.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 5243-5265
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00551H
Aptamers 101: aptamer discovery and in vitro applications in biosensors and separations
A primer that covers the discovery and validation process for novel aptamers and highlights recent applications of aptamers in biosensing and cell separations.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 4961-4978
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00439B
A copper(II) peptide helicate selectively cleaves DNA replication foci in mammalian cells
We report a CuII peptide helicate that selectively binds DNA 3WJs in cells, damaging DNA replication foci by ROS production, thus demonstrating for the first time the selective cleavage of this noncanonical DNA structure with a chemical nuclease.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 14082-14091
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03303A
Self-assembly of cyclic peptide monolayers by hydrophobic supramolecular hinges
A novel supramolecular tryptophan hinge motif enables the self-assembly of nanotube monolayers by hierarchical non-covalent polymerisation of cyclic peptides in lateral contact.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 14074-14081
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03930G
1,2-Disubstituted bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes as saturated bioisosteres of ortho-substituted benzene
1,2-Disubstituted bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes have been synthesized, characterized, and biologically validated as saturated bioisosteres of the ortho-substituted benzene ring.
![Graphical abstract: 1,2-Disubstituted bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes as saturated bioisosteres of ortho-substituted benzene](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D3SC05121H&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2023)
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 14092-14099
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC05121H
Ligand-centered to metal-centered activation of a Rh(III) photosensitizer revealed by ab initio molecular dynamics simulations
Excited state evolution of the rhodium(III) complex [Rh(III)(phen)2(NH3)2]2+ (phen = 1,10-phenanthroline) has been investigated theoretically to gain a better understanding of light-driven activation of high-energy metal centered states.
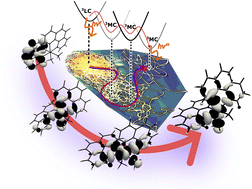
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 13713-13721
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04381A
Accelerating water oxidation – a mixed Co/Fe polyoxometalate with improved turnover characteristics
A novel mixed-metal cobalt–iron polyoxometalate (POM) aids the understanding of the role of the inner, coordinatively saturated metal ions in Weakley archetype POMs on the catalytic OER activity.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 13722-13733
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04002J
Spontaneous generation of singlet oxygen on microemulsion-derived manganese oxides with rich oxygen vacancies for efficient aerobic oxidation
We fabricated a range of Ny-MnOx using compartmentalized microemulsion crystallization followed by post-calcination. These materials have the unique ability to generate sufficient 1O2 at room temperature without requiring an external field.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 13402-13409
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04418A
Kinetically-driven reactivity of sulfinylamines enables direct conversion of carboxylic acids to sulfinamides
Sulfinamides can now be readily accessed from carboxylic acids and amines in a direct decarboxylative reaction enabled by the kinetically-driven reactivity of sulfinylamines and acridine photocatalysis.
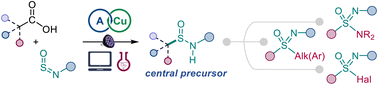
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 13384-13391
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04727J
Δ2 machine learning for reaction property prediction
Newly developed Δ2-learning models enable state-of-the-art accuracy in predicting the properties of chemical reactions.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 13392-13401
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02408C
Autofluorescent antimalarials by hybridization of artemisinin and coumarin: in vitro/in vivo studies and live-cell imaging
First antimalarial autofluorescent artemisinin–coumarin hybrids are highly in vitro/in vivo active, able to overcome drug resistances and are suitable for investigating their mode of action in living P. falciparum parasites by fluorescence microscopy.
