Themed collection Sustainable Food Technology – Editors Choice Collection 2023

Digitalization of the agro-food sector for achieving sustainable development goals: a review
Digitalization holds the potential to transform the agro-food sector by enhancing sustainability and addressing crucial global developmental challenges.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 783-802
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00124E
Current status and future prospects of bioactive molecules delivered through sustainable encapsulation techniques for food fortification
In a world of growing population and changing climate, health and sustainable food production are nowadays considered the most pressing challenges.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 500-510
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00015J
Plasma processing: a sustainable technology in agri-food processing
Overview of the different applications of plasma in pre and post-harvest processing of agri-food chain.
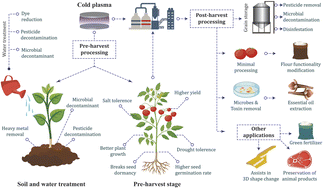
Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 9-49
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00014H
Biodegradable biopolymers for active packaging: demand, development and directions
Biodegradable active food packaging addresses key environmental issues including plastic waste and food waste.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 50-72
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00004K
Sustainable production of prodigiosin from rice straw derived xylose by using isolated Serratia marcescens (CMS 2): statistical optimization, characterization, encapsulation & cost analysis
Prodigiosin-producing isolate Serratia marcescens, with sustainable media produced 1.9 times more prodigiosin, encapsulation increased its water solubility and whole process for prodigiosin production is cost-effective.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 837-849
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00100H
Novel naturally derived encapsulation agents in the ionic liquid form for sustainable emulsion-based products
Naturally derived ionic liquids are efficient encapsulation agents for sustainable emulsion-based products.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 275-279
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00054G
Acid-derived bacterial cellulose nanocrystals as organic filler for the generation of high-oxygen barrier bio-nanocomposite coatings
This study investigates the effect of the hydrolysis process on bacterial cellulose (BC) to obtain bacterial cellulose nanocrystals (BCNCs) used to create high oxygen barrier nanocomposite coatings for food packaging applications.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 941-950
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00147D
Fortification of vegetable fat with natural antioxidants recovered by bergamot pomace for use as an ingredient for the production of biscuits
Modern consumers are increasingly interested in eating healthy food and paying attention to the reduction of synthetic preservatives and the increased use of natural preservatives.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 951-961
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00125C
Pulsed electric field assisted extraction of soluble proteins from nettle leaves (Urtica dioica L.): kinetics and optimization using temperature and specific energy
The efficiency of protein extraction from leaves can be boosted by PEF application. The soluble protein yield is strongly impacted by the linear temperature and quadratic specific energy effects, both of which are highly significant.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 886-895
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00053B
Simultaneous production of proteases and antioxidant biopeptides by solid-state fermentation
We showed the concomitant production of proteases and biopeptides in SSF by A. niger for performing the valuation of agro-food residues.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 874-885
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00077J
Effects of high-pressure and transglutaminase, individually and simultaneously applied, on pea and soy protein isolates
Microbial transglutaminase (MTG) can improve proteins’ properties. High pressure processing (HPP) enhances MTG accessibility due to conformation changes in pea and soy proteins. When combined, MTG and HPP can have synergistic/antagonistic effects.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 696-708
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00039G
Sustainable processing of Greek yogurt acid-whey waste to develop folic acid encapsulated millet powders
Folic acid can be encapsulated using acid whey, kodo and proso millet. Spray drying and extrusion can be used for encapsulation wherein the product has high flowability. The acid whey and millet matrix act as a source of divalent ions that help produce folic acid gel.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 437-454
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00009E
Encapsulation of essential oils using hemp protein isolate–gum Arabic complex coacervates and evaluation of the capsules
Complex coacervates of hemp protein isolate and gum Arabic were prepared. These complex coacervates were used to encapsulate essential oils (EOs). The nature of the EO affected the physical properties, structure and bioactives of capsules.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 426-436
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FB00004D
Use of response surface methodology to optimise vacuum impregnation of β-carotene from Daucus carota in Pachyrhizus erosus
Consuming carotenoid-rich foods prevent and reduce certain types of cancer and cardiovascular and degenerative diseases.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 404-414
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00036A
Towards a sustainable and green extraction of curcuminoids using the essential oil of Cinnamomum cassia
A natural and sustainable alternative to conventional solvents in terms of solubilization and extraction of curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. was investigated by examining different naturally occurring aroma compounds and cinnamon oils.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 319-327
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00026A
Lamination of starch/polyesters by thermocompression for food packaging purposes
Tri-layer films were obtained to produce laminates that better-fit food packaging requirements. Overall improvement of barrier and tensile properties of PLA–starch laminates with respect to the individual films regardless of the type of starch.

Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 296-305
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00038E
Utilization of quince (Cydonia oblonga) seeds for production of mucilage: functional, thermal and rheological characterization
Optimum extraction conditions for QSM were found to be pH value of 9, extraction temperature of 60 °C, extraction time of 15 min and W/S ratio of 19 : 1. The mucilage obtained exhibited very good functional, thermal and rheological properties.
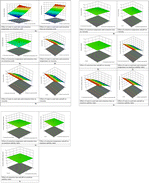
Sustainable Food Technol., 2023,1, 107-115
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FB00010E
About this collection
This collection highlights some of the very best work published in Sustainable Food Technology in 2023, hand-picked by our dedicated editorial team and the Editor-in-Chief, Jorge Barros Velázquez.