Themed collection Atmospheric chemistry

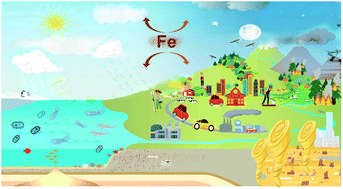
A perspective on iron (Fe) in the atmosphere: air quality, climate, and the ocean
We engage in research motivated by climate change and the impacts of pollution on air, water, and human health. The scientific community need to improve communication and knowledge exchange across disciplines to address pressing research questions holistically.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 151-164
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00176D
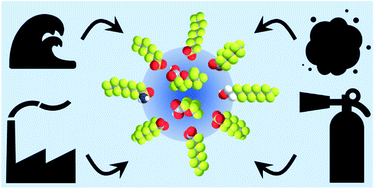
PFAS on atmospheric aerosol particles: a review
PFAS are detected in particulate matter around the world.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 133-150
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00002D
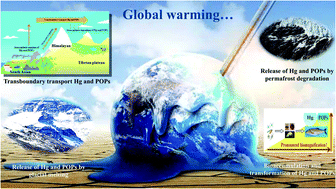
Impact of global warming on regional cycling of mercury and persistent organic pollutants on the Tibetan Plateau: current progress and future prospects
Global warming profoundly affects not only mountainous and polar environments, but also the global and regional cycling of pollutants.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1616-1630
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00550B
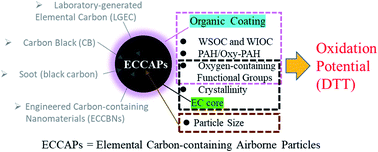
The oxidative potential of fresh and aged elemental carbon-containing airborne particles: a review
EC-containing airborne particles have diverse oxidative potentials dependent on their physical and chemical properties, which can be also changed by atmospheric aging processes.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 525-546
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00497B
Secondary organic aerosol formation from monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: insights from laboratory studies
This review summarizes in detail the current knowledge in the chemical compositions, formation mechanisms, and physicochemical properties of secondary organic aerosols formed from monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
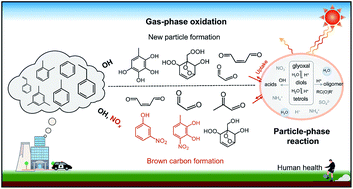
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 351-379
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00409C
Indoor surface chemistry variability: microspectroscopic analysis of deposited particles in dwellings across the United States
The indoor surfaces of dwellings across the United States range exhibit a wide range of chemical compositions and physical properties, which impacts semi-volatile partitioning, heterogeneous chemistry and the overall properties of indoor air.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1704-1713
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00816B
Long-term prediction of climate change impacts on indoor particle pollution – case study of a residential building in Germany
The Indoor Air Quality Climate Change (IAQCC) model was applied to predict the long-term impact of atmospheric changes on indoor particle concentrations based on different climate scenarios.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1688-1703
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00663A
Kinetic multilayer models for surface chemistry in indoor environments
Multiphase interactions and chemical reactions at indoor surfaces are of particular importance due to their impact on air quality in indoor environments with high surface to volume ratios.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1640-1653
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00549J
Commercial kitchen operations produce a diverse range of gas-phase reactive nitrogen species
Gas phase reactive nitrogen (Nr) species in a commercial kitchen are mainly composed of expected species with many additional species completing the budget.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1517-1534
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00491D
The gas phase ozonolysis and secondary OH production of cashmeran, a musk compound from fragrant volatile chemical products
We quantified the lifetime of cashmeran, a musk compound, against 20 ppbv of O3 to be 85 days. In the presence of O2, cashmeran may influence the oxidative capacity indoors via production of secondary OH radicals (up to 5.1 × 105 molec cm−3).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1504-1516
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00452C
Organic aerosol formation from 222 nm germicidal light: ozone-initiated vs. non-ozone pathways
Ozone production can explain most indoor air quality impacts of 222 nm germicidal ultraviolet light (GUV222). However, GUV222 causes more new particle formation than is explained by ozone chemistry.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1619-1628
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00384E
Dynamics of residential indoor gas- and particle-phase water-soluble organic carbon: measurements during the CASA experiment
A system for semi-continuous real-time monitoring of gas- and particle-phase water soluble organic carbon (WSOC) was used to provide quantitative insights into the concentrations dynamics of WSOC in indoor air.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1535-1550
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00340C
The impact of surfaces on indoor air chemistry following cooking and cleaning
Cooking and cleaning are common sources of indoor air pollutants, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1583-1602
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00410H
Oxidant concentrations and photochemistry in a vehicle cabin
Indoor oxidant concentrations in vehicles strongly depends on the ventilation rates and photochemistry within the vehicle.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1573-1582
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00319E
Yearlong study of indoor VOC variability: insights into spatial, temporal, and contextual dynamics of indoor VOC exposure
