Pterostilbene alleviates abdominal aortic aneurysm via inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis by activating the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis†
Abstract
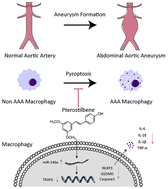
Pterostilbene (PTE), a natural stilbene found in blueberries and several varieties of grapes, has several pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidative activities. However, its role in abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), which is a severe inflammatory vascular disease, remains incompletely understood. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of natural stilbene PTE on AAA formation and the underlying mechanism. Two AAA mouse models (Ang II-induced model and PPE-induced model) were used to examine the effect of PTE on AAA formation. We showed that PTE administration attenuated AAA formation in mice. Furthermore, we found that PTE significantly inhibited inflammatory responses in mouse aortas, as PTE suppressed macrophage pyroptosis and prevented macrophage infiltration in aortas, resulting in reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in aortas. We also observed similar results in LPS + ATP-treated Raw 264.7 cells (a macrophage cell line) and primary peritoneal macrophages in vitro. We showed that pretreatment with PTE restrained inflammatory responses in macrophages by inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis. Mechanistically, miR-146a-5p and TRAF6 interventions in vivo and in vitro were used to investigate the role of the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis in the beneficial effect of PTE on macrophage pyroptosis and AAA. We found that PTE inhibited macrophage pyroptosis by miR-146a-5p-mediated suppression of downstream TRAF6 expression. Moreover, miR-146a-5p knockout or TRAF6 overexpression abrogated the protective effect of PTE on macrophage pyroptosis and AAA formation. These findings suggest that miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis activation by PTE protects against macrophage pyroptosis and AAA formation. PTE might be a promising agent for preventing inflammatory vascular diseases, including AAA.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...