Prebiotics alleviate cartilage degradation and inflammation in post-traumatic osteoarthritic mice by modulating the gut barrier and fecal metabolomics†
Abstract
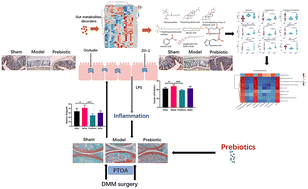
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by articular cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone sclerosis, synovial hyperplasia and inflammation as the main pathological manifestations. This study aims to investigate the protective effect of prebiotics in post-traumatic osteoarthritic (PTOA) mice by modulating the gut barrier and fecal metabolomics. The results suggested that cartilage degeneration, osteophyte formation and inflammation were significantly reduced by prebiotics in PTOA mice. In addition, the gut barrier was protected by the increased expression of tight junction proteins ZO-1 and occludin in the colon. High-throughput sequencing found that 220 fecal metabolites were affected by joint trauma, 81 of which were significantly recovered after probiotic intervention, and some metabolites (valerylcarnitine, adrenic acid, oxoglutaric acid, etc.) were closely associated with PTOA. Our study demonstrates that prebiotics can delay the progression of PTOA by regulating the metabolites of the gut microbiota and protecting the gut barrier, which is expected to be an intervention method for PTOA.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...