A comprehensive study of indoor VOCs, revealing how seasonality and location shape indoor VOC exposure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1025-1040
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00756E
The INGENIOUS project: towards understanding air pollution in homes
This paper provides an overview of the INGENIOUS (UnderstandING the sourcEs, traNsformations and fates of IndOor air pollUtantS) project, aiming to better understand air pollution in homes.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 355-372
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00634H
Modelling indoor radical chemistry during the HOMEChem campaign
Measurements from the HOMEChem campaign have been constrained and modelled, identifying how cooking and cleaning affect indoor radical reactivities and concentrations.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 188-201
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00628C
Mobile monitoring reveals the importance of non-vehicular particulate matter sources in London
A novel application of mobile monitoring to investigate the spatial distribution of vehicular and non-vehicular urban particulate matter sources in London, UK.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2145-2157
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00552J
Experimental and theoretical investigation of benzothiazole oxidation by OH in air and the role of O2
Products of the oxidation of BTH by OH in air.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2177-2188
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00461B
Physicochemical properties and their impact on ice nucleation efficiency of respiratory viral RNA and proteins
Ice nucleation processes in the earth's atmosphere are critical for cloud formation, radiation, precipitation, and climate change.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2010-2019
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00411F
Emerging investigator series: secondary organic aerosol formation from photooxidation of acyclic terpenes in an oxidation flow reactor
Organic aerosol formed from ocimene photooxidation has more oligomers compared to organic aerosol formed from other acyclic terpene precursors.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1156-1170
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00063C
Reactive oxygen species on indoor surfaces
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are present on indoor surfaces and form dynamically on surfaces coated with lipid mixtures that simulate indoor surface coatings.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1198-1204
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00031E
Ozone generation and chemistry from 222 nm germicidal ultraviolet light in a fragrant restroom
Devices using 222 nm germicidal ultraviolet light (GUV222) have been marketed to reduce virus transmission indoors. However, GUV222 generates ozone which can react with gases and surfaces to create undesirable air byproducts.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1090-1106
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00144C
Measurement of the vertical distributions of atmospheric pollutants using an uncrewed aerial vehicle platform in Xi'an, China
PM and CO concentrations below 500 m increased substantially during haze. Influences of horizontal and vertical transport were observed on vertical profiles.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1077-1089
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00020J
Unrecognized volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds from brake wear
This study shows that volatile and semi-volatile organic gases are emitted during light and heavy braking. These emissions will remain as we transition to zero exhaust emission vehicles and must be included in air pollution and climate assessments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 928-941
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00024B
New insights into the mechanism and kinetics of the addition reaction of unsaturated Criegee intermediates to CF3COOH and tropospheric implications
When the unsaturated CIs at the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C-terminal vinyl electrophilic center react with the O
C-terminal vinyl electrophilic center react with the O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–OH moiety (TFA), a new adduct, TFAAAH, is formed, and it can act as a potential source of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs).
C–OH moiety (TFA), a new adduct, TFAAAH, is formed, and it can act as a potential source of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 751-764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00554B
Does green mean clean? Volatile organic emissions from regular versus green cleaning products
Cleaning products emit a range of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including some which are hazardous or can undergo chemical transformations to generate harmful secondary pollutants.
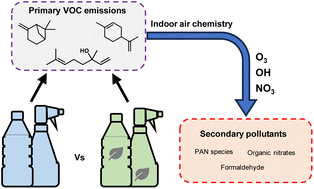
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 436-450
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00439B
Composition of indoor organic surface films in residences: simulating the influence of sources, partitioning, particle deposition, and air exchange
Monte Carlo simulations of long-term indoor organic surface film growth were done. Film composition was resolved by volatility, particle deposition or gas absorption formation mechanisms, and indoor source process.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 305-322
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00399J
Wildfire plume ageing in the Photochemical Large Aerosol Chamber (PHOTO-LAC)
We establish laboratory-photochemical ageing in the 1800 m3 environmental chamber “PHOTO-LAC” to study the atmospheric processing of dense wildfire plumes.
