Gasdermin D (GSDMD) as a new target for the treatment of infection
Abstract
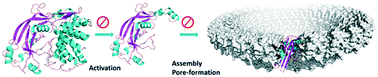
The discovery of a previously unknown protein, gasdermin D (GSDMD), as the key effector that leads to pyroptosis and NETosis has created much excitement. Since its initial report in Oct. 2015, more than 200 papers have been published on studies of the structure and mechanism of GSDMD and its homologues. The clear connection between infection and inflammasome activation made GSDMD a promising target for the development of anti-infection treatment. In this mini review, we discuss first the current understanding of the structure and mechanism of GSDMD, focusing on its potential as a druggable target, and then recent efforts in the development of inhibitors to interfere with the pore-forming function of GSDMD and thus alleviate the detrimental effects due to pyroptotic cell death.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Antimicrobial Resistance


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
