Themed collection Food & Function HOT Articles 2023

Ingredients, structure and reconstitution properties of instant powder foods and the potential for healthy product development: a comprehensive review
The structure of instant powder foods is significantly influenced by their ingredients. Instant powder foods potentially can be formulated with functional or beneficial compounds to provide health benefits.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 37-61
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04216B
Research progress on ginger polysaccharides: extraction, purification and structure–bioactivity relationship
Ginger is a widespread source of herbal medicine and traditional spices.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10651-10666
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03552B
The sources, properties, extraction, biosynthesis, pharmacology, and application of lycopene
Lycopene is an important pigment with an alkene skeleton from Lycopersicon esculentum, which is also obtained from some red fruits and vegetables.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9974-9998
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03327A
Protein-based nutritional strategies to manage the development of diabetes: evidence and challenges in human studies
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the most prevalent diseases in modern society, governed by both genetic and environmental factors, such as nutritional habits. Dietary habits have a relevant impact on its development.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9962-9973
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02466K
Polyphenols as NLRP3 inflammasome modulators in cardiometabolic diseases: a review of in vivo studies
Steps of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation pathway where some selected polyphenols have shown a positive modulatory effect on different cardiometabolic alterations.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9534-9553
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03015F
Emerging trends and applications of metabolomics in food science and nutrition
The study of all chemical processes involving metabolites is known as metabolomics.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9050-9082
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01770B
Advances in the protection of intestinal mucosal barrier function by milk-derived miRNAs
We focus on summarizing the biological stability of miRNAs and its molecular mechanism in regulating the intestinal mucosa barrier.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 3909-3928
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00137G
Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the effects of probiotics in Parkinson's disease
Patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) demonstrate intestinal dysbiosis and substantial gastrointestinal dysfunction.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 3406-3422
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03825K
Dose–response meta-analysis of ultra-processed food with the risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: evidence from prospective cohort studies
Each additional daily serving of UPF is associated with a 4% higher risk of CVEs and a 2% higher risk of total death. For maintaining good health, one should consume less UPF and more unprocessed or minimally processed food.
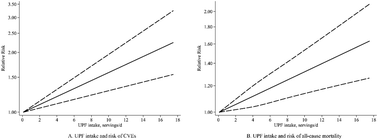
Food Funct., 2023,14, 2586-2596
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO02628G
Urolithin A production drives the effects of pomegranate on the gut microbial metabolism of bile acids and cholesterol in mild dyslipidaemic overweight and obese individuals
Urolithin-A drives the effects of pomegranate on the microbial metabolism of bile acids and cholesterol with possible consequences on human health.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 2422-2432
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05014A
Dietary supplementation with α-ionone alleviates chronic UVB exposure-induced skin photoaging in mice
Dietary α-ionone mitigates chronic UVB-induced skin photoaging by reducing wrinkles, alleviating dryness, promoting extracellular matrix, and inhibiting cellular senescence in mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 1884-1898
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04379G
Switching the polarity of mouse enteroids affects the epithelial interplay with prenylated phenolics from licorice (Glycyrrhiza) roots
A novel 3D-apical-out mouse enteroid model to investigate effects on the intestinal epithelium, including cytotoxicity, cell viability, and biotransformation. Evaluating the impact of prenylated phenolics from licorice (Glycyrrhiza) roots.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 1852-1866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02961A
A quinoa peptide protects impaired mucus barriers in colitis mice by inhibiting NF-κB-TRPV1 signaling and regulating the gut microbiota
A novel anti-inflammatory peptide TPGAFF from quinoa protects impaired mucus barriers by inhibiting NF-κB-TRPV1 signaling and regulating the gut microbiota in DSS-induced colitis mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 1223-1236
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04905A
Relationship of dietary intake of food folate and synthetic folic acid intake from fortified foods with all-cause mortality in individuals with chronic kidney disease
The current study found that higher intake of dietary natural folate, but not synthetic folic acid intake from fortified foods, was associated with lower risks of all-cause mortality among chronic kidney disease (CKD) participants.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 559-568
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03927G
Effects of pectin's degree of methyl esterification on TLR2-mediated IL-8 secretion and tight junction gene expression in intestinal epithelial cells: influence of soluble TLR2
Low DM-pectins have strong anti-inflammatory effects and prevents dysregulation of TJ-related genes. The effects of pectin are dependent on DM of the pectin, the magnitude of TLR2 expression and on circulating sTLR2 in blood.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 569-579
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03673A
Astaxanthin slows down skeletal muscle atrophy in H22 tumor-bearing mice during sorafenib treatment by modulating the gut microbiota
Astaxanthin supplementation altered the amino acid metabolism in tumor-bearing mice by modulating intestinal flora, thereby reducing the rate of skeletal muscle atrophy in tumor-bearing mice undergoing treatment.