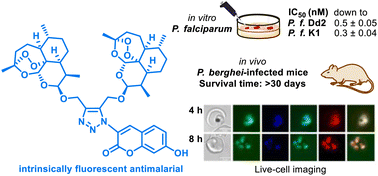
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12941-12952
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03661H
A dual-responsive ratiometric indicator designed for in vivo monitoring of oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity
A novel H2O2 and NAD(P)H indicator for in vivo monitoring oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity in the model of acute myocardial infarction and trichloroethylene exposure has been reported.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12961-12972
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04081J
Conformational control enables boroxine-to-boronate cage metamorphosis
The conformational control of boronic acid building blocks allows efficient self-assembly into a tetrahedral boroxine cage. The nano-sized cage displays molecular metamorphosis, converting from a boroxine tetrapod to a boronate bipyramid.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12953-12960
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02920D
Discovery of reactive peptide inhibitors of human papillomavirus oncoprotein E6
A covalent peptide ligand mimicking the binding motif in the E6AP protein selectively crosslinks to HPV16 E6 with quantitative conversion. This ‘reactide’ provides a starting point in the development of inhibitors against HPV-driven cancers.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12484-12497
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02782A
Fast and scalable solvent-free access to Lappert's heavier tetrylenes E{N(SiMe3)2}2 (E = Ge, Sn, Pb) and ECl{N(SiMe3)2} (E = Ge, Sn)
Lappert's heavier tetrylenes E{N(SiMe3)2}2 (E = Ge, Sn, Pb) have been efficiently prepared from GeCl2·(1,4-dioxane), SnCl2 or PbCl2 and Li{N(SiMe3)2} via a completely solvent-free one-pot mechanochemical route followed by sublimation.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12477-12483
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02709K
N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides deliver genotoxic formaldehyde to human cells
N-Acyloxymethyl-phthalimides are esterase-sensitive chemical tools that enable controllable delivery of formaldehyde to human cells.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12498-12505
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02867D
Impact of library input on the hit discovery rate in DNA-encoded chemical library selections
Exploring the impact of varied DNA-encoded chemical library (DEL) inputs on hit discovery rates in DEL screenings.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12026-12033
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03688J
Borylation directed borylation of N-alkyl anilines using iodine activated pyrazaboles
Doubly electrophilic pyrazabole derivatives (pyrazabole = [H2B(μ-C3N2H3)]2) combined with one equiv. of base effect the ortho-borylation of N-alkyl anilines.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12041-12048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04269C
Nitrenium ions as new versatile reagents for electrophilic amination
Bench-stable N-heterocyclic nitrenium ions were used for the efficient electrophilic amination of organometallic nucleophiles. The previously unexplored N-alkyl/aryl triazane intermediates were reduced to produce a diverse scope of primary amines.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 12034-12040
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04268E
Realizing long range π-conjugation in phenanthrene and phenanthrene-based molecular crystals for anomalous piezoluminescence
A long range π-conjugation has been realized by the designed π–π interactions in phenanthrene/phenanthrene-based molecular crystals, forming the “transannular effect”, which can be amplified by high pressure and induce novel piezoluminescence.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11629-11637
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04006B
Reverse thiophosphorylase activity of a glycoside phosphorylase in the synthesis of an unnatural Manβ1,4GlcNAc library
A carbohydrate phosphorylase is utilised in the synthesis of unnatural Manβ1,4-GlcNAc and longer β-mannan like glycans, including formation of phosphorolysis-stable thioglycoside linkages via novel "reverse thiophosphorylase" enzymatic activity.
