Themed collection Antimicrobial Resistance

The global antibiotic research and development partnership (GARDP): researching and developing new antibiotics to meet global public health needs

Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1227-1230
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD90010A
Resisting resistance: gearing up for war
Where do we stand in our fight against antimicrobial resistance?
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1512-1516
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00330D
Quinolone antibiotics
The quinolone antibiotics arose in the early 1960s, with the first examples possessing a narrow-spectrum activity with unfavorable pharmacokinetic properties.
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1719-1739
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00120D
Pursuing DHDPS: an enzyme of unrealised potential as a novel antibacterial target
DHDPS represents a novel enzyme target for the development of new antibiotics to combat multidrug resistance.
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1581-1588
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00107G
On the road to structure-based development of anti-virulence therapeutics targeting the type III secretion system injectisome
Targeting the T3SS injectisome using the anti-virulence strategy offers an alternative to antibiotic therapeutic approaches when dealing with resistance.
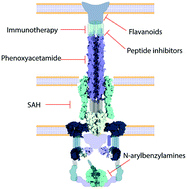
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1273-1289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00146H
Drug-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: where we stand
Tuberculosis (TB), an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), has burdened vulnerable populations in modern day societies for decades.
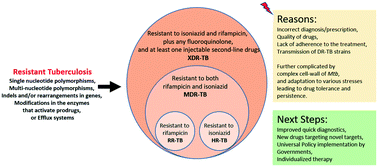
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1342-1360
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00057G
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): antibiotic-resistance and the biofilm phenotype
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is an asymptomatic colonizer of 30% of all human beings. It is also the most dangerous of all Staphylococcal bacteria.
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1231-1241
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00044E
Revitalizing antifolates through understanding mechanisms that govern susceptibility and resistance
Mechanisms of antifolate resistance in bacterial and mammalian cells.
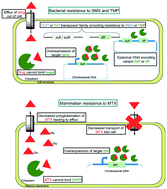
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 880-895
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00078J
Inhibiting bacterial secretion systems in the fight against antibiotic resistance
The search for new ammunition to combat antibiotic resistance has uncovered diverse inhibitors of the bacterial type IV secretion system.
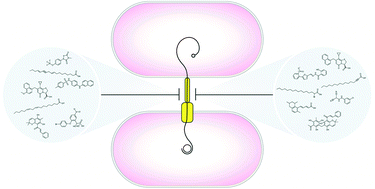
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 682-692
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00076C
Gasdermin D (GSDMD) as a new target for the treatment of infection
Inhibition of pyroptosis through targeting the activation or pore-formation of GSDMD.
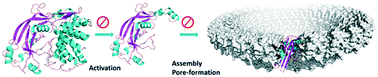
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 660-667
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00059C
The calcium-dependent lipopeptide antibiotics: structure, mechanism, & medicinal chemistry
To push back the growing tide of antibacterial resistance the discovery and development of new antibiotics is a must.
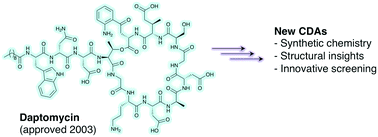
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 634-646
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00126C
Connecting iron acquisition and biofilm formation in the ESKAPE pathogens as a strategy for combatting antibiotic resistance
Biofilms are linked to resistance development in the ESKAPE pathogens. This perspective summarizes several strategies for affecting iron homeostasis that have been implicated in biofilm inhibition.
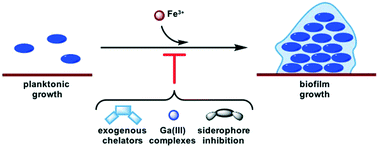
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 505-512
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00032A
Characterization of the genomically encoded fosfomycin resistance enzyme from Mycobacterium abscessus
FosM from Mycobacterium abscessus is a Mn2+-dependent FosX-type hydrase.
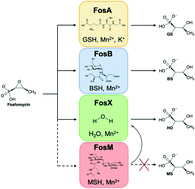
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1948-1957
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00372J
Small antibacterial molecules highly active against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
The rapid growth of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus coupled with their biofilm forming ability has made the infections difficult to treat with conventional antibiotics.
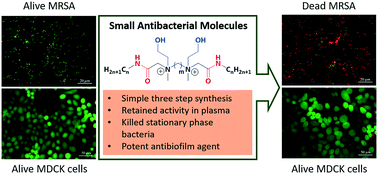
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1907-1915
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00329K
Synthetic studies on the reverse antibiotic natural products, the nybomycins
We report a new scalable and robust synthetic route to the nybomycin natural products and the activity of novel analogues of this family.
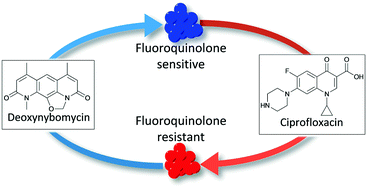
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1438-1444
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00207C
Iridium piano stool complexes with activity against S. aureus and MRSA: it is past time to truly think outside of the box
Iridium based antimicrobial agents have shown efficacy against S. aureus, including MRSA, and appear to be safe in mice.
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1391-1398
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00140A
Biochemical and microbiological evaluation of N-aryl urea derivatives against mycobacteria and mycobacterial hydrolases
N-Aryl urea derivatives were synthesized and some showed activity against mycobacterial hydrolases while others showed antimicrobial activity against mycobacterial species.
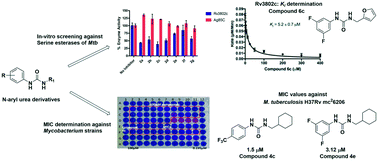
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 1197-1204
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00122K
Novel zafirlukast derivatives exhibit selective antibacterial activity against Porphyromonas gingivalis
Eleven new zafirlukast derivatives selective and bactericidal against Porphyromonas gingivalis.
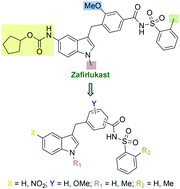
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 926-933
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00074G
Fluoroquinolone-derived fluorescent probes for studies of bacterial penetration and efflux
Fluorescent probes derived from the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin were synthesised using a Cu(I)-catalysed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) to link a ciprofloxacin azide derivative with alkyne-substituted green and blue fluorophores.

Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 901-906
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00124G
Anthranilic amide and imidazobenzothiadiazole compounds disrupt Mycobacterium tuberculosis membrane potential
Compounds 1 and 2 disrupt M. tuberculosis membrane potential and demonstrate bactericidal activity against non-replicating M. tuberculosis in pH 4.5 buffer.
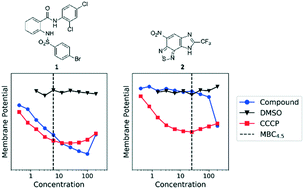
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 934-945
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00088G
Synthesis, ribosomal selectivity, and antibacterial activity of netilmicin 4′-derivatives
We describe the synthesis and evaluation of 4′-subsituted netilmicin derivatives by selective functionalization at the 4′-position of the endocyclic enolether function.
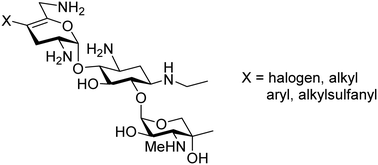
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 946-950
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00153K
Eradicating uropathogenic Escherichia coli biofilms with a ciprofloxacin–dinitroxide conjugate
Biofilm-related UTIs are problematic infectious diseases worldwide; here we have developed a novel ciprofloxacin–dinitroxide conjugate with potent UPEC biofilm-eradication activity.
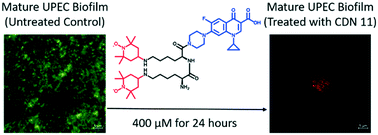
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 699-711
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00062C
Rapid kill assessment of an N-arylated NH125 analogue against drug-resistant microorganisms
N-Arylated NH125 analogue 1 rapidly eradicates a diverse panel of drug-resistant bacteria and fungi (≥99.9% kill in 1 to 10 minutes).
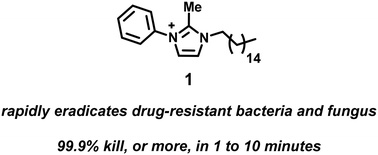
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 712-716
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MD00613J
Synthesis of saccharocin from apramycin and evaluation of its ribosomal selectivity
We describe a facile synthesis of saccharocin from apramycin by regioselective tetra-azidation and stereospecific oxidative deamination of the amino group.
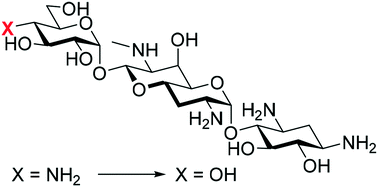
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 554-558
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00093C
Polybasic peptide–levofloxacin conjugates potentiate fluoroquinolones and other classes of antibiotics against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria
To address the rising threat of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria, new therapeutic strategies must be developed.
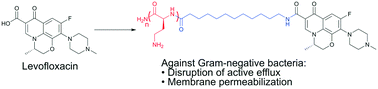
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 517-527
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00051H
Using 2-aminobenzimidazole derivatives to inhibit Mycobacterium smegmatis biofilm formation
Biofilm formation by mycobacteria can lead to enhanced antibiotic tolerance.
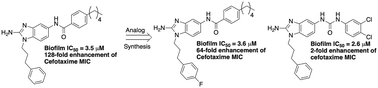
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 456-459
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00025A
‘Second-generation’ 1,2,3-triazole-based inhibitors of Porphyromonas gingivalis adherence to oral streptococci and biofilm formation
This study details the design, synthesis and bioassay of ‘click’ peptidomimetic compounds which inhibit the adherence of P. gingivalis to S. gordonii, a primary step toward pathogenic colonization of the subgingival pocket.
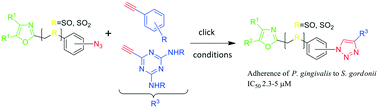
Med. Chem. Commun., 2019,10, 268-279
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MD00405F
Structure–activity relationship of the cinnamamide family of antibiotic potentiators for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
MIC of oxacillin against S. aureus (MRSA252 strain) reduced from 256 μg mL−1 to 2 μg mL−1.

Med. Chem. Commun., 2018,9, 2008-2016
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8MD00479J