Themed collection Multiply charged ions (MCIs) in the gas-phase

Multiply charged ions in the gas phase
PCCP Themed Issue on multiply charged ions in the gas phase.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18251-18252
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP90163J
Doubly-charged ions in the planetary ionospheres: a review
Results from numerical simulations of the densities of doubly-charged ions in the ionospheres of Venus, the Earth, Mars and Titan.
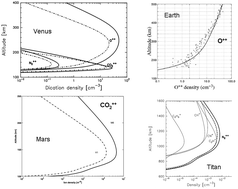
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18264-18287
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21957J
Multiply-charged ions and interstellar chemistry
Multiply-charged ions formed when molecules and ions harvest ambient energy are reactive intermediates that can influence the ionization and chemical structure of the interstellar medium.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18253-18263
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21814J
Single and multiple photoionisation of H2S by 40–250 eV photons
Multi-electron coincidence spectroscopy combined with synchrotron radiation elucidates double and triple ionization and core-hole decay in H2S.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18428-18435
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21654F
Metastable states in NO2+ probed with Auger spectroscopy
Potential energy curves of NO2+ were determined using Auger spectroscopy subsequent to O 1s and N 1s core ionization.
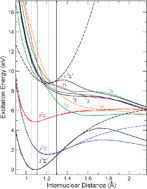
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18436-18446
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21584A
Modeling the interactions between peptide functions and Sr2+: formamide –Sr2+ reactions in the gas phase
In formamide–Sr2+ interactions the dominant process is a Coulomb explosion yielding SrOH+ + HCNH+. Some lighter doubly charged species such as NH3Sr2+, COSr2+ and H2OSr2+ are also produced.
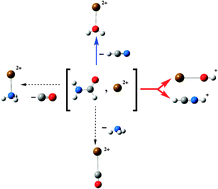
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18409-18417
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21578G
Microsolvation of Co2+ and Ni2+ by acetonitrile and water : photodissociation dynamics of M2+(CH3CN)n(H2O)m
M2+(CH3CN)n(H2O)m (M = Co, Ni) photolyze via solvent loss, proton transfer and electron transfer, depending on the cluster size and composition.
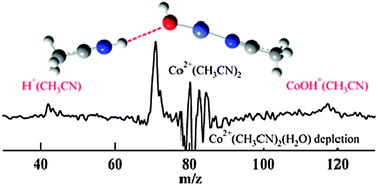
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18347-18354
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21586H
Coulomb explosion of nitrogen and oxygen molecules through non-Coulombic states
We systematically study Coulomb explosion of nitrogen and oxygen molecules in intense 8 and 24 fs laser pulses.
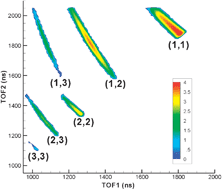
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18398-18408
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21345H
The effect of reagent charge state on the charge inversion efficiency of singly charged polyatomic ions in the gas phase
Charge inversion efficiency in an ion trap varies with reagent charge state for both dynamic and instrumental reasons.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18418-18427
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21581G
Al(CN) 3−6 and Al(NC)3−6 trianions
The gas phase trianion Al(CN)3−6 is metastable with respect to dissociation, but the Coulomb barrier is so high that it can be considered to be stable for all practical purposes.
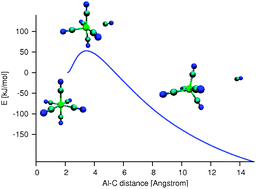
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18393-18397
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21570A
Gas-phase reactions of doubly charged actinide cations with alkanes and alkenes —probing the chemical activity of 5f electrons from Th to Cm
Gas-phase activation of alkanes and alkenes by doubly charged actinide cations, Th2+ through Cm2+, proceeds along several pathways.
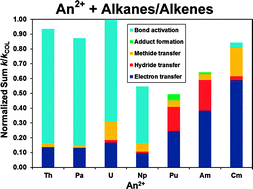
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18322-18329
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21399G
Treating highly charged carbon and fullerene clusters as dielectric particles
Difference between image charge and dielectric particle models for treating the fragmentation of highly charged fullerenes.
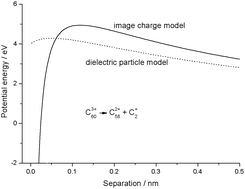
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18339-18346
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21573F
Electronic state selectivity in dication-molecule single electron transfer reactions: NO2+ + NO
Single-electron transfer between NO2+ and NO generates pairs of NO+ ions which behave very differently to the products from the analogous CO22+/CO2 and O22+/O2 collision systems.
