Themed collection Environmental Science – coronavirus research

Editorial Perspectives: will SARS-CoV-2 reset public health requirements in the water industry? Integrating lessons of the past and emerging research
Brian Pecson and Daniel Gerrity present an Editorial Perspective which focuses on the impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the water industry.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1761-1764
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW90031A
Editorial Perspectives: 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): what is its fate in urban water cycle and how can the water research community respond?
Vincenzo Naddeo and Haizhou Liu present an ‘Editorial Perspective’ on coronavirus in wastewater and discuss the water research needs to combat viral outbreaks.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 1213-1216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW90015J
Influence of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a review from the climate change perspective
This perspective article reports the possible relationships between climate change and the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 pandemic and vice versa.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1060-1078
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00154J
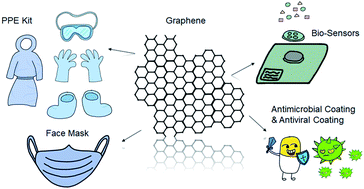
A case study of SARS-CoV-2 transmission behavior in a severely air-polluted city (Delhi, India) and the potential usage of graphene based materials for filtering air-pollutants and controlling/monitoring the COVID-19 pandemic
This review summarizes the role of graphene-based nanomaterials, which show antimicrobial behavior and have antiviral efficacy, in reducing the spread of COVID-19.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 923-946
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00034A
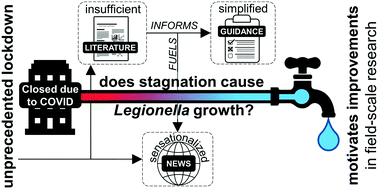
Growth of Legionella during COVID-19 lockdown stagnation
While “avoiding stagnation” has been the mantra of building water experts, support for how this terminology is used is not overly convincing. Carefully nuanced COVID stagnation studies can improve water quality research and communication strategies.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 10-15
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00819B
Particulate matter and ultrafine particles in urban air pollution and their effect on the nervous system
Pollutant particulate matter and ultrafine particles have been related to the rise of neurodegenerative diseases and other brain disorders. It is necessary to understand their potential health impacts in order to develop strategies to reduce risks.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 704-726
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00276K
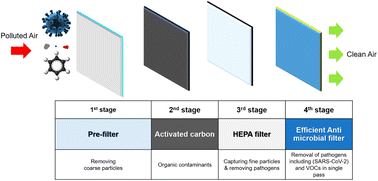
SARS-CoV-2 airborne transmission: a review of risk factors and possible preventative measures using air purifiers
This critical review presents the best remedy to protect human health by efficient materials-based air filters that can be used to air-purify and kill the dangerous SARS-CoV-2 virus and remove the other air pollutants.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2191-2216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00333C
Recent advances on gold and silver nanoparticle-based colorimetric strategies for the detection of different substances and SARS-CoV-2: a comprehensive review
Nanoparticle (NP)-based colorimetric methods are extensively used for the rapid detection of different substances and SARS-CoV-2 in various fields such as environmental science, virology, pollution research, food industry, as well as biomedicine.
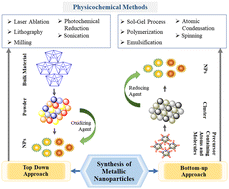
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3684-3710
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00503D
Emerging investigators series: the source and fate of pandemic viruses in the urban water cycle
This review provides a comprehensive look at whether a pandemic enveloped virus would pose challenges for the wastewater and drinking water industries.
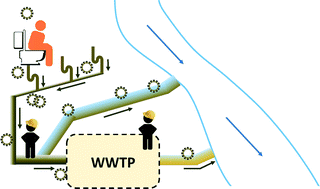
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2015,1, 735-746
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00125K
Nano-dry-salt deposition on electret nonwoven confers anticoronaviral effect while retaining aerosol filtration performance
Direct deposition of nano-dry-salt on nonwovens was developed as a process that can be incorporated into conventional nonwoven production for timely application of biosafe anticoronaviral surfaces and reliable aerosol filtration performance.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2780-2791
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00369K
Standardizing data reporting in the research community to enhance the utility of open data for SARS-CoV-2 wastewater surveillance
We propose a minimum set of meta-information to accompany the reporting of SARS-CoV-2 occurrence in wastewater for improved data interpretation.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1545-1551
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00235J
Aerosol presence reduces the diurnal temperature range: an interval when the COVID-19 pandemic reduced aerosols revealing the effect on climate
DTRs from February to June during the COVID-19 pandemic are greater than 3 standard deviations above the climatological mean DTR.