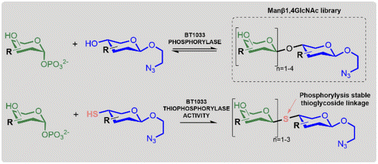
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11638-11646
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04169G
Resolving a guanine-quadruplex structure in the SARS-CoV-2 genome through circular dichroism and multiscale molecular modeling
Parallel or hybrid? A combination of multiscale molecular modeling and circular dichroism is used to predict a G-quadruplex structure at atomistic resolution in the SARS-CoV-2 genome.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11332-11339
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04004F
Electron count and ligand composition influence the optical and chiroptical signatures of far-red and NIR-emissive DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters
AgN-DNAs emitters at the far red/NIR spectral border have either 6 or 8 valence electrons and at least three distinct ligand compositions. Stokes shift magnitude and CD signatures are correlated with ligand composition.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11340-11350
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02931J
NMR exchange dynamics studies of metal-capped cyclodextrins reveal multiple populations of host–guest complexes in solution
Utilizing lanthanide-modified cyclodextrins and implementing the 19F-paraGEST method, up to three different co-existing populations of Ln-β-CD-guest complexes were experimentally identified, despite having similar thermodynamic and kinetic properties.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11351-11358
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03630H
Catalytic olefin metathesis in blood
A Ru-based artificial metalloenzyme (ArM) at just 1–5 mol% could catalyze olefin metathesis in blood to construct various molecular scaffolds. The cancer-targeting ArM at a low dosage could elicit tumor growth inhibition by in vivo drug synthesis.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11033-11039
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03785A
Photocyclization by a triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion pair in water – avoiding UV-light and oxygen removal
A commercially available upconversion pair is applied to promote a photocyclization for the synthesis of bioisosteres using green light irradiation. The reaction concept is enabled to run in water without oxygen removal by a micellar medium.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11040-11044
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03242F
A heterologous expression platform in Aspergillus nidulans for the elucidation of cryptic secondary metabolism biosynthetic gene clusters: discovery of the Aspergillus fumigatus sartorypyrone biosynthetic pathway
Secondary metabolites are important for the pathogenesis of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus which causes lethal Aspergillosis. Expressing groups of A. fumigatus genes in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans reveals new A. fumigatus secondary metabolites.
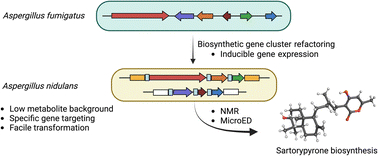
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 11022-11032
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02226A
Magainin 2-derived stapled peptides derived with the ability to deliver pDNA, mRNA, and siRNA into cells
We have developed cell-penetrating stapled peptides based on the amphipathic antimicrobial peptide magainin 2 for intracellular delivery of nucleic acids such as pDNA, mRNA, and siRNA.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10403-10410
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04124G
Visible-light-induced [3+2] cycloadditions of donor/donor diazo intermediates with alkenes to achieve (spiro)-pyrazolines and pyrazoles
Visible-light-induced [3+2] cycloadditions of donor/donor diazo precursors with alkenes to afford pyrazoles and (spiro)pyrazolines have been reported. Mechanistic and DFT studies suggested the non-covalent interactions promote the reaction.
![Graphical abstract: Visible-light-induced [3+2] cycloadditions of donor/donor diazo intermediates with alkenes to achieve (spiro)-pyrazolines and pyrazoles](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D3SC04188C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2023)
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10411-10419
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC04188C
Gaining control on optical force by the stimulated-emission resonance effect
The resonance between an electronic transition and an incident photon flux induces a pushing optical force. Instead, non-linear stimulated emission process induces a pulling force which direction is opposition to absorption processes.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10087-10095
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01927F
Mesomerism induced temperature-dependent multicomponent phosphorescence emissions in ClBDBT
The existence of two mesomerism structures could emit two phosphorescence bands simultaneously and well balance the distribution of excitons for multicomponent emissions.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10096-10102
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03963C
Transport limitations in polyolefin cracking at the single catalyst particle level
Catalytic cracking could enable low temperature conversion of hard-to recycle polyolefin plastics. However, traditional cracking catalysts suffer from macro and microscopic mass transport limitations, which call for plastic pre-treatment.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10068-10080
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03229A
Organocatalyst-mediated, pot-economical total synthesis of latanoprost
The six-pots synthesis of latanoprost has been accomplished with excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities through an organocatalyst-mediated Michael reaction, a substrate-controlled intramolecular Mukaiyama aldol reaction as key steps.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 10081-10086
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02978F
Modulating paired Ir–O–Ir via electronic perturbations of correlated Ir single atoms to overcome catalytic selectivity
The active center of a paired Ir–O–Ir structure was generated via electronic perturbations of correlated Ir single atoms on Co3O4 nanosheets, and the O atom of which functioned as the main active site for the selective electrocatalysis of As(III).