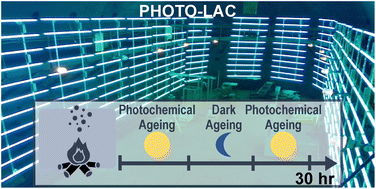
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 35-55
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00280B
Kinetics of hypochlorous acid reactions with organic and chloride-containing tropospheric aerosol
This study describes laboratory experiments on the reaction HOCl with chloride-containing aerosol and aerosol containing selected organic compounds with and without chloride.
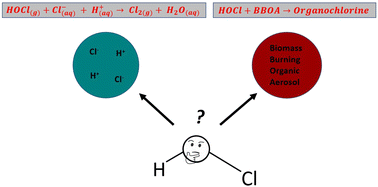
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1645-1656
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00292F
Wildfires in the western United States are mobilizing PM2.5-associated nutrients and may be contributing to downwind cyanobacteria blooms
Wildfire activity is increasing in the continental U.S. and can be linked to climate change effects and nutrient emissions, with potential effects on downwind ecosystems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1049-1066
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00042G
The fate of organic peroxides indoors: quantifying humidity-dependent uptake on naturally soiled indoor window glass
The effect of humidity on organic hydroperoxide (ROOH) removal from air to real indoor surface films was investigated. A novel flow reactor for studying uptake kinetics of indoor pollutants on indoor materials is introduced.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1031-1048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00041A
Indoor and outdoor air quality impacts of cooking and cleaning emissions from a commercial kitchen
Online gas- and particle-phase measurements in a commercial kitchen reveal exposure risks and outdoor air impacts during cooking and cleaning.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 964-979
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00484D
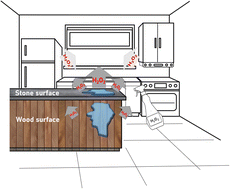
Hydrogen peroxide emissions from surface cleaning in a single-family residence
High levels of reactive chemicals may be emitted to the indoor air during household surface cleaning, leading to poorer air quality and potential health hazards.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 781-790
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00434H
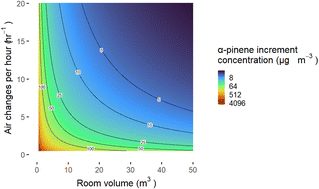
The impact of plug-in fragrance diffusers on residential indoor VOC concentrations
The effect of adding a plug-in air freshener into 60 houses was hard to detect due to pre-existing VOCs from other sources; in homes with low ventilation rates however small increases in monoterpenes were seen, consistent with emission rates.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 805-817
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00444E
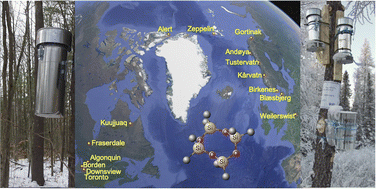
Seasonal and latitudinal variability in the atmospheric concentrations of cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes in the Northern Hemisphere
The spatial and temporal patterns in the concentrations of D4, D5 and D6 in the atmosphere measured with passive samplers along a European and a Canadian transect are largely consistent with the current understanding of their atmospheric fate.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 496-506
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00467D
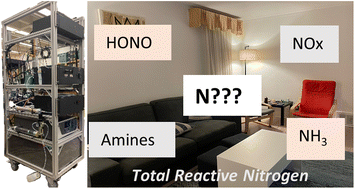
Emerging investigator series: an instrument to measure and speciate the total reactive nitrogen budget indoors: description and field measurements
A robust and quantitative instrument that measures total gas-phase reactive nitrogen (tNr) has been developed for indoor air quality surveys. It can focus on NOx, HONO, and NH3 levels indoors, from the complete tNr budget, on timescales of 5–20 min.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 389-404
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00446A
Kinetics of the nitrate-mediated photooxidation of monocarboxylic acids in the aqueous phase
This work highlights how the pH of the atmospheric aqueous phase can influence the degradation of carboxylic acids during nitrate-mediated photooxidation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 461-471
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00458E
Gaseous and soil OCPs and PCBs along the Indus River, Pakistan: spatial patterns and air–soil gradients
Results of this study indicate the contribution of regional as well local sources towards long range atmospheric transport (LRAT) of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) to the colder areas of Pakistan, where these act as a secondary source of POPs.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 531-541
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00363E
From the HOMEChem frying pan to the outdoor atmosphere: chemical composition, volatility distributions and fate of cooking aerosol
New measurements show that cooking aerosol released indoors can partition as it dilutes through a home and to the outdoor atmosphere, impacting both indoor and outdoor air quality.
