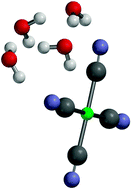
Low-energy collision induced dissociation has been used to investigate the structure and stability of microsolvated clusters of the prototypical, aprotic multiply charged anion, Pt(CN)42−, i.e. Pt(CN)42−·(H2O)nn = 1–4, Pt(CN)42−·(MeCN)mm =1, 2, and Pt(CN)42−·(H2O)3·MeCN. For all of the systems studied, the lowest energy fragmentation pathway was found to correspond to decay of the cluster with loss of the entire solvent ensemble. No sequential solvent evaporation was observed. These observations suggest that the Pt(CN)42−solvent clusters studied here form hydrogen-bonded “surface solvated” structures. Electronic structure calculations are presented to support the experimental results. In addition, the detailed fragmentation patterns observed are interpreted with reference to the differential solvation of the ionic fragmentation and electron detachment potential energy surfaces of the core Pt(CN)42− dianion. The results described represent some of the first experiments to probe the microsolvation of this important class of multiply charged anions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...