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9678-9688
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03285J
Guest-induced pore breathing controls the spin state in a cyanido-bridged framework
Variation of three different stimuli: the type of guest molecules, temperature and light enables intentional manipulation of the mechanical, electronic and magnetic properties of a cyanido-bridged coordination polymer.
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9651-9663
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03255H
Why surface hydrophobicity promotes CO2 electroreduction: a case study of hydrophobic polymer N-heterocyclic carbenes
Polymer NHCs as a strong binding motif together with hydrophobicity control the accessibility of substrates at catalyst–electrolyte interface and enhance CO2 electroreduction on metal catalysts.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9664-9677
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02658B
Dynamic self-assembly of supramolecular catalysts from precision macromolecules
Synthetic precision oligomers with complementary sticky ends and functional catalytic groups form dynamic constitutional libraries comprising cyclic di(oligomer)s which prove much more efficient for catalysis than other components of the library.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9283-9292
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03133K
Solvent-controlled formation of alkali and alkali-earth-secured cucurbituril/guest trimers
Cucurbit[7]uril complexes aggregate into well-defined trimers in dimethyl sulfoxide in the presence of a selection of cations, as long as the host cavity is filled with a guest that leaves one carbonylated portal available for cation binding.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9258-9266
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02032K
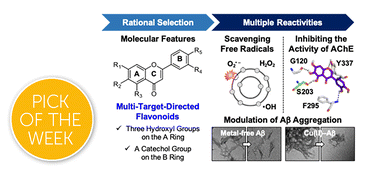
Designing multi-target-directed flavonoids: a strategic approach to Alzheimer's disease
Rational structure–mechanism-based strategies for identifying small molecules that are able to control multiple pathological targets in Alzheimer's disease are established, with an example of developing a promising multi-target-directed flavonoid.
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9293-9305
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00752A
A transient vesicular glue for amplification and temporal regulation of biocatalytic reaction networks
A transient vesicular assembly enables gluing of enzymes, with augmented catalysis. Efficient temporal control of the enzyme activities is achieved even in complex reaction networks.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9267-9282
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00195D
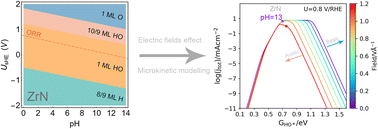
Origin of the superior oxygen reduction activity of zirconium nitride in alkaline media
This work identifies a new mechanism for the origin of the superior ORR activity of ZrN in alkaline media, combining electrochemical surface state analysis, density functional theory, and pH-dependent microkinetic modeling.
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 9000-9009
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01827J
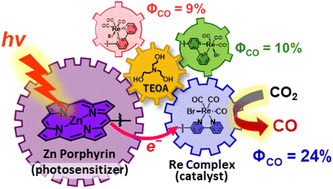
Significance of the connecting position between Zn(II) porphyrin and Re(I) bipyridine tricarbonyl complex units in dyads for room-temperature phosphorescence and photocatalytic CO2 reduction: unexpected enhancement by triethanolamine in catalytic activity
In three Zn porphyrin–Re complex dyads, we explored room-temperature phosphorescence and photocatalytic CO2 reduction. The dyad with a 5-position linkage to the bipyridine ligand showed notable activity due to dual triethanolamine coordination to Zn and Re ions.