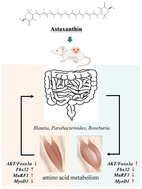
Food Funct., 2024,15, 543-558
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04633H
Ganoderma lucidum methyl ganoderate E extends lifespan and modulates aging-related indicators in Caenorhabditis elegans
Ganoderma lucidum methyl ganoderate E (MGE) improves healthspan and extends lifespan through the insulin/IGF-1 pathway, modulating neuroactive signaling and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis.
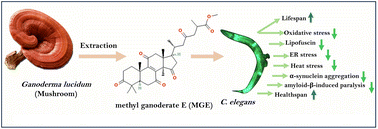
Food Funct., 2024,15, 530-542
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04166B
Pterostilbene alleviates abdominal aortic aneurysm via inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis by activating the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis
Our findings provide evidence that macrophage pyroptosis contributes to the development of AAA and that the activation of the miR-146a/TRAF6 axis by pterostilbene protects against macrophage pyroptosis and AAA formation.
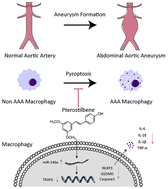
Food Funct., 2024,15, 139-157
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01235B
Diallyl trisulfide inhibits 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced lung cancer via modulating gut microbiota and the PPARγ/NF-κB pathway
DATS ameliorated NNK-induced lung tumorigenesis by the modulation of gut microbiota and regulation of the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby reducing the accumulation of inflammatory factors.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 158-171
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03914E
Preparation of a novel expandable konjac fiber at different freezing temperatures and exploration of its digestion regulation functions
A new form of konjac fiber can instantaneously expand in the digestive tract and inhibit the digestion of the chyme.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 125-138
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03814A
In vitro-simulated intestinal flora fermentation of Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides obtained by different assisted extractions and their fermented products against HT-29 human colon cancer cells
Herein, the in vitro-simulated intestinal flora fermentation of Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides with microwave, ultrasonic, ultra-high pressure-assisted extraction and their fermented products against HT-29 human colon cancer cells were studied.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10747-10758
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04421A
Fermented cereal-origin gerobiotic cocktails promote healthy longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Gerobiotic synergism reveals the secrets to healthy longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Food Funct., 2023,14, 10430-10442
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02984K
Unveiling the influence of daily dietary patterns on brain cortical structure: insights from bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Cognitive impairment is a significant concern in aging populations.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10418-10429
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02879H
Assessment of human inter-individual variability of phloretin metabolites in urine after apple consumption. AppleCOR study
This study aimed to assess the inter-individual variation in phloretin absorption and metabolism and to seek possible phloretin metabotypes following apple snack consumption.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10387-10400
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02985A
Inhibition of the NF-κB and mTOR targets by urolithin A attenuates D-galactose-induced aging in mice
The dose-effect relationship between colonic perfusion of urolithin A and its anti-aging effect was investigated. Urolithin A inhibits NF-κB and mTOR targets to attenuate D-galactose-induced motor and cognitive decline.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10375-10386
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03847E
Akkermansia muciniphila attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by modulating the gut microbiota and SCFAs in mice
Akkermansia muciniphila attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by modulating the gut microbiota and SCFAs in mice.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10401-10417
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04051H
Dietary Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG extracellular vesicles enhance antiprogrammed cell death 1 (anti-PD-1) immunotherapy efficacy against colorectal cancer
