Themed collection Horizons Community Board Themed Collection – Nanobiomedicine

Horizons Community Board Collection – Nanobiomedicine
A themed collection on nanobiomedicine, guest edited by Nanoscale Horizons Community Board Member Chandra Kumar Dixit and Materials Horizons Community Board Member Christopher M. Proctor.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 256-257
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH90006C
DePEGylation strategies to increase cancer nanomedicine efficacy
PEGylation of nanoparticles prolongs circulation lifetimes and maximizes nanoparticle accumulation in target tumors. However, PEGylation comes at the cost of reduced cellular uptake of nanoparticles and concomitant drug delivery. This review discusses the various stimuli-responsive dePEGylation strategies that have been employed to overcome this “PEG dilemma”.
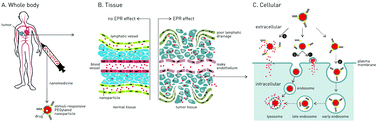
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 378-387
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NH00417J
Graphene oxide and carbon dots as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents – a minireview
Complex antibacterial mechanisms of graphene oxide and carbon dots.
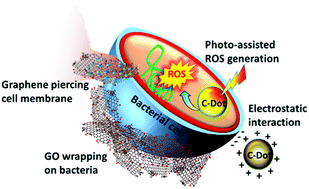
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 117-137
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NH00174J
Carbon-based nanomaterials as an emerging platform for theranostics
Carbon-based nanomaterials emerge as promising platforms for theranostic applications in disease treatment and tissue repair.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 434-469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00966J
Hydrogels that listen to cells: a review of cell-responsive strategies in biomaterial design for tissue regeneration
This review discusses the recent advances and design principles for dynamic and cell-responsive hydrogels – biomaterials that respond to locally produced stimuli in and around cells or tissues without external influence.
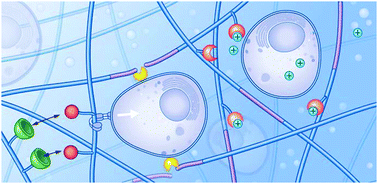
Mater. Horiz., 2017,4, 1020-1040
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MH00373K
3D quantum theranosomes: a new direction for label-free theranostics
Quantum-scale materials offer great potential in the field of cancer theranostics.
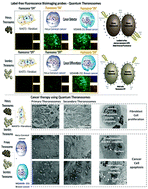
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 495-515
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NH00287H
Hydrogel nanotubes with ice helices as exotic nanostructures for diabetic wound healing
Hydrogel nanotubes with ice helices entrapped within their internal conduits are a promising material for diabetic wound healing.

Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 274-284
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01298A
Close-loop dynamic nanohybrids on collagen-ark with in situ gelling transformation capability for biomimetic stage-specific diabetic wound healing
A self-regulated dynamic nanohybrid that can sensitively respond to hyperglycemic microenvironment is developed. The nanohybrid with a core/shell structure is produced through a single-step microfluidics nanoprecipitation method, where drugs-loaded porous silicon (PSi) nanoparticles are encapsulated by H2O2 responsive polymeric matrix.
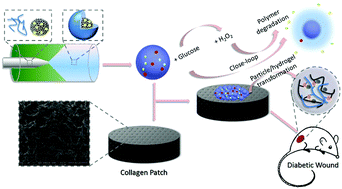
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 385-393
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01145A
Ferrous-cysteine–phosphotungstate nanoagent with neutral pH fenton reaction activity for enhanced cancer chemodynamic therapy
Chelating strategy and electron shuttle armed nanoagent for killing cancer cells at both an acidic and neutral pH with high CDT efficiency.
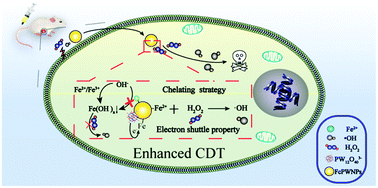
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 369-374
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH01176A
Identifying glioblastoma margins using dual-targeted organic nanoparticles for efficient in vivo fluorescence image-guided photothermal therapy
Dual-targeted organic nanoparticles efficiently target the margin of glioblastoma and successfully suppress the tumour growth through photothermal therapy.
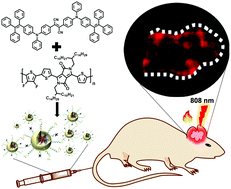
Mater. Horiz., 2019,6, 311-317
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00946E
A single-step multi-level supramolecular system for cancer sonotheranostics
A multi-level supramolecular system produced by single-step Fe3+-mediated ionic crosslinking self-assembly can overcome the critical issues of current sonodynamic therapy (SDT) and address the need to monitor therapeutic effects in vivo with a non-invasive approach.
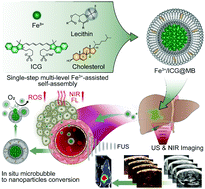
Nanoscale Horiz., 2019,4, 190-195
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NH00276B
Nanodiamond-based non-canonical autophagy inhibitor synergistically induces cell death in oxygen-deprived tumors
Blockage of autophagic flux by nanodiamonds induces apoptosis in hypoxic tumor cells with minimal toxicity to normal tissues and enhances the effects of anti-angiogenic therapy.
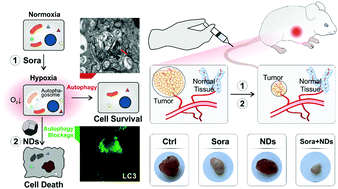
Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 1204-1210
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00993G
Vitamin metal–organic framework-laden microfibers from microfluidics for wound healing
Vitamin MOF-laden microfibers with alginate shells and copper- or zinc-vitamin framework cores are controllably generated for improving tissue wound healing.
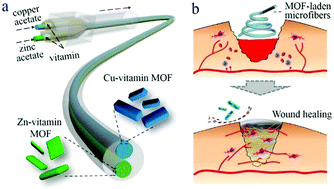
Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 1137-1142
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00647D
An immunological electrospun scaffold for tumor cell killing and healthy tissue regeneration
An immunological tissue engineering scaffold is fabricated using anti-CD40 antibody grafted in electrospun fibers for inducing cancer cell apoptosis, activating immune response and promoting healthy tissue regeneration.
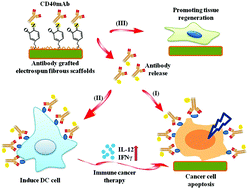
Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 1082-1091
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00704G
Crystallographic snapshots of host–guest interactions in drugs@metal–organic frameworks: towards mimicking molecular recognition processes
We report a novel highly crystalline MOF, featuring hydroxyl-decorated channels, capable of distinctly organizing guest organic molecules within its pores.
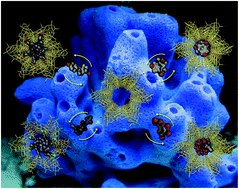
Mater. Horiz., 2018,5, 683-690
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MH00302E
A programmable lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle system for localized, sustained antibiotic delivery to Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial biofilms
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle enhances antibiotic efficacy through localised, sustained delivery to bacterial biofilms.
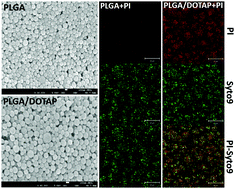
Nanoscale Horiz., 2018,3, 305-311
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NH00167C
Fully degradable protein nanocarriers by orthogonal photoclick tetrazole–ene chemistry for the encapsulation and release
Tetrazole–ene click chemistry was used to prepare fully biodegradable protein nanocarriers with high drug encapsulation and enzymatically-triggered intracellular release.
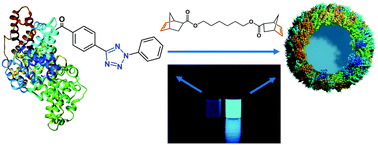
Nanoscale Horiz., 2017,2, 297-302
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NH00062F
Primary microglia maintain their capacity to function despite internalisation and intracellular loading with carbon nanotubes
When internalised in microglia, functionalised carbon nanotubes did not alter viability, induce inflammation or damage phagocytosis and migration abilities.

Nanoscale Horiz., 2017,2, 284-296
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NH00055C
Assembly of hepatitis E vaccine by ‘in situ’ growth of gold clusters as nano-adjuvants: an efficient way to enhance the immune responses of vaccination
Vaccine-based immunotherapy plays an integral role in the development of present and future clinical therapies.
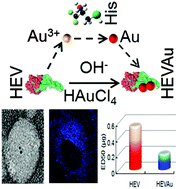
Nanoscale Horiz., 2016,1, 394-398
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NH00087H
About this collection
Guest Edited by Chandra Kumar Dixit, Qiagen Sciences and Nanoscale Horizons Community Board, and Christopher Proctor, University of Cambridge and Materials Horizons Community Board.
Advancements in nanotechnology are impacting biology and medicine. In this themed collection we are compiling some noteworthy articles in the areas related to targeted delivery, vaccine, diagnostics, wound healing, and self-healing scaffolds & materials. Theranostics, which is a new branch specifically dealing with point-of-care, involves diagnostics and therapy in a single agent. Carbon-based materials are proving to be effective agents in this quest as indicated by Kapil Patel et al. in their research published in Materials Horizons (2018). Anand et al. (2019) emphasized in their review article the potential of carbon-based nanomaterials as antimicrobial agents. Scaffolds and matrices based on nanomaterials, as illustrated through the research works of Yu et al. (2018, Materials Horizons), Singh et al. (2018, Materials Horizons), Ooi (2017, Materials Horizons), and Liu (2018, Materials Horizons) have shown tremendous potential in surgery, wound healing, controlled release skin patches etc. Given how all these materials show potential in their respective fields, it will be important to see how these will shape the future of biomedicine. We hope that the readers find this themed collection informative and useful.