Rationalising pKa shifts in Bacillus circulans xylanase with computational studies†
Abstract
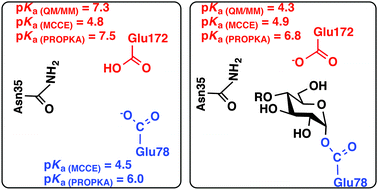
Bacillus circulans xylanase (BcX), a family 11 glycoside hydrolase, catalyses the hydrolysis of xylose polymers with a net retention of stereochemistry. Glu172 in BcX is believed to act as a general acid by protonating the aglycone during glycosylation, and then as a general base to facilitate the deglycosylation step. The key to the dual role of this general acid/base lies in its protonation states, which depend on its intrinsic pKa value and the specific environment which it resides within. To fully understand the detailed molecular features in BcX to establish the dual role of Glu172, we present a combined study based on both atomistic simulations and empirical models to calculate pKa shifts for the general acid/base Glu172 in BcX at different functional states. Its pKa values and those of nearby residues, obtained based on QM/MM free energy calculations, MCCE and PROPKA, show a good agreement with available experimental data. Additionally, our study provides additional insights into the effects of structural and electrostatic perturbations caused by mutations and chemical modifications, suggesting that the local solvation environment and mutagenesis of the residues adjacent to Glu172 establish its dual role during hydrolysis. The strengths and limitations of various methods for calculating pKas and pKa shifts have also been discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Insights from advanced methods in molecular dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...