Dietary Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG extracellular vesicles (LGG-EV) synergistically enhanced anti-PD-1 immunotherapy efficacy against colorectal cancer. It was associated with improved tumor immunosuppressive environment, the abundance of beneficial bacteria and elevated specific serum metabolites.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10314-10328
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02018E
β-Carbolines norharman and harman change neurobehavior causing neurological damage in Caenorhabditis elegans
β-Carbolines norharman and harman, belonging to the class of heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs), are typical hazardous substances produced during the thermal processing of food.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 10031-10040
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03732K
Oligonol ameliorates liver function and brain function in the 5 × FAD mouse model: transcriptional and cellular analysis
5 × FAD Alzheimer's disease male mice were treated orally with oligonol at a daily dose of 50 mg kg−1 for 8 weeks. Oligonol oral treatment was found to improve cognitive function, and to reduce anxiety and depression in 5 × FAD Alzheimer's disease mouse.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9650-9670
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03451H
Effect of red wheat, aleurone, and testa layers on colon cancer biomarkers, nitrosative stress, and gut microbiome composition in rats
Red wheat, aleurone, and testa reduce aberrant crypt foci and 3-nitrotyrosine and modify gut microbiome composition.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9617-9634
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03438K
Comparison of the taste mechanisms of umami and bitter peptides from fermented mandarin fish (Chouguiyu) based on molecular docking and electronic tongue technology
Key indicators of molecular docking related to taste intensity were specified in umami and bitter peptides to develop a rapid screening technique for taste peptides.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9671-9680
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02697C
Maize near-isogenic lines with enhanced flavonoids alleviated dextran sodium sulfate-induced murine colitis via modulation of the gut microbiota
Anthocyanins and phlobaphenes enriched maize lines restored intestinal barrier function, mucosal integrity and modulated gut microbiota to display a protective effect against DSS-induced colitis.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9606-9616
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02953K
Development of a novel (poly)phenol-rich diet score and its association with urinary (poly)phenol metabolites
Estimating (poly)phenol intake is challenging due to inadequate dietary assessment tools and limited food content data.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9635-9649
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01982A
Lactiplantibacillus biofilm and planktonic cells ameliorate ulcerative colitis in mice via immunoregulatory activity, gut metabolism and microbiota modulation
Since ulcerative colitis (UC) has become a global concern, Lactiplantibacillus is considered an effective, safe strategy for alleviating intestinal inflammation in UC patients.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9181-9193
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02733C
Designing sustainable weaning foods for developing countries: not only a matter of nutrients
Blended complementary foods from cereals and high-protein sources are used to cope with infants’ malnutrition. Our results demonstrate that a combination of strategies and technologies is needed to balance nutritional and physical quality.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9194-9203
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02832A
Association between all aspects of dietary diversity and risk of depressive symptoms in US adults
Dietary diversity score, Healthy Food Diversity Index, and Healthy Eating Index were inversely associated with the risk of depressive symptoms.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 9204-9211
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00642E
Mangiferin alleviates trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO)-induced atherogenesis and modulates gut microbiota in mice
Mangiferin effectively alleviated TMAO-induced atherosclerosis through its cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and gut microbial modulatory activities in mice on a high-choline diet.