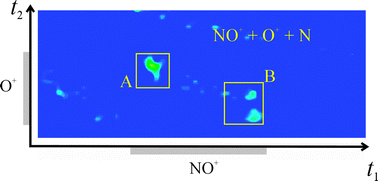
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18386-18392
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21612K
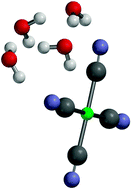
Evidence for hydrogen bond network formation in microsolvated clusters of Pt(CN)42−: collision induced dissociation studies of Pt(CN)42−·(H2O)nn = 1–4, and Pt(CN)42−·(MeCN)mm = 1, 2 cluster ions
Low energy collision induced dissociation has been used to investigate the microsolvation of Pt(CN)42− revealing “surface” solvated structures.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18379-18385
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21538H
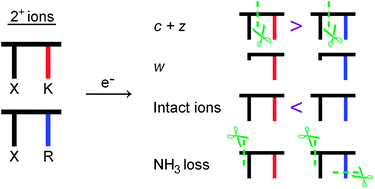
Electron-capture induced dissociation of doubly charged dipeptides : on the neutral losses and N–Cα bond cleavages
Electron capture induced dissociation experiments on a series of dipeptide dications reveal that the yields of c, z and w ions, ammonia loss and charge reduced intact species strongly depend on the peptide composition.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18373-18378
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21549C
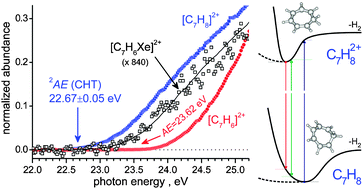
Double ionization of cycloheptatriene and the reactions of the resulting C7Hn2+ dications (n = 6, 8) with xenon
A benchmark study for fragmentation dynamics and ionic reactivity of medium sized hydrocarbon dications approached by experimental and theoretical methodologies.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18330-18338
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21634A
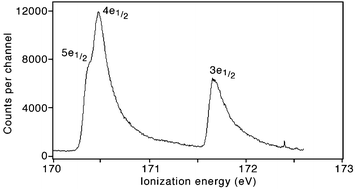
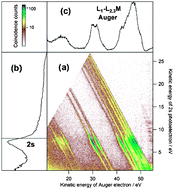
Multi-electron spectroscopy : Auger decays of the argon 2s hole
The complete cascade decay of the Ar 2s hole is retrieved. Coincidences between photo- and Auger electrons reveal Ar2+ intermediate states as demonstrated in the figure.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18355-18364
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21546A
Doubly charged protonated a ions derived from small peptides
Charge separation in the CID of [LaIII(peptide)(CH3CN)m]3+ gives novel protonated an ions; stability depends on the residue at the N-terminus.
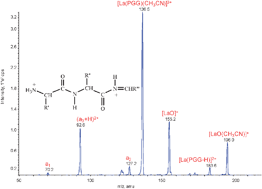
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18307-18314
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21522A
Metastable ClO2+ and ClO3+ ions in the gas phase: a combined theoretical and mass spectrometric investigation
Theoretical and mass spectrometric investigation of the ClO2+ dication.
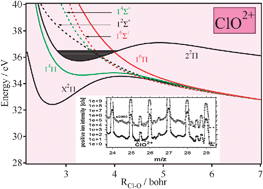
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18315-18321
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21567A
Electronic structure and lifetimes of GaX2+ (X = N, O, F) in the gas phase. Unraveling stability trends
GaN2+ and GaF2+ can be considered as bound systems in the gas phase. The former is kinetically stable and the latter thermodynamically stable in clear contrast with GaO2+ which was found to be metastable.
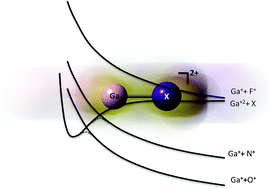
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18365-18372
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21534E
Calcium-containing diatomic dications in the gas phase
Novel calcium-containing diatomic dications in the gas phase are detected experimentally and their thermodynamic and spectroscopic properties predicted theoretically.
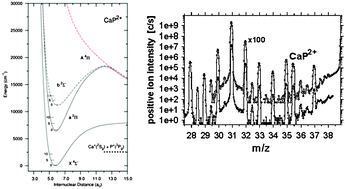
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18297-18306
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP20735K
The role of conformational flexibility on protein supercharging in native electrospray ionization
Protein conformational changes induced by supercharging reagents late in the ESI droplet lifetime causes increased charging from aqueous solutions.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 18288-18296
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP20277D
Oxygen-containing gas-phase diatomic trications and tetracations: ReOz+, NbOz+ and HfOz+ (z = 3, 4)
Experimental and theoretical investigations reveal the existence of three gas-phase diatomic trications ReO3+, NbO3+ and HfO3+ and the diatomic tetracation NbO4+.
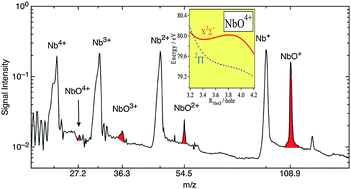
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13, 15233-15243
https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21566C
About this collection
PCCP Themed Issue on multiply charged ions in the gas phase.