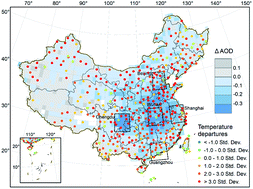
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 208-213
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00021G
High-throughput wastewater analysis for substance use assessment in central New York during the COVID-19 pandemic
Wastewater analysis provides insights into population lifestyle and health status during the coronavirus pandemic.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 2147-2161
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00377H
Selected pharmaceutical analysis in a wastewater treatment plant during COVID-19 infection waves in South Africa
Concentrations of pharmaceuticals (sulfamethoxazole, sulfamethoxazole hydroxylamine, prednisolone and ivermectin) showed good correlation with the number of COVID-19 infections in South Africa.
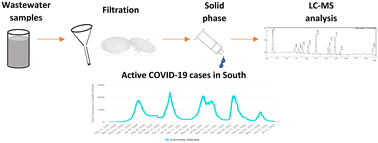
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1566-1576
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EW00059A
Prewhitening and normalization help detect a strong cross-correlation between daily wastewater SARS-CoV-2 RNA abundance and COVID-19 cases in a community
Significant cross-correlation was observed between daily wastewater SARS-CoV-2 RNA abundance and clinical case numbers (with a two-day lag) after prewhitening and normalization of the time series data.
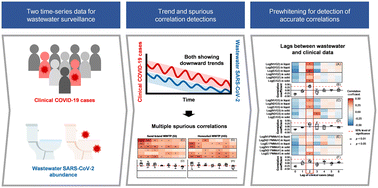
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1403-1412
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00951J
Evaluation of intra- and inter-lab variability in quantifying SARS-CoV-2 in a state-wide wastewater monitoring network
Wastewater-based SARS-CoV-2 monitoring is an effective tool for rapid management of the pandemic. Evaluating methodologies during the height of this crisis strengthens the field to ensure reproducibility across states, nations, and the globe.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 1053-1068
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00737A
Antibiotic removal by metal–organic framework and 2D nanomaterial based polyetherimide mixed matrix membranes using a membrane bioreactor
The ZIF-8, MoS2 and h-BN based PEI MMMs are fabricated to investigate their removal performance for antibiotics (favipiravir, ivermectin and azithromycin) using the MBR system. The MMMs show significant removal of antibiotics from synthetic wastewater.
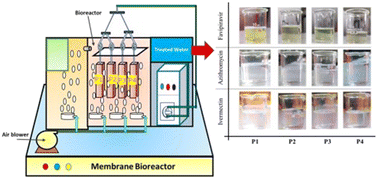
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2023,9, 86-103
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00620K
Eco design for Ag-based solutions against SARS-CoV-2 and E. coli
An effective, eco-friendly and easily scalable nanosilver-based technology offers affordable and broad-spectrum antimicrobial solutions against SARS-CoV-2 and Escherichia coli.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 4295-4304
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00178K
Wiping conditions and fabric properties influenced the microfiber shedding from non-woven products
Microfibers released from the simulated daily wiping process of disposable wipes and masks were studied, with emphasis on the effects of wiping conditions and fabric properties.
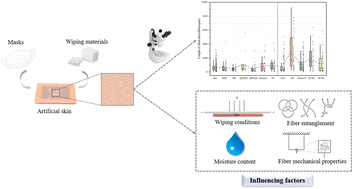
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1855-1866
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00292B
Assessing residential indoor and outdoor bioaerosol characteristics using the ultraviolet light-induced fluorescence-based wideband integrated bioaerosol sensor
We assessed and compared indoor and outdoor residential aerosol particles in a third-floor apartment from August through September 2020.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1790-1804
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00177B
CRISPR/Cas12a-mediated electrochemiluminescence platform for environmental and human serum SARS-CoV-2 RNA monitoring using a self-enhanced ruthenium complex linked to zeolitic imidazole framework-8
Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using self-enhancing ruthenium compounds attached to ZIF-8 and CRISPR–Cas12a trans-cleavage properties.
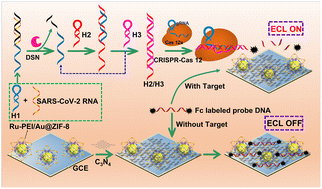
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 3417-3426
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00595F
Microplastics interact with SARS-CoV-2 and facilitate host cell infection
SARS-CoV-2 binds to microplastics which facilitates viral host infection with enhanced inflammatory responses.
