Themed collection Applied Computational Chemistry

Foreword: Applied computational chemistry
A foreword from Professor Kendall N. Houk for the Applied Computational Chemistry themed issue of Chemical Society Reviews.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4905-4905
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS90049A
Applied computational chemistry
Guest editors Israel Fernández and Fernando Cossío introduce this themed issue of Chemical Society Reviews on the topic of applied computational chemistry in honour of the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4906-4908
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS90040E
New bonding modes of carbon and heavier group 14 atoms Si–Pb
Molecules which possess chemical bonds where a bare group-14 atom C–Pb is bonded to σ-donor ligands L or to a transition metal fragment [TM] through donor–acceptor interactions are discussed together with an analysis of the bonding situation with modern quantum chemical methods.
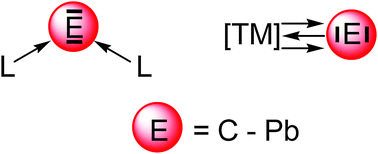
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5106-5139
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00073K
The role of aromaticity in determining the molecular structure and reactivity of (endohedral metallo)fullerenes
The molecular structure and chemical reactivity of endohedral metallofullerenes can be greatly predicted and rationalized by their local and global aromaticity.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5089-5105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00040D
Quantum-chemical insights into mixed-valence systems: within and beyond the Robin–Day scheme
The application of quantum-chemical methods to both organic and transition-metal mixed-valence systems is reviewed, with particular emphasis on how to describe correctly delocalisation vs. localisation near the borderline between Robin–Day classes II and III.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5067-5088
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60481K
A theoretical view of protein dynamics
Moving from a traditional static picture of proteins to an alternative dynamic paradigm is one of the biggest challenges of structural biology, and the point where modeling can contribute the most. I review here the current state of the art in theoretical methods for dynamic representation of proteins.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5051-5066
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60474H
How cyclobutanes are assembled in nature – insights from quantum chemistry
Theoretical work on the biosynthetic production of complex, cyclobutane-containing natural products is described.
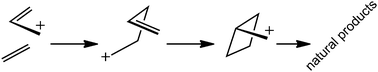
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5042-5050
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60452G
Chemical applications carried out by local pair natural orbital based coupled-cluster methods
Local pair natural orbital coupled-cluster methods are suitable for accurate assessment of the energies of large molecular and supramolecular systems.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5032-5041
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00050A
Versatile reactivity of Pd-catalysts: mechanistic features of the mono-N-protected amino acid ligand and cesium-halide base in Pd-catalyzed C–H bond functionalization
The C–H functionalization strategies, complexity in Pd-catalyzed chemical transformations, unprecedented Pd-clustering, base (Cs-halide) and weakly coordinated amino acid ligand effects.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5009-5031
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60447K
Conceptual DFT: chemistry from the linear response function
This review highlights the evaluation, visualization and interpretation of the linear response function, retrieving physical and chemical concepts like the atomic shell structure, electron delocalisation, aromaticity and anti-aromaticity,….

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4989-5008
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60456J
A tutorial for understanding chemical reactivity through the valence bond approach
This tutorial teaches the interested how to comprehend and predict reactivity patterns in a variety of reaction types.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4968-4988
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00043A
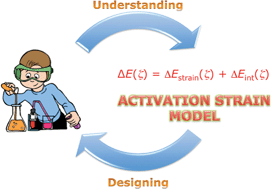
The activation strain model and molecular orbital theory: understanding and designing chemical reactions
In this Tutorial Review, we make the point that a true understanding of trends in reactivity (as opposed to measuring or simply computing them) requires a causal reactivity model.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4953-4967
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00055B
Challenges in modelling homogeneous catalysis: new answers from ab initio molecular dynamics to the controversy over the Wacker process
The controversial reaction mechanism considering experimental results and theoretical treatment from static to ab initio molecular dynamic simulations is reviewed.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4940-4952
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60469A
Aromaticity in transition structures
This tutorial review presents interpretative computational tools to describe and quantify the different manifestations of aromaticity in transition structures.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4909-4921
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00012A
Understanding the reactivity of metallic nanoparticles: beyond the extended surface model for catalysis
Metallic nanoparticles (NPs) constitute a new class of chemical objects which are used in different fields as diverse as plasmonics, optics, catalysis, or biochemistry.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 4922-4939
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60421G
About this collection
This themed issue of Chemical Society Reviews, guest edited by Israel Fernández and Fernando, P. Cossío, focusses on the application of computational/theoretical methods to chemical problems of interest to a wide computational and experimental audience. The issue is published in honour of the 2013 Nobel Prize for Chemistry which was awarded to Martin Karplus, Michael Levitt and Arieh Warshel "for the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems".