Versatile reactivity of Pd-catalysts: mechanistic features of the mono-N-protected amino acid ligand and cesium-halide base in Pd-catalyzed C–H bond functionalization
Abstract
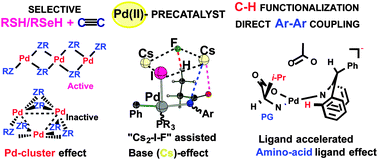
The widely used C–H functionalization strategies and some complexities in the Pd-catalyzed chemical transformations were analyzed. It was emphasized that in the course of catalysis various Pd-intermediates (including nano-scale Pd-clusters) could act as active catalysts. However, both identification of these catalytically active species and determination of factors controlling the overall catalytic process require more comprehensive and multi-disciplinary approaches. Recent joint computational and experimental approaches were instrumental in: (1) demonstrating that the addition of Pd(OAc)2 as a catalyst precursor to RSeH and RSH reagents forms the [Pd(SeR)2]n and [Pd(SR)2]n clusters, respectively, which show an unprecedented ability for selective synthesis of Markovnikov-type products starting with a mixture of reagents RSH/RSeH and acetylenic hydrocarbons; (2) predicting a valid mechanism of the amino acid ligand-assisted Pd(II)-catalyzed C–H activation that is shown to proceed via the formation of the catalytically active Pd(II) intermediate with a bidentately coordinated dianionic amino acid ligand; (3) demonstrating that the amino acid ligand plays crucial roles in the ligand-assisted Pd(II)-catalyzed C–H activation by acting as: (a) a weakly coordinating ligand to stabilize the desirable Pd(II)-precatalyst, (b) a soft proton donor and a bidentately coordinated dianionic ligand in the catalytically active Pd(II) intermediate, and (c) a proton acceptor accelerating the C–H deprotonation via the CMD mechanism; and (4) revealing the roles of the CsF base (and “cesium effect”) in the Pd(0)/PCy3-catalyzed intermolecular arylation of the terminal β-C(sp3)–H bond of aryl amide and predicting the unprecedented “Cs2-I-F cluster” assisted mechanism for this reaction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Applied Computational Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...