Themed collection Hydrogen

Photo-hydrogen-evolving molecular devices driving visible-light-induced water reduction into molecular hydrogen: structure–activity relationship and reaction mechanism
This article describes the structure–activity relationship and reaction mechanism of photo-hydrogen-evolving molecular devices made up of Ru(II) sensitizers and Pt(II) molecular catalysts.
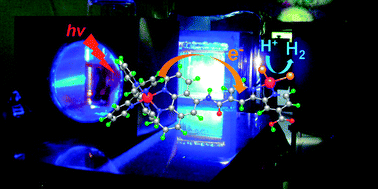
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 2227-2242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC04708B
Activation of dihydrogen by non-metal systems
This article reviews advances in the metal-free activation of hydrogen and the utilization of these and related systems in catalytic hydrogenations.
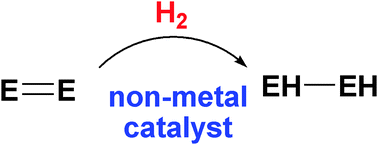
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8526-8533
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03313H
Transition metal catalysed ammonia-borane dehydrogenation in ionic liquids
Significant advantages result from combining the disparate hydrogen release pathways for ammonia-borane (AB) dehydrogenation using ionic liquids (ILs) and transition metal catalysts. With the RuCl2(PMe3)4 catalyst precursor, AB dehydrogenation selectivity and extent are maximized in an IL with the moderately coordinating ethylsulfate anion.
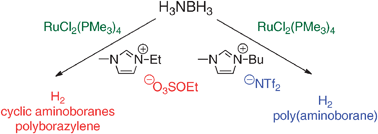
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 3177-3179
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC05408A
Transition metal catalysed dehydrogenation of amine -borane fuel blends
Mixtures containing ammonia-borane and sec-butylamine-borane remain liquid throughout the hydrogen release process that affords tri(N-sec-butyl)borazine and polyborazylene.
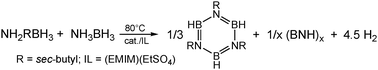
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 2922-2924
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03585H
Porous nanotube network: a novel 3-D nanostructured material with enhanced hydrogen storage capacity
Porous nanotube networks are a novel family of ‘carbon superstructures’ with superior structural characteristics and many potential applications.
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 2303-2305
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03002C
Heterobimetallic rhodium–gold halide and hydride complexes
Thermal and photochemical reactions relevant to photocatalytic hydrogen production have been investigated on rhodium–gold heterobimetallic constructs.
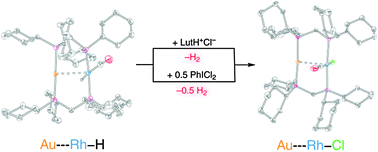
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1485-1487
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03261A
Facile metal free regioselective transfer hydrogenation of polarized olefins with ammonia borane
Transfer hydrogenation of polarized olefins with ammonia borane was achieved at room temperature proceeding stepwise with a unique hydroboration intermediate.
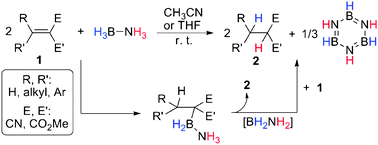
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 2053-2055
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03163A
Towards a structure-performance relationship for hydrogen storage in Ti-doped NaAlH4 nanoparticles
By adding a Ti catalyst to nanosized NaAlH4 (<20 nm) hydrogen desorption rates are enhanced. Adding the Ti catalyst before the alanate resulted in a superior material.
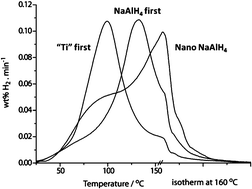
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 2143-2145
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02787A
Photocatalytic H2 evolution from neutral water with a molecular cobalt catalyst on a dye -sensitised TiO2 nanoparticle
A cobaloxime catalyst evolves H2 photocatalytically when attached on dye-sensitised TiO2.
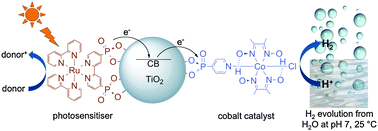
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1695-1697
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC04658B
A novel catalyst precursor K2TiF6 with remarkable synergetic effects of K, Ti and F together on reversible hydrogen storage of NaAlH4
A synergetic effect of K, Ti and F together on improving the reversible hydrogen storage properties of NaAlH4 is found by intruding K2TiF6 as catalyst precursor.