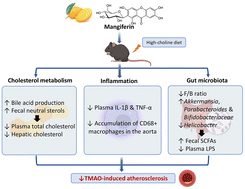
Food Funct., 2023,14, 9212-9225
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02791K
Effects of hazelnut protein isolate-induced food allergy on the gut microenvironment in a BALB/c mouse model
We established a hazelnut protein isolate (HPI)-allergic mouse model and the effects of HPI allergy on the duodenum, jejunum, ileum and colon microenvironment were investigated.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 8761-8774
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02324A
Konjac glucomannan-assisted curcumin alleviated dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice colitis via regulating immune response and maintaining intestinal barrier integrity
Curcumin has been proven to be an effective strategy for reducing inflammatory responses.
Food Funct., 2023,14, 8747-8760
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01068F
Xylooligosaccharides from corn cobs alleviate loperamide-induced constipation in mice via modulation of gut microbiota and SCFA metabolism
This study aimed to investigate the potential of xylooligosaccharides extracted from corn cobs in alleviating constipation and the mechanism of action in vivo.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 8734-8746
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02688D
Impact of polyphenol oxidase on the bioavailability of flavan-3-ols in fruit smoothies: a controlled, single blinded, cross-over study
Flavan-3-ols are important dietary bioactives. While fruits are significant sources of these compounds, fruit smoothies, particularly those with high levels of polyphenol oxidase, do not represent a viable option to increase flavan-3-ol intake.
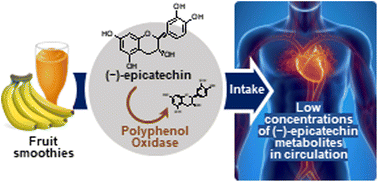
Food Funct., 2023,14, 8217-8228
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01599H
Lactobacillus co-fermentation of Cerasus humilis juice alters chemical properties, enhances antioxidant activity, and improves gut microbiota
Fermentation with Lactobacillus has been shown to improve the nutritional value of juice.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 8248-8260
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO02583G
Comparison of four digestion protocols on the physical characteristics of gastric digesta from cooked couscous using the Human Gastric Simulator
Differences between in vitro digestion protocols such as variations in pH, ionic strength, enzyme activity, and amount of gastric secretions result in modifications in the digesta properties of the same meal.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 8229-8247
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01920A
GABA and fermented litchi juice enriched with GABA promote the beneficial effects in ameliorating obesity by regulating the gut microbiota in HFD-induced mice
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and fermented litchi juice enriched with GABA dietary interventions are considered to have therapeutic potential against obesity.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 8170-8185
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO04038G
Selenium-enriched peptides identified from selenium-enriched soybean protein hydrolysate: protective effects against heat damage in Caco-2 cells
Selenium-enriched peptides identified from the hydrolysate alleviate heat damage by reducing intestinal epithelial cell permeability, protecting tight junction proteins, and regulating Nrf2-Keap1 and NLRP3 signaling pathways.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 7882-7896
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01103H
Protein blends and extrusion processing to improve the nutritional quality of plant proteins
Utilizing protein blends improved the amino acid profile of the ingredients, and extrusion processing effectively reduced trypsin inhibitors in all extrudates but only enhanced the in vitro protein digestibility of the pulse-rich extrudates.
