Themed collection Insights from advanced methods in molecular dynamics

Elucidation of the conformational dynamics of multi-body systems by construction of Markov state models
Recent algorithmic progresses in Markov State Model construction that enable optimal state definition and efficient estimation of the slow uphill kinetics are expected to boost investigations of complex multi-body processes.
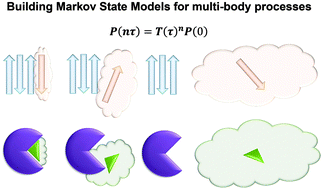
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30228-30235
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02545E
On the calculation of equilibrium thermodynamic properties from molecular dynamics
We explain the necessity of performing ensemble simulations to compute macroscopic properties in classical molecular dynamics simulation.
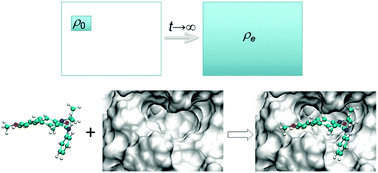
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30236-30240
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02349E
Lipid molecules can induce an opening of membrane-facing tunnels in cytochrome P450 1A2
The structure and dynamics of the membrane-bound full-length human cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) in aqueous solution determined by coarse-grained and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations.
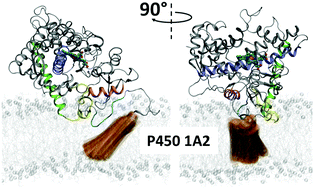
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30344-30356
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP03692A
The i-TTM model for ab initio-based ion–water interaction potentials. II. Alkali metal ion–water potential energy functions
A new set of i-TTM potential energy functions describing the interactions between alkali metal ions and water molecules is reported.
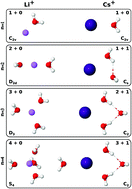
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30334-30343
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02553F
Simulations of the water exchange dynamics of lanthanide ions in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate ([EMIm][EtSO4]) and water
Molecular dynamics simulations have been carried out to explain the water-exchange rates of lanthanide ions in water and water/[EMIm][EtSO4] observed from 17O-NMR experiments. Our simulations are in agreement with experimental results with respect to water-exchange trends.
![Graphical abstract: Simulations of the water exchange dynamics of lanthanide ions in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate ([EMIm][EtSO4]) and water](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CP04957E&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30323-30333
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP04957E
Toward polarizable AMOEBA thermodynamics at fixed charge efficiency using a dual force field approach: application to organic crystals
First principles prediction of the structure, thermodynamics and solubility of organic molecular crystals, which play a central role in chemical, material, pharmaceutical and engineering sciences, challenges both potential energy functions and sampling methodologies.
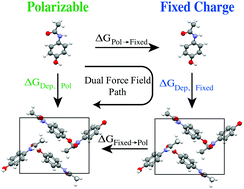
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30313-30322
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02595A
Rationalising pKa shifts in Bacillus circulans xylanase with computational studies
Molecular mechanism for pKa shifts for the key residues in wild-type and mutants of BcX based on three different computational methods.
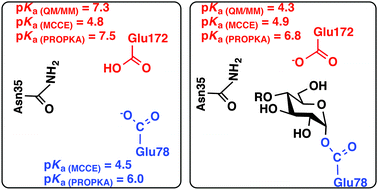
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30305-30312
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02526A
Getting excited: challenges in quantum-classical studies of excitons in polymeric systems
A combination of classical molecular dynamics (MM/MD) and quantum chemical calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT) and many-body Green's functions theory (GW-BSE) was performed to describe the conformational and optical properties of diphenylethyne (DPE), methylated-DPE and poly para phenylene ethynylene (PPE).
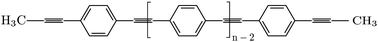
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30297-30304
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02944B
Reaction mechanism of the dengue virus serine protease: a QM/MM study
The dengue virus (DENV) is the causative agent of the viral infection dengue fever. It utilizes the NS2B-NS3pro serine protease to cleave the viral polyprotein into its constituents. We present here a QM/MM to study of the first step (acylation) of the reaction catalyzed by NS2B-NS3pro, using PDDG/PM3 for the QM subsystem, and Amber ff99SB for the MM subsystem.
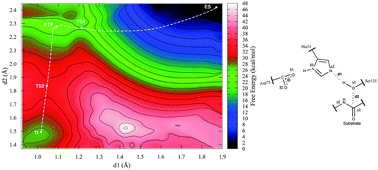
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30288-30296
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP03209E
Lagrangian descriptors in dissipative systems
In noisy chemical reactions with dissipation a reweighted Lagrangian descriptor reveals invariant manifolds.
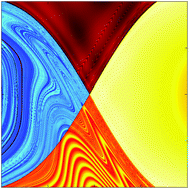
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30282-30287
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02532C
Transition state geometry of driven chemical reactions on time-dependent double-well potentials
The minimum contour in the forward Lagrangian descriptor overlaps the invariant manifold (in green) dividing reactant and product regions.
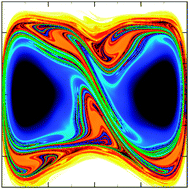
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30270-30281
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02519F
Calculating binding free energies of host–guest systems using the AMOEBA polarizable force field
Cucurbit[7]uril host–guest binding free energies are investigated using the AMOEBA polarizable force field.
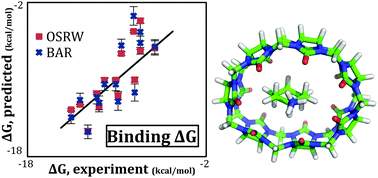
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30261-30269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02509A
Correction: Simulations of the water exchange dynamics of lanthanide ions in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate ([EMIm][EtSO4]) and water
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18, 30877-30877
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP90231F
About this collection
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are nowadays routinely used to complement experimental results and to predict properties or behaviours of myriad systems. Recent advances on the development of algorithms and potentials have broadened the applicability of MD calculations. This issue of PCCP aims to highlight the new insights and applications that have been enabled by the use of advanced MD techniques and potentials. The issue is guest-edited by G. Andres Cisneros (Wayne State University), Haiyan Liu (University of Science & Technology of China), Jean-Philip Piquemal (Sorbonne Université) and Pengyu Ren (University of Texas at Austin).