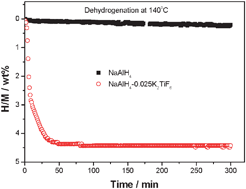
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1740-1742
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03264F
Hydrogen
storage properties and neutron scattering studies of Mg2(dobdc)—a metal–organic framework with open Mg2+ adsorption sites
The hydrogen storage properties of Mg2(dobdc) are probed by adsorption experiments, infrared spectroscopy, and neutron scattering techniques, demonstrating that the open coordination sites are of benefit for high-density storage."
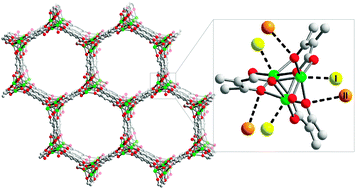
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1157-1159
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03453C
Reversible dehydrogenation of magnesium borohydride to magnesium triborane in the solid state under moderate conditions
The solid state dehydrogenation of Mg(BH4)2 to Mg(B3H8)2 has been shown to be reversible under the conditions of moderate temperature and pressure that preclude the formation of polyboranes through condensation reactions.
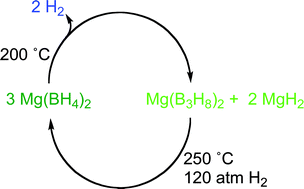
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1330-1332
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03461D
Structure and dynamics of ammonium borohydride
H atom disorder and rapid reorientation of NH4+ and BH4− ions in hydrogen storage material NH4BH4.
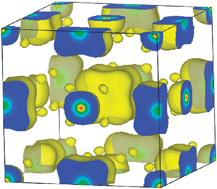
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 9164-9166
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03297B
Dihydrogen activation by sulfido -bridged dinuclear Ru /Ge complexes: insight into the [NiFe ] hydrogenase unready state
Molecular H2 was activated by S/SH bridged dinuclear Ru/Ge complexes, which model the activation process of the “unready” state of [NiFe] hydrogenase.
![Graphical abstract: Dihydrogen activation by sulfido-bridged dinuclear Ru/Ge complexes: insight into the [NiFe] hydrogenase unready state](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C0CC03391J&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2011)
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 1030-1032
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03391J
Diiron species containing a cyclic PPh2NPh2 diphosphine related to the [FeFe]H2ases active site
Preliminary investigations of proton and electron transfers on new dissymmetrically disubstituted diiron dithiolate species [Fe2(CO)4(κ2-PPh2NPh2)(μ-pdt)] have been done.
![Graphical abstract: Diiron species containing a cyclic PPh2NPh2 diphosphine related to the [FeFe]H2ases active site](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C0CC03295F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2011)
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 878-880
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03295F
Double addition of H2 to transition metal–borane complexes: a ‘hydride shuttle’ process between boron and transition metal centres
The addition of H2 across a transition metal–borane bond is reported for the first time. Successive hydrogen addition to a rhodium–norbornadiene complex leads to the elimination of the organic species and a recharging of the boron–hydrogen bond providing active hydrogenation catalysts.
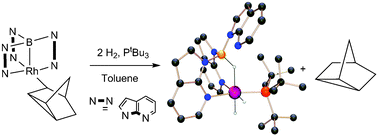
Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 484-486
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02245D
The diammoniate of diborane : crystal structure and hydrogen release
The crystal structure of the diammoniate of diborane is presented for the first time since its discovery in 1923.

Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8564-8566
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03249B
Hydrogen oxidation catalysis by a nickel diphosphine complex with pendant tert-butyl amines
A bis-diphosphine nickel complex with tert-butyl functionalized pendant amines functions as a highly active electrocatalyst for the oxidation of hydrogen in the presence of base.
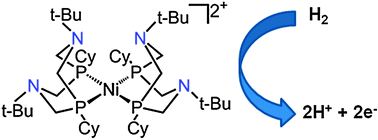
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8618-8620
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03246H
Intramolecular heterolytic dihydrogen cleavage by a bifunctional frustrated pyrazolylborane Lewis pair
A bifunctional pyrazolylborane is introduced that is capable of heterolytic dihydrogen activation at ambient temperature and pressure; the resulting zwitterionic dihydro congener represents a potential metal-free hydrogenation catalyst.

Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8561-8563
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03474F
Gas pressure effects on the rates of catalytic H2 oxidation by hydrogenases
Investigations of an observation that the rate of H2 oxidation by a hydrogenase decreases as the dissolved gas concentration increases.
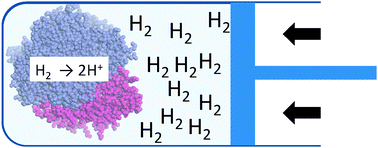
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8463-8465
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03292A
Altered thermodynamic and kinetic properties of MgH2 infiltrated in microporous scaffold
The enthalpy of formation of MgH2 is lowered by 11 kJ mol−1 if the hydride particles are smaller than 3 nm.
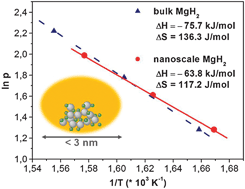
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8353-8355
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03072D
Multimode hydriding /dehydriding reactions of CaPd
Multimode hydriding/dehydriding reactions of CaPd proceed via hydrogen solution/dissolution and phase decomposition/recombination over wide temperature ranges.
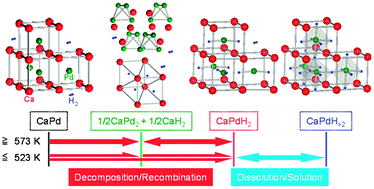
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8380-8382
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02626C
Photocatalytic hydrogen production from water in self-assembled supramolecular iridium –cobalt systems
Self-assembled supramolecular photocatalytic systems produced H2 in aqueous solutions upon visible light irradiation.
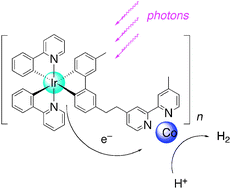
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8466-8468
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02486D
Electric field induced activation of H2—Can DFT do the job?
The applicability of different density functional methods to the problem of dihydrogen dissociation in an electric field as a model for FLP activation and the bi-radical character of the reaction are investigated.
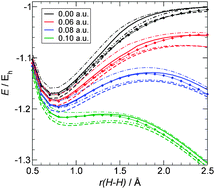
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 7942-7944
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02569K
Chain mechanism for exchange of D2 with a ruthenium hydride
The ruthenium hydride of (Ar4CpOH)Ru(CO)2H exchanges cleanly and rapidly with D2 at room temperature to generate the ruthenium deuteride. A chain mechanism is proposed to explain the much more rapid exchange of RuH/D2 than RuCO exchange with 13CO.
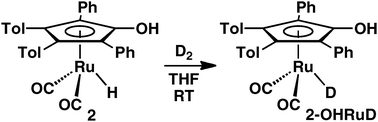
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 7915-7917
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02875D
Azulene based metal–organic frameworks for strong adsorption of H2
MOFs comprised of internally polarized 1,3-azulenedicarboxylate were synthesized. The guest free MOF exhibits strong MOF-H2 interactions (7.8–6.8 kJ mol−1) revealing the significant impact of internally polarized azulene backbone to stabilized H2 molecules in the framework.
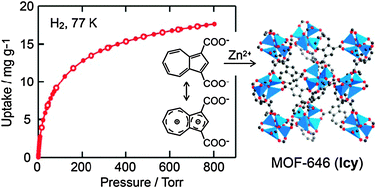
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 7981-7983
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02589E
Hydrogen generation by electrolysis of liquid ammonia
Hydrogen gas is generated by the electrolysis of liquid ammonia which has high hydrogen capacity of 17.8 mass%.
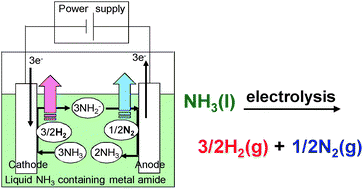
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 7775-7777
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01982H
Robust photocatalytic water reduction with cyclometalated Ir(III) 4-vinyl-2,2′-bipyridine complexes
Novel [Ir(C⁁N)2(N⁁N)]+ complexes with N⁁N ligands containing vinyl groups were synthesized resulting in quintupled turn-over numbers for the photocatalytic hydrogen production compared to analogous non-vinyl compounds.
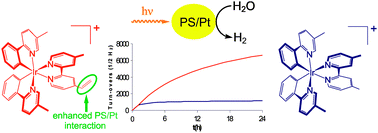
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 7551-7553
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01827A
Thermodynamic and kinetic destabilization in LiBH4/Mg2NiH4: promise for borohydride-based hydrogen storage
The LiBH4/Mg2NiH4 hydride system reversibly cycles hydrogen via a new reaction path with exceptionally low enthalpy and entropy.