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8743-8765
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02430J
In vitro characterization of nonribosomal peptide synthetase-dependent O-(2-hydrazineylideneacetyl)serine synthesis indicates a stepwise oxidation strategy to generate the α-diazo ester moiety of azaserine
Identification of azaserine biosynthetic gene cluster and in vitro reconstitution of O-(2-hydrazineylideneacetyl)serine synthesis showed that the diazo group of azaserine is synthesized by the stepwise oxidation of a hydrazinoacetic acid moiety.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8766-8776
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01906C
A visible-light-driven molecular motor based on barbituric acid
Yeehaw! The rotation of a visible-light-driven molecular motor based on barbituric acid is tamed by a hydrogen bonding “lasso” mechanism between its serendipitously-formed tertiary hydroxy stereocentre and its lower half carbonyl groups.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8458-8465
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03090C
Chemistry of zipping reactions in mesoporous carbon consisting of minimally stacked graphene layers
The progress of graphene-zipping reactions in graphene-based materials is successfully visualized using advanced temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) up to 2073 K.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8448-8457
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02163G
Vacuum ultraviolet photodissociation of sulfur dioxide and its implications for oxygen production in the early Earth's atmosphere
The emergence of molecular oxygen (O2) in the Earth's primitive atmosphere is an issue of major interest.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8255-8261
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC03328G
Simple purification of small-molecule-labelled peptides via palladium enolate formation from β-ketoamide tags
A solid-supported palladium complex successfully captured β-ketoamide-tagged peptides as palladium enolates and released them in high yield upon acid treatment.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8249-8254
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC03112D
Cationic tetranuclear macrocyclic CaCo3 complexes as highly active catalysts for alternating copolymerization of propylene oxide and carbon dioxide
We found that a cationic hetero tetranuclear complex including a calcium and three cobalts exhibited high catalytic activity toward alternating copolymerization of propylene oxide (PO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8262-8268
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00974B
Therapeutic efficacy of 211At-radiolabeled 2,6-diisopropylphenyl azide in mouse models of human lung cancer
We developed 211At-radiolabeled 2,6-diisopropylphenyl azide (ADIPA) for targeted α-particle therapy. In the experiment using a mouse model, low-dose (70 kBq) administration of ADIPA effectively suppressed tumor growth without causing adverse effects.
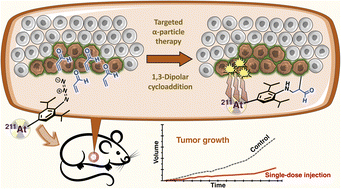
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8054-8060
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02513F
Total synthesis of atropisomeric indolosesquiterpenoids via N–N bond formation: dixiamycins A and B
The total synthesis of the naturally occurring N–N atropo-diastereomers dixiamycin A (1a) and dixiamycin B (1b) using a key Cu(I)-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of xiamycin A methyl ester (2b) was developed.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 8047-8053
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC07119C
Development of 8–17 XNAzymes that are functional in cells
Modified 8–17 DNAzymes that can induce target gene silencing in cells were developed based on the X-ray crystal structure of 8–17 DNAzyme and the modifications used in designing antisense oligonucleotides.
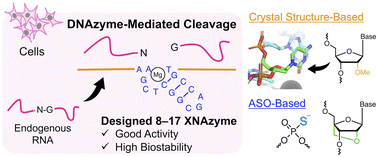
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7620-7629
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01928D
Semi-enzymatic acceleration of oxidative protein folding by N-methylated heteroaromatic thiols
We report the first example of a synthetic thiol-based compound that promotes oxidative protein folding upon 1-equivalent loading to the disulfide bonds in the client protein to afford the native form in over 70% yield.
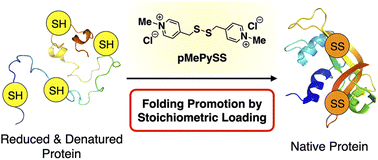
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7630-7636
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01540H
Synthesis and comparison of iso-structural f-block metal complexes (Ce, U, Np, Pu) featuring η6-arene interactions
Reaction of a terphenyl bis(anilide) ligand with trivalent halide precursors of Ce and early actinides yield both neutral and “-ate” complexes. These molecules afford comparative insight into f-block metal–arene bonding.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7438-7446
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02194G
First principles reaction discovery: from the Schrodinger equation to experimental prediction for methane pyrolysis
The methane pyrolysis reaction network is constructed from first principles in the ab initio nanoreactor, going from reaction discovery through ab initio molecular dynamics to chemical kinetic modeling and comparison to experiments.