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 2653-2664
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EN00019A
Emerging investigator series: meta-analyses on SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA levels in wastewater and their correlations to epidemiological indicators
Recent applications of wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) have demonstrated its ability to track the spread and dynamics of COVID-19 at the community level.
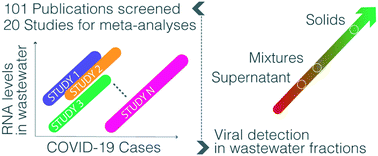
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1391-1407
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00084A
Removal of 26 corticosteroids, potential COVID-19 remedies, at environmentally relevant concentrations in water using UV/free chlorine, UV/monochloramine, and UV/hydrogen peroxide
Corticosteroids (CSs) with two double bonds in ring A are sensitive to UV. CSs were poorly removed by individual Cl2, NH2Cl, and H2O2 treatment. Combining UV with Cl2, NH2Cl, or H2O2 promoted UV-insensitive CS removal.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1078-1091
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00919B
Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater during New York City's second wave of COVID-19: sewershed-level trends and relationships to publicly available clinical testing data
SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in New York City were significantly correlated with clinical case rates in corresponding sewersheds.
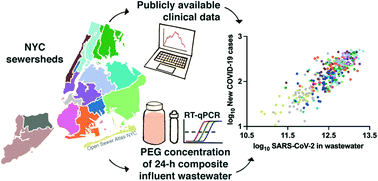
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 1021-1035
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00747E
SARS-CoV-2 RNA abundance in wastewater as a function of distinct urban sewershed size
SARS-CoV-2 community wastewater surveillance across a range of scales to establish optimal sampling strategies.
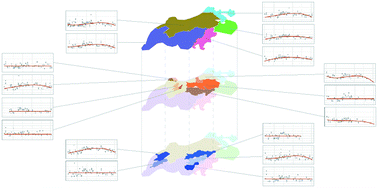
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 807-819
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00672J
SARS-CoV-2 RNA is enriched by orders of magnitude in primary settled solids relative to liquid wastewater at publicly owned treatment works
We compared SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations in primary settled solids and raw wastewater samples matched in date to investigate the relationship between the two matrices.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 757-770
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00826A
Modeling SARS-CoV-2 RNA degradation in small and large sewersheds
Hydrological model demonstrated a reduction in wastewater travel time by more than 60% when using a novel metric for placement of upstream samplers within a large sewershed, thus reducing SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA degradation.
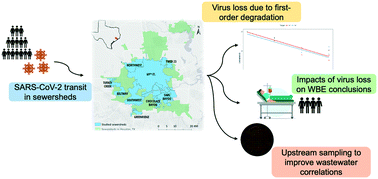
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 290-300
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00717C
Exploring the entropy-driven amplification reaction and trans-cleavage activity of CRISPR-Cas12a for the development of an electrochemiluminescence biosensor for the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene in real samples and environmental surveillance
An ECL biosensor based on entropy-driven amplification and CRISPR-Cas12a shear for the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene in environmental surveillance was reported.
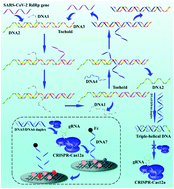
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 162-172
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00645B
Speech-generated aerosol settling times and viral viability can improve COVID-19 transmission prediction
Speech generates droplets averaged 6 μm in size. Their settling time and SARS-CoV-2 viral viability inside those droplets, both calculated from temperature and relative humidity, predict COVID transmission rates within one-sigma interval.
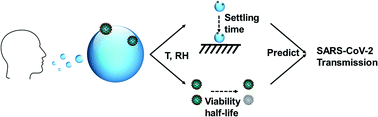
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2022,2, 34-45
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00013F
Development of a rapid pre-concentration protocol and a magnetic beads-based RNA extraction method for SARS-CoV-2 detection in raw municipal wastewater
We demonstrate the application of a rapid pre-concentration protocol and a magnetic bead-based RNA extraction method for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from raw wastewater without the need for extensive sample treatment.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 47-61
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00539A
Building-level wastewater surveillance using tampon swabs and RT-LAMP for rapid SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection
This study evaluated a passive sampling and rapid LAMP detection of SARS-CoV-2 for near-source (i.e., building-level) wastewater based epidemiology applications.
