Biochemical and microbiological evaluation of N-aryl urea derivatives against mycobacteria and mycobacterial hydrolases†
Abstract
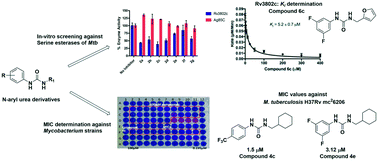
A focused library of 24 N-aryl urea derivatives was prepared and evaluated against serine esterases of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) Rv3802c and Mtb Ag85C. The members of the library were evaluated for both selectivity and mode of inhibition. Furan-based urea derivative 6c was found to be the most potent non-covalent inhibitor of Rv3802c with a Ki value of 5.2 ± 0.7 μM. On the other hand, triazole-based ureas 10a and 10b selectively inhibited Ag85C irreversibly with a kinact/Ki value of 2.3 ± 0.3 and 5.5 ± 0.4 × 10−3 μM−1 min−1, respectively. The library was also evaluated for minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against two strains of Mtb, Mycobacterium smegmatis, and Mycobacterium abscessus. Compounds 4a and 4c were active against Mtb H37Rv mc26206 with MIC values of 3.12 and 1.5 μM, respectively. Closely related 4e showed similar activity against Mtb H37Rv mc26206 but also possessed activity against Mtb H37Ra, Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium abscessus. Compounds 4a, 4c, and 4e all contained a common 1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-3-phenylurea motif. In summary, we identified a selective non-covalent inhibitor of Rv3802c and covalently irreversible inhibitors of Ag85C as well as the 1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-3-phenylurea motif which showed activity against a variety of mycobacteria.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Antimicrobial Resistance


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...