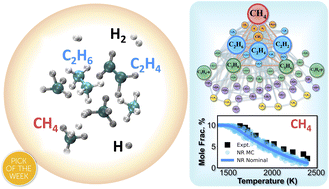
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7447-7464
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01202F
Gel transformation as a general strategy for fabrication of highly porous multiscale MOF architectures
The transformation of inorganic gels into MOFs is developed as a general strategy to construct complex porous MOF architectures at nano, micro, and millimeter length scales.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7114-7125
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00905J
Self-assembly of achiral building blocks into chiral cyclophanes using non-directional interactions
The transfer of stereo-electronic information from achiral building blocks and templates to chiral cyclophanes is rationalized and exploited to produce self-assembled macrocyclic species carrying up to 16 stereogenic elements.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7126-7135
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01235B
Cyclic peptides target the aromatic cage of a PHD-finger reader domain to modulate epigenetic protein function
We report the development of a potent and selective de novo cyclic peptide ligand for epigenetic methyllysine reader domain. The cyclic peptide binds at the aromatic cage of PHD-finger and modulates the JmjC lysine demethylase activity of KDM7.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 7136-7146
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC05944D
A conductive catecholate-based framework coordinated with unsaturated bismuth boosts CO2 electroreduction to formate
A conductive MOF, named Bi-based catecholate BiHHTP, exhibited excellent catalytic performance towards CO2 electroreduction.
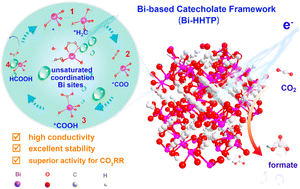
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6860-6866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01876H
Highly efficient light harvesting of a Eu(III) complex in a host–guest film by triplet sensitization
Very high photoluminescence intensity of a Eu(III) complex is achieved using a host–guest system. The intensity is 400 times larger than that of the Eu(III) complex itself.
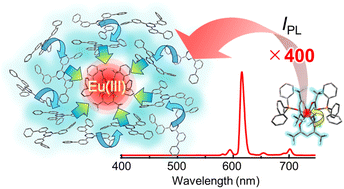
Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6867-6875
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01817B
Structural and dimensional control of porphyrin capsules using Group 15 tris(3-pyridyl) linkers
Changing the bridgehead atom of E(3-Py)3 (E = P, Sb, Bi) ligands can modulate the size and shape of supramolecular capsules, while coordination to the appropriate metalloporphyrin allows formation of discrete molecular capsules or extended structures.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6522-6530
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC02151C
Probing collective terahertz vibrations of a hydrogen-bonded water network at buried electrochemical interfaces
In a density of states format of the frequency-extended surface-enhanced Raman spectrum, potential-induced variations of the lifetime of hydrogen bonds and their dynamic behavior were observed at aqueous solution/Au interfaces.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6531-6537
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01734F
Photoluminescence control by atomically precise surface metallization of C-centered hexagold(I) clusters using N-heterocyclic carbenes
The properties of metal clusters are highly dependent on their molecular surface structure.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6207-6215
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01976D
Unveiling catalyst-free electro-photochemical reactivity of aryl diazoesters and facile synthesis of oxazoles, imide-fused pyrroles and tetrahydro-epoxy-pyridines via carbene radical anions
First ever catalyst-free electro-photochemical generation of carbene radical anion from aryl diazoester with direct application into synthesis of interesting N-heterocycles with broad substrate scope and excellent diastereo-selectivity.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 6216-6225
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC00089C
AI facilitated fluoro-electrochemical phytoplankton classification
Schematic of fluoro-electrochemical microscopy. (a) Cartoon E. huxleyi is green under normal light, but (b) emits red fluorescence under UV. (c) Placed near an oxidizing electrode, its fluorescence fades and ultimately (d) “switches off”.

Chem. Sci., 2023,14, 5872-5879
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SC01741A
About this collection
This collection includes all the articles featured on the covers of Chemical Science in 2023. We hope you enjoy browsing through the collection and seeing the cover images on the front page of each Advance Article PDF! As with all Chemical Science articles, they are completely free to access and read. If a particular cover image appeals to you, do feel free to share on social media using the buttons on each article landing page and use our hashtag: #ChemSciCovers