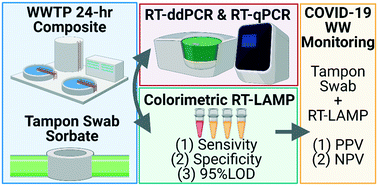
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2022,8, 173-183
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00496D
Long-term surveillance of wastewater SARS-CoV-2 in Los Angeles County
Temporal measurement of wastewater SARS-CoV-2 can be used to monitor the disease burden on multiple communities. Estimates of the Covid-19 infected population from wastewater SARS-CoV-2 data provide a complementary comparison to clinical data.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 2282-2294
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00586C
Importance of meteorology and chemistry in determining air pollutant levels during COVID-19 lockdown in Indian cities
Comparison of diurnally-average NOx pre- and during phase-I lockdown in two Indian cities. This work highlights that ambient levels post-lockdown were a complex interaction between emissions, meteorology, and chemistry.
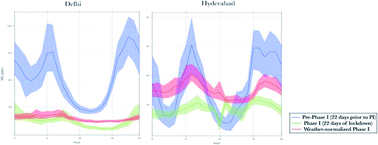
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1718-1728
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00187F
A case study on tap water quality in large buildings recommissioned after extended closure due to the COVID-19 pandemic
Extensive building closures due to the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic resulted in long-term water stagnation within the plumbing of large buildings.
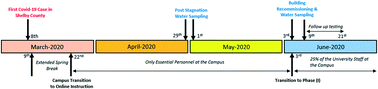
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1996-2009
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00428J
A novel passive sampling approach for SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater in a Canadian province with low prevalence of COVID-19
A simple passive sampling protocol using cheesecloth and electronegative filters coupled with a Tween®20-based elution technique provided reliable detection of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater at targeted locations in a region of low COVID-19 prevalence.
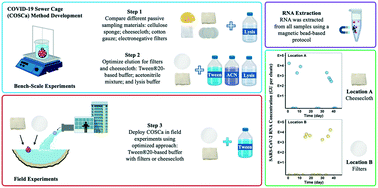
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 1576-1586
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EW00207D
Modeling the effect of reduced traffic due to COVID-19 measures on air quality using a chemical transport model: impacts on the Po Valley and the Swiss Plateau regions
Our results indicate that lockdown measures induced a mild increase in secondary organic aerosol (SOA) concentrations in areas with substantial reductions in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) concentrations, i.e. the “Greater Milan” area.
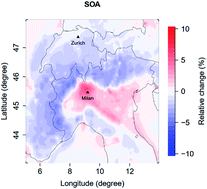
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 228-240
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00036E
Emerging Investigator Series: COVID-19 lockdown effects on aerosol particle size distributions in northern Italy
Impact of lockdown measures on the air pollutants and particle number size distribution.
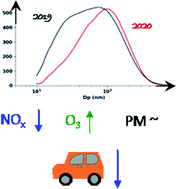
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 214-227
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00016K
Non-woven materials for cloth-based face masks inserts: relationship between material properties and sub-micron aerosol filtration
Sub-micron aerosol filtration of non-woven materials and fabric treatments were investigated. Select low-cost, readily available and easily cut non-woven materials were identified as suitable filter inserts for cloth-based masks.
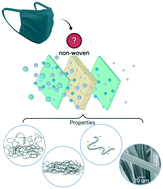
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 1603-1613
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00277E
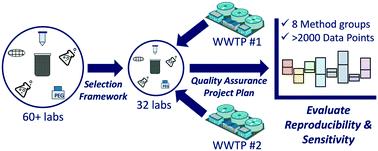
Reproducibility and sensitivity of 36 methods to quantify the SARS-CoV-2 genetic signal in raw wastewater: findings from an interlaboratory methods evaluation in the U.S.
The reproducibility and sensitivity of 36 methods for quantifying the genetic signal of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater was evaluated in a nationwide interlaboratory assessment in the U.S.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2021,7, 504-520
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00946F
COVID-19 lockdowns induced land surface temperature variability in mega urban agglomerations in India
Reduced anthropogenic activities during COVID-19 lockdowns improved air quality and dampened LST in highly populated and polluted Indian megacities.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 144-159
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00358A
Characterization of a commercially-available, low-pressure UV lamp as a disinfection system for decontamination of common nosocomial pathogens on N95 filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) material
A commercially-available UV disinfection system used for hospital room disinfection was characterized and used for N95 filtering facepiece respirator (FFR) material disinfection.
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2020,6, 2089-2102
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00404A
About this collection
The coronavirus pandemic has shaken the world, and the role of environmental scientists, modelers, and engineers, will be integral towards developing sustainable solutions for tackling COVID-19. Knowledge and appreciation of the environmental context is central to understanding transmission of the disease, and we wish to highlight the important steps that the environmental science community is taking to address the global situation.
Read more Royal Society of Chemistry articles on coronavirus research in this free collection: www.rsc.li/covid_articles.