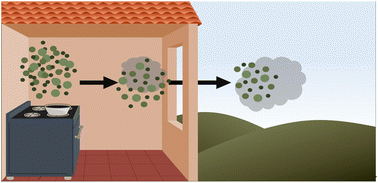
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 314-325
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00250G
Elevated levels of chloramines and chlorine detected near an indoor sports complex
Chlorinated cleaning products containing hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite ion (OCl−) act as sources of toxic chloramines (NH2Cl, NHCl2, NCl3) and atmospheric oxidant precursors (i.e. Cl2) which impact air quality.
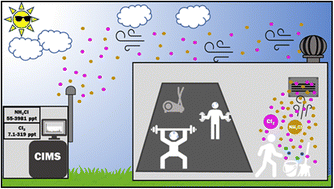
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 304-313
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00411A
Exploring controls on perfluorocarboxylic acid (PFCA) gas–particle partitioning using a model with observational constraints
The atmospheric fate of perfluorocarboxylic acids (PFCAs) has attracted much attention in recent decades due to the role of the atmosphere in global transport of these persistent chemicals.
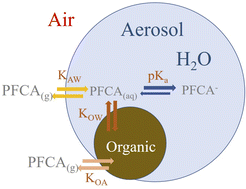
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 264-276
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00261B
Aqueous processing of water-soluble organic compounds in the eastern United States during winter
The uptake of WSOCg from biomass burning into ALW results in compounds that remain in the particle phase upon drying.
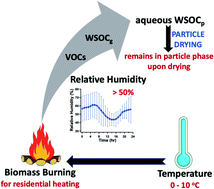
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 241-253
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00115B
Hygroscopicity of nitrogen-containing organic carbon compounds: o-aminophenol and p-aminophenol
As nitrogen-containing organic carbon of atmospheric relevance, the water uptake of two phenolic compounds, o-aminophenol and p-aminophenol, is investigated under sub- and supersaturated conditions through the lens of aerosol-cloud interactions.
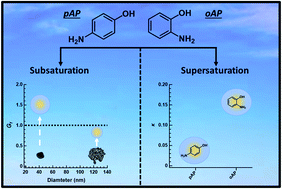
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 229-240
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00163B
Iodine emission from the reactive uptake of ozone to simulated seawater
We suggest a re-evaluation of two reaction rate constants to be able to better model iodine emission from the ozonolysis of iodide in the presence of chloride.
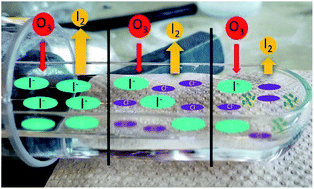
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 254-263
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00111J
Kinetics of oligomer-forming reactions involving the major functional groups present in atmospheric secondary organic aerosol particles
Measurements of the kinetics of accretion reactions involving organic compounds typical of those present in atmospheric aerosol particles demonstrate the potential importance of peroxyhemiacetal and ester formation in a single organic phase and in phase-separated organic/aqueous mixtures containing a sulfuric acid catalyst.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 214-228
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00124A
Molecular investigation of the multi-phase photochemistry of Fe(III)–citrate in aqueous solution
The comprehensive reaction mechanism of FeIII–citrate multiphase photochemistry and formation of unexplored colloidal reaction products that contribute to terrestrial light-absorbing materials.
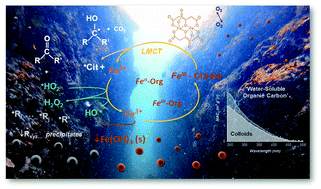
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 190-213
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00503K
pH affects the aqueous-phase nitrate-mediated photooxidation of phenolic compounds: implications for brown carbon formation and evolution
This work highlights how the pH of the atmospheric aqueous phase can influence the reactivities of phenolic compounds and brown carbon formation/evolution during nitrate-mediated photooxidation.
