Calculating binding free energies of host–guest systems using the AMOEBA polarizable force field†
Abstract
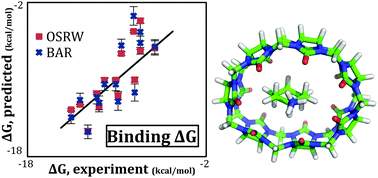
Molecular recognition is of paramount interest in many applications. Here we investigate a series of host–guest systems previously used in the SAMPL4 blind challenge by using molecular simulations and the AMOEBA polarizable force field. The free energy results computed by Bennett's acceptance ratio (BAR) method using the AMOEBA polarizable force field ranked favorably among the entries submitted to the SAMPL4 host–guest competition [Muddana, et al., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des., 2014, 28, 305–317]. In this work we conduct an in-depth analysis of the AMOEBA force field host–guest binding thermodynamics by using both BAR and the orthogonal space random walk (OSRW) methods. The binding entropy–enthalpy contributions are analyzed for each host–guest system. For systems of inordinate binding entropy–enthalpy values, we further examine the hydrogen bonding patterns and configurational entropy contribution. The binding mechanism of this series of host–guest systems varies from ligand to ligand, driven by enthalpy and/or entropy changes. Convergence of BAR and OSRW binding free energy methods is discussed. Ultimately, this work illustrates the value of molecular modelling and advanced force fields for the exploration and interpretation of binding thermodynamics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Insights from advanced methods in molecular dynamics


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...