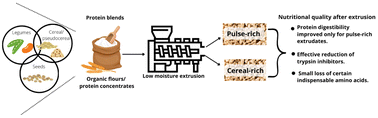
Food Funct., 2023,14, 7361-7374
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03912E
Sea cucumber chondroitin sulfate polysaccharides attenuate OVA-induced food allergy in BALB/c mice associated with gut microbiota metabolism and Treg cell differentiation
Sea cucumber chondroitin sulfate polysaccharides can attenuate OVA-induced food allergy in BALB/c mice, which associated with gut microbiota metabolism and Treg cell differentiation.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 7375-7386
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00146F
Effect of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain Shirota supplementation on clinical responses and gut microbiome in Parkinson's disease
The current randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed that Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain Shirota supplementation improved non-motor symptoms and specific gastrointestinal symptoms in Parkinson's disease patients.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6828-6839
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00728F
Enzymatic preparation of casein hydrolysates with high digestibility and low bitterness studied by peptidomics and random forests analysis
The release pattern and structural characteristics of bitter peptides affected the bitterness increase behaviors of casein hydrolysates. A high-digestibility and low-bitterness casein hydrolysate was obtained.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6802-6812
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01222K
Prevention of DSS-induced colitis in mice with water kefir microbiota via anti-inflammatory and microbiota-balancing activity
Water kefir microbiota exerted preventive roles in DSS-induced colitis by modulating the expression of tight junction proteins, reducing inflammation via inactivating the NF-κB signaling pathway, and regulating microbial dysbiosis.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6813-6827
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00354J
Capsicum chinense var. BRS Moema: chemical characterization by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and antiproliferative screening
BRS Moema showed considerable quantities of capsiate and phenolic compounds (in free, esterified, glycosylated, and insoluble-bound forms) quantified by UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6432-6442
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01698F
Binding behavior and antioxidant study of spice extract piperine with respect to meat myoglobin
Spectroscopic and simulation methods were used to report the binding behavior and antioxidant activity of piperine with respect to myoglobin and to explain the effects of piperine on protein structure.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6422-6431
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00617D
Revealing the role of leucine in improving the social avoidance behavior of depression through a combination of untargeted and targeted metabolomics
A significant correlation between decreased levels of leucine and social avoidance behavior utilized a combination of untargeted and targeted metabolomics. The supplementation of leucine has a positive impact on social avoidance behavior.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6397-6409
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01876H
Acid-tolerant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZDY2013 shows a colonization niche preference and interacts with enterotoxigenic Bacillus cereus in specific-pathogen-free mice
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZDY2013 shows a colonization niche preference and interacts with the food-borne pathogen Bacillus cereus in the complex gut environment.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 6410-6421
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01468A
Modulatory effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on depressive-like behaviors in rats with chronic sleep deprivation: potential involvement of melatonin receptor pathway and brain lipidome
Clinical evidence suggests that a bidirectional relationship is present between sleep loss and psychiatric disorders.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 5977-5993
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01452E
A systematic review of the inhibitory effect of extracts from edible parts of nuts on α-glucosidase activity
Inhibition of α-glucosidases can slow carbohydrate digestion to reduce postprandial glycaemia and lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Our systematic review found no studies that tested the inhibitory potential of nut extracts against human α-glucosidases.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 5962-5976
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00328K
Ginsenoside Rd, a natural production for attenuating fibrogenesis and inflammation in hepatic fibrosis by regulating the ERRα-mediated P2X7r pathway
Rd regulates fibrogenesis and inflammatory responses in hepatic fibrosis by mediating the ERRα-P2X7r signaling pathway.
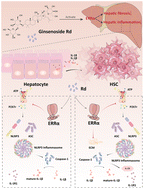
Food Funct., 2023,14, 5606-5619
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01315D
Sugarcane molasses essential oils: mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers to improve their slow-release activity and the study on their anti-inflammatory activities in vivo
SMEOs was extracted by MAHD, the composition of SMEOs was identified and analyzed by GC-MS. SMEOs was loaded into MSNPs to evaluate its sustained release activity, and the anti-inflammatory activity of SMEOs in vivo was determined.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 5012-5022
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO02960J
Urinary excretion of organosulfur compounds after acute ingestion of black onion
Study on the urinary excretion of organosulfur compounds after acute ingestion of black onion, a newly derived product from onion (Allium cepa L.).

