Themed collection Emerging AI Approaches in Physical Chemistry

High-fidelity first principles nonadiabaticity: diabatization, analytic representation of global diabatic potential energy matrices, and quantum dynamics
This Perspective discusses recent advances in constructing high fidelity diabatic potential energy matrices for nonadiabatic systems and the associated quantum dynamics.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 24962-24983
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP03008F
Molecular modelling of compounds used for corrosion inhibition studies: a review
This perspective review features, among others, the use of DFT, QSAR modeling, artificial neural network (ANN) modeling, molecular dynamics simulations and Monte Carlo simulations in modelling organic corrosion inhibitors. It is a compendium of studies on the subject.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 19987-20027
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00244A
Perspective on computational reaction prediction using machine learning methods in heterogeneous catalysis
Machine learning algorithms can facilitate the reaction prediction in heterogeneous catalysis.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 11155-11179
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP01349A
Computational approaches to dissociative chemisorption on metals: towards chemical accuracy
The theoretical description of dissociative chemisorption of isolated molecules on metal surfaces is discussed. Emphasis is put on methods that deliver chemical accuracy for the dissociative chemisorption probability S0, so that Δ ≤ 1 kcal mol−1.
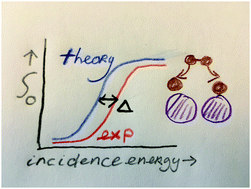
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 8962-9048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00044F
Perspective on multi-scale simulation of thermal transport in solids and interfaces
Phonon-mediated thermal transport is inherently multi-scale. The nature of multi-scale thermal transport is that there are different heat transfer physics across different length scales with strong entanglement and interaction with each other.
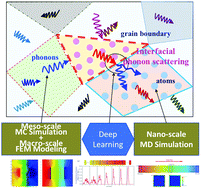
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 1785-1801
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03372C
High-throughput experimentation meets artificial intelligence: a new pathway to catalyst discovery
High throughput experimentation in heterogeneous catalysis provides an efficient solution to the generation of large datasets under reproducible conditions.
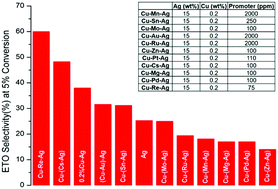
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 11174-11196
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00972E
A review of mathematical representations of biomolecular data
Recently, machine learning (ML) has established itself in various worldwide benchmarking competitions in computational biology, including Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) and Drug Design Data Resource (D3R) Grand Challenges.
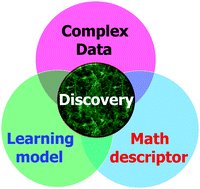
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 4343-4367
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP06554G
Temperature effects on the ionic conductivity in concentrated alkaline electrolyte solutions
Reactive molecular dynamics simulations show how ion-paring, cross-correlated ion motions and proton transfer contribute to the ionic conductivity in concentrated NaOH solutions at elevated temperatures.
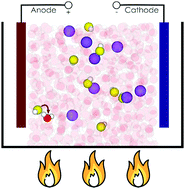
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 10426-10430
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP06479F
Electronic and thermal transport in novel carbon-based bilayer with tetragonal rings: a combined study using first-principles and machine learning approach
The structural, electronic and thermal transport characteristics of novel carbon-based bilayer tetragonal graphene are systematically explored with a combination of first-principles calculations and machine-learning interatomic potential approaches.
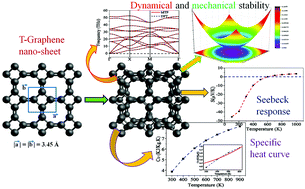
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 14608-14616
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP01423D
Determining usefulness of machine learning in materials discovery using simulated research landscapes
Simulated research landscapes are used to create data mimicking experimental datasets. We populate the landscapes with different exploration strategies, and compare them to predict the benefit of using particular machine learning-guided strategies.
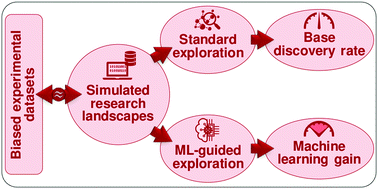
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 14156-14163
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP01761F
A general QSPR protocol for the prediction of atomic/inter-atomic properties: a fragment based graph convolutional neural network (F-GCN)
This study proposed a fragment-based graph convolutional neural network (F-GCN) that can predict atomic and inter-atomic properties and is suitable for few-shot learning.
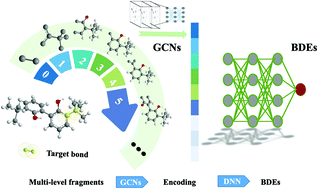
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 13242-13249
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00677K
Machine learning for reparameterization of four-site water models: TIP4P-BG and TIP4P-BGT
Two high-precision water models are established based on the combination of a back-propagation neural network and genetic algorithm.