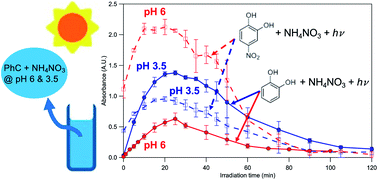
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 176-189
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00004K
Formation pathways of aldehydes from heated cooking oils
We studied the mechanisms of cooking oil decomposition that lead to emission of aldehydes, an important group of air pollutants, from food cooking.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 165-175
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00532D
Near-source hypochlorous acid emissions from indoor bleach cleaning
Cleaning surfaces with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) bleach can lead to high levels of gaseous chlorine (Cl2) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl); these have high oxidative capacities and are linked to respiratory issues.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 56-65
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00405D
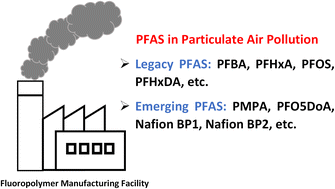
Legacy and emerging airborne per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) collected on PM2.5 filters in close proximity to a fluoropolymer manufacturing facility
Large fluoropolymer manufacturing plants are major sources of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to the environment; we measured legacy and emerging PFAS in air to provide insights into near-source PFAS profiles.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2272-2283
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00358A
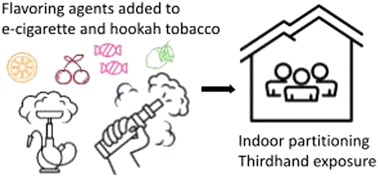
Indoor partitioning and potential thirdhand exposure to carbonyl flavoring agents added in e-cigarettes and hookah tobacco
The residents are likely to experience harmful thirdhand exposure due to the indoor partitioning of flavoring agents added to the e-cigarettes and hookah tobacco.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2294-2309
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00365A
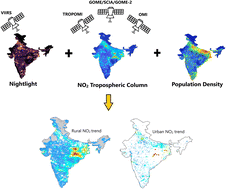
Air quality trends in rural India: analysis of NO2 pollution using satellite measurements
India is a country with more than 67% of its population (947 million) residing in rural areas and 33% in urban areas (472 million) as of 2020.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2437-2449
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00293K
Direct measurement of the deposition of submicron soot particles on leaves of Platanus acerifolia tree
Submicron soot particles (<1.0 μm in aerodynamic diameter) are responsible for global warming and health burdens worldwide.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2336-2344
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00328G
Partitioning of reactive oxygen species from indoor surfaces to indoor aerosols
Ozone chemistry taking place on indoor surfaces is predicted to increase inhalation exposure of reactive oxygen species in indoor aerosols.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2310-2323
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00307D
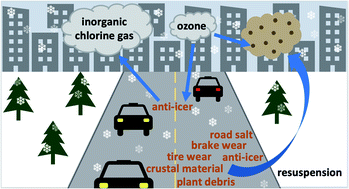
Emerging investigator series: ozone uptake by urban road dust and first evidence for chlorine activation during ozone uptake by agro-based anti-icer: implications for wintertime air quality in high-latitude urban environments
In this study, we report the heterogeneous chemistry of ozone with urban road dust and anti-icer. We present a novel pathway for chlorine activation during ozone uptake by anti-icer and discuss its potential air quality impacts in cold-climate urban regions.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2070-2084
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00393C
The dependence of soot particle ice nucleation ability on its volatile content
The removal of volatile content enhances the ice nucleation of soot particles by increasing the particle porosity and surface wettability.
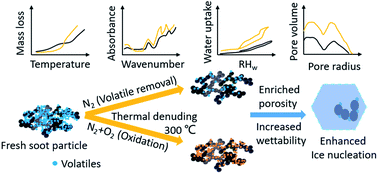
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2043-2069
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00158F
Effect of calcium on enhanced carbon capture potential of coal fly ash zeolites. Part II: a study on the adsorption mechanisms
The conversion of coal fly ash to zeolites is a sustainable solution for its utilization. One important issue is to clarify the effect of coal fly ash composition on the carbon sequestration potential of the derived zeolites.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1934-1944
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00252C
A new theoretical investigation on ·OH initiated oxidation of acephate in the environment: mechanism, kinetics, and toxicity
The degradation of acephate by OH radicals in the environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1912-1922
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00254J
Falling nickel concentrations in ambient air in South Wales – 50 years of progress
The effect on population exposure of falling nickel concentrations in air in the Swansea Valley over the last 50 years is assessed.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1821-1829
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00282E
Quantification and physical analysis of nanoparticle emissions from a marine engine using different fuels and a laboratory wet scrubber
A marine test-bed diesel engine was used to study how international fuel sulfur content (FSC) regulations and wet scrubbing can affect physical properties of submicron exhaust particles.