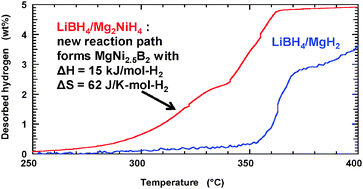
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 6687-6689
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01026J
Bimetallic nickel -iridium nanocatalysts for hydrogen generation by decomposition of hydrous hydrazine
Bimetallic NiIr alloy nanocatalysts exhibit 100% H2 selectivity for complete decomposition of hydrous hydrazine at room temperature.
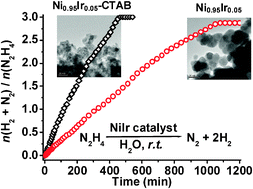
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 6545-6547
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01879A
Parahydrogen -induced polarization in alkyne hydrogenation catalyzed by Pd nanoparticles embedded in a supported ionic liquid phase
Parahydrogen-induced polarization was observed in the gas phase heterogeneous hydrogenation of propyne catalyzed by Pd0 nanoparticles embedded in an ionic liquid phase supported on activated carbon fibers (Pd0/SILP/ACF). The essential role of the ionic liquid is demonstrated.
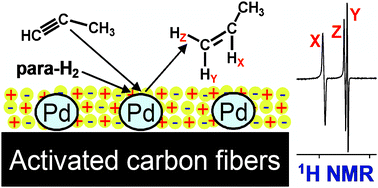
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 5764-5766
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC01411G
Metal-free reductions of N-heterocycles via Lewis acid catalyzed hydrogenation
N-Heterocycles are reduced in the presence of a catalytic amount of the borane B(C6F5)3 and H2.
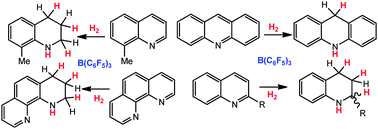
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 4884-4886
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC00719F
DFT characterization of the reaction pathways for terminal- to μ-hydride isomerisation in synthetic models of the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site
The mechanism of terminal- to μ-hydride isomerisation in models of synthetic complexes resembling the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site has been elucidated by DFT calculations.
![Graphical abstract: DFT characterization of the reaction pathways for terminal- to μ-hydride isomerisation in synthetic models of the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C0CC02821E&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2010)
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8824-8826
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02821E
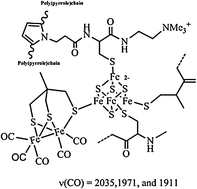
Artificial hydrogenases: assembly of an H-cluster analogue within a functionalised poly(pyrrole) matrix
Building an H-cluster analogue within a poly(pyrrole) modified electrode.
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8189-8191
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02962A
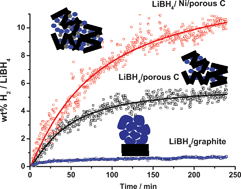
Reversibility of the hydrogen desorption from LiBH4: a synergetic effect of nanoconfinement and Ni addition
Reversible hydrogen uptake in LiBH4 is greatly enhanced by a combined effect of nanoconfinement in mesoporous carbon and Ni addition.
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8201-8203
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC03218B
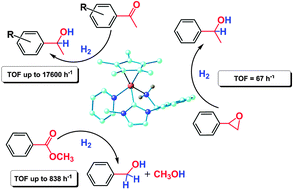
The hydrogenation of molecules with polar bonds catalyzed by a ruthenium(II) complex bearing a chelating N-heterocyclic carbene with a primary amine donor
A ruthenium(II) complex bearing a chelating N-heterocyclic carbene with an NH2 group (C–NH2) is a catalyst for the H2-hydrogenation of polar bonds in basic solution.
Chem. Commun., 2010,46, 8240-8242
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CC02664F
About this collection
This web-based themed issue showcases high quality articles covering all aspects of hydrogen generation, storage and activation. The invited, peer-reviewed articles highlight cutting-edge contributions by international leaders and celebrate current achievements and future perspectives in this exciting field of research.
The guest editors of this issue are Ferdi Schüth, Daniel DuBois, Mary DuBois and Douglas Stephan.
Articles in this web themed issue will be added to the list below as soon as possible, after they are published. Please return to this page frequently to see this collection grow.