Food Funct., 2023,14, 5023-5031
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO01099F
Phenyl lactic acid alleviates Helicobacter pylori infection in C57BL/6 mice
PLA is vital to the effective suppression of H. pylori growth and the prevention of gastritis by reducing oxidative stress, improving gastrointestinal microbiota, and mitigating inflammatory responses.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 5032-5047
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00099K
Curcumin inhibits liquid–liquid phase separation of fused in sarcoma and attenuates the sequestration of pyruvate kinase to restore cellular metabolism
The abnormal accumulation of fused in sarcoma (FUS) is a pathological hallmark in a proportion of patients with frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4621-4631
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03224D
Chitosan-grafted-caffeic acid combined with ultrasound inhibits the oxidation and degradation of myofibrillar proteins in pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) during ice storage
This study aimed to investigate the impact of chitosan-grafted-caffeic acid (CS-g-CA) and ultrasound (US) on myofibrillar proteins (MPs) in pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) during 24 days of ice storage.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4595-4606
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03952D
Static in vitro digestion model adapted to the general older adult population: an INFOGEST international consensus
Physiological parameters of the static in vitro digestion model adapted to the general older adult.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4569-4582
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00535F
Moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharides exert anti-lung cancer effects upon targeting TLR4 to reverse the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype and promote T-cell infiltration
MOLP demonstrate anti-Lewis lung cancer effects by reversing the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype and restoring T-cell function.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4607-4620
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03685A
Structural modification of zein-based oil-in-glycerol emulsion gels for improved textural and digestion behaviors
The current study focused on modulating the structures of zein-based emulsion gels by the addition of a surface active ingredient (Span 20, SP) to improve textural and digestion behaviors.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4583-4594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00834G
Protective effect and mechanism of Lycium ruthenicum polyphenols against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity
This study aimed to investigate the potential neuroprotective effects of Lycium ruthenicum polyphenols (LRP) against acrylamide (ACR)-induced neurotoxicity and the mechanism of action in vitro and in vivo.
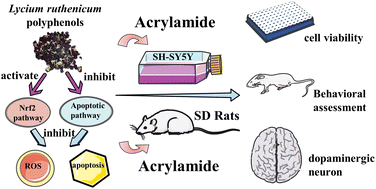
Food Funct., 2023,14, 4552-4568
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00623A
Inhibition of Ca2+-calpain signaling is a new mechanism using Laminaria japonica polysaccharide to prevent macrophage foam cell formation and atherosclerosis
The LJP61A suppressed macrophage foam cell formation and atherosclerotic progression by modulating Ca2+-calpain mediated autophagy inhibition.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4036-4048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO04099A
Citrate-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for the nano-enabled biofortification of wheat
Citrate-coated cobalt ferrite nanoparticles enhance wheat's nutritional quality by improving grain yield and increasing Fe concentration, contributing to sustainable agri-food systems and combating hidden hunger.

Food Funct., 2023,14, 4017-4035
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03835H
Anti-inflammatory activities of black raspberry seed ellagitannins and their structural effects on the stimulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and intestinal bitter taste receptors
This study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of ellagitannins from black raspberry seeds in vivo and the structural effects of ellagitannins on glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and mouse bitter taste receptor (mTAS2R).
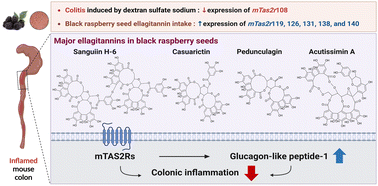
Food Funct., 2023,14, 4049-4064
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO04052B
Prebiotics alleviate cartilage degradation and inflammation in post-traumatic osteoarthritic mice by modulating the gut barrier and fecal metabolomics
Prebiotics can delay the progression of PTOA by regulating the metabolites of gut microbiota and protecting the gut barrier, which gives a new perspective for the application of prebiotics to PTOA.
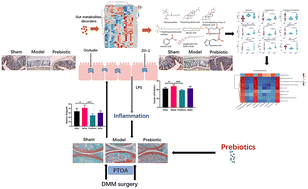
Food Funct., 2023,14, 4065-4077
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO00775H
About this collection
This themed collection features articles published in Food & Function marked as HOT by the handling editor or as recommended by referees. Congratulations to all the authors whose articles are featured.