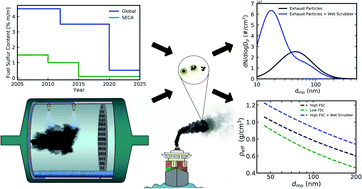
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1769-1781
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00054G
Impact of atmospheric anthropogenic nitrogen on new production in the northern Indian Ocean: constrained based on satellite aerosol optical depth and particulate nitrogen levels
Deposition of atmospheric pollutants enhances soluble reactive nitrogen by 1.7 and 0.9 TgN per year in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal, respectively, leading to an increase in primary production.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1895-1911
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00234E
Phase state of organic aerosols may limit temperature-driven thermodynamic repartitioning following outdoor-to-indoor transport
Monte Carlo simulations suggest that organic aerosol repartitioning during transport indoors is often kinetically limited due to a low bulk diffusivity, but liquid and some semisolid particles can achieve equilibrium repartitioning during indoor particle lifetimes.
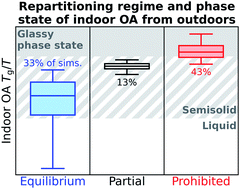
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1678-1696
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00093H
Evaluating atmospheric mercury (Hg) uptake by vegetation in a chemistry-transport model
We study the uptake of atmospheric mercury by vegetation in a chemical transport model and available observations. Due to the importance of this sink in the global mercury cycle, perturbations to forested areas can elevate mercury risks.
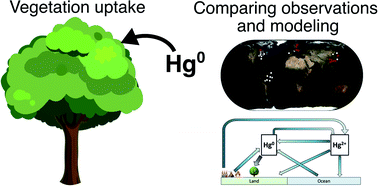
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1303-1318
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00032F
Reactive uptake of ozone to azo dyes in a coated-wall flow tube
Observations of reactive uptake of ozone to commercial azo dyes used in consumer products suggest multi-phase ozonolysis of azo dyes in the indoor environment.
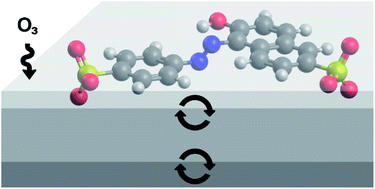
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 973-981
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00478F
Mercury in air and soil on an urban-rural transect in East Africa
Spatially resolved atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) concentrations from an urban area in the Southern Hemisphere are reported for the first time.
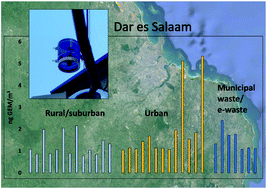
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 921-931
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00040G
Emerging investigator series: aqueous-phase processing of atmospheric aerosol influences dissolution kinetics of metal ions in an urban background site in the Po Valley
Fog processing of atmospheric aerosol enhances the solubility and the dissolution kinetics of particle-bound metal ions.
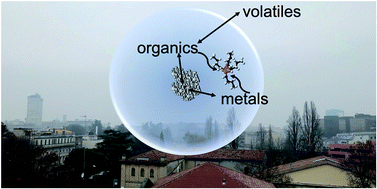
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 884-897
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00023G
Causal discovery of drivers of surface ozone variability in Antarctica using a deep learning algorithm
We use a causal discovery algorithm based on a temporal convolution network (TCN) to discover the drivers of surface ozone variability over Antarctica.
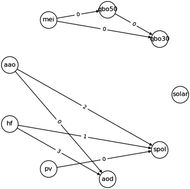
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 447-459
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00383F
The Sea Spray Chemistry and Particle Evolution study (SeaSCAPE): overview and experimental methods
The SeaSCAPE campaign replicated the marine atmosphere in the laboratory to investigate the links between biological activity in the ocean and the properties of primary sea spray aerosols, volatile organic compounds, and secondary marine aerosols.
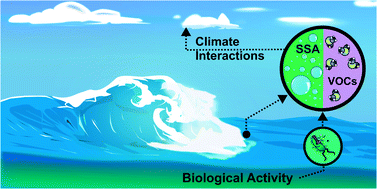
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 290-315
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00260K
About this collection
This web collection features research articles published in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts focussed on atmospheric chemistry.