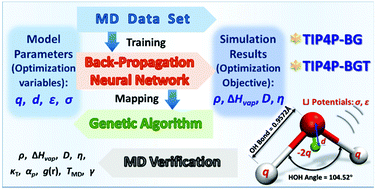
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 10164-10173
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05831A
Enhancing the analysis of disorder in X-ray absorption spectra: application of deep neural networks to T-jump-X-ray probe experiments
We demonstrate the power of our deep neural network to predict the X-ray absorption spectra of disordered systems in the presence of thermal energy.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 9259-9269
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP06244H
A neural network potential energy surface for the F + H2O ↔ HF + OH reaction and quantum dynamics study of the isotopic effect
We report here a global and full dimensional neural network potential energy surface for the F + CH4 reaction and investigate the isotopic effect on the total reaction probabilities using the time-dependent wave packet method.
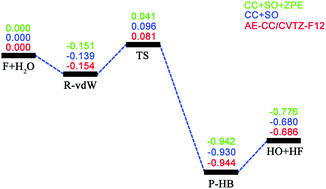
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 8809-8816
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00641J
HCl–H2O dimer: an accurate full-dimensional potential energy surface and fully coupled quantum calculations of intra- and intermolecular vibrational states and frequency shifts
The present work reports a new full-dimensional potential energy surface (PES) of the HCl–H2O dimer, and the first fully coupled 9D quantum calculations of the intra- and intermolecular vibrational states of the complex, utilizing this PES.
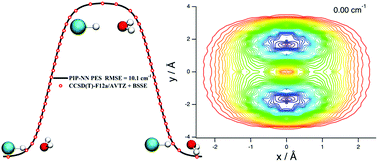
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 7101-7114
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP00865J
A new global potential energy surface of the SH2+(X4A′′) system and quantum calculations for the S+ + H2(v = 0–3, j = 0) reaction
A new global potential energy surface (PES) for the ground state of the SH2+(X4A′′) system is constructed using a permutation invariant polynomial neural network method.
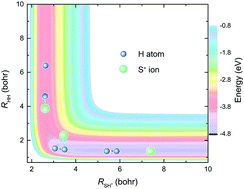
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 4757-4767
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP06335E
Quantum and classical effects in DNA point mutations: Watson–Crick tautomerism in AT and GC base pairs
Proton transfer along the hydrogen bonds of DNA can lead to the creation of short-lived, but biologically relevant point mutations that can further lead to gene mutation and, potentially, cancer.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 4141-4150
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05781A
Towards bridging the structure gap in heterogeneous catalysis: the impact of defects in dissociative chemisorption of methane on Ir surfaces
The negatively activated region in CH4 dissociation is attributed to a precursor-mediated mechanism involving surface defects.
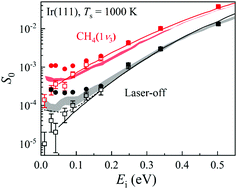
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 4376-4385
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP06535H
Machine learning approaches to understand and predict rate constants for organic processes in mixtures containing ionic liquids
Machine learning models were developed for an organic reaction in ionic liquids and validated on a selection of ionic liquids.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 2742-2752
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04227G
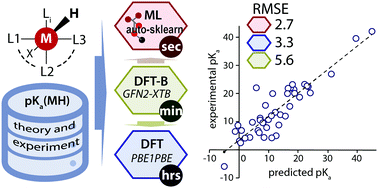
Accurate and rapid prediction of pKa of transition metal complexes: semiempirical quantum chemistry with a data-augmented approach
Data-augmented high-throughput QM approach to compute pKa of transition metal hydride complexes with hDFT accuracy and low cost.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 2557-2567
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05281G
Accelerating atomistic simulations with piecewise machine-learned ab Initio potentials at a classical force field-like cost
Combining piecewise switching functions with embedded atom neural networks to accelerate atomistic simulations with ab initio accuracy.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 1815-1821
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05089J
Modeling microsolvation clusters with electronic-structure calculations guided by analytical potentials and predictive machine learning techniques
A random-forest machine learning classifier promotes an efficiency enhancement in the DFT re-optimization of microsolvation clusters by selecting promising minimum structures that were searched by an evolutionary algorithm on an analytical PES.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 1738-1749
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05200K
A fundamental invariant-neural network representation of quasi-diabatic Hamiltonians for the two lowest states of H3
The FI-NN approach is capable of representing highly accurate diabatic PESs with particular and complicated symmetry problems.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 1082-1091
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05047D
Application and assessment of deep learning for the generation of potential NMDA receptor antagonists
In this study, we assess the application of a generative model to the NMDAR and provide source code for a variety of ligand- and structure-based assessment techniques used in standard drug discovery analyses to the deep learning-generated compounds.
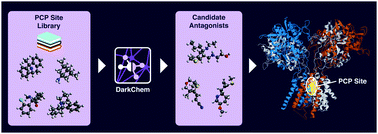
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 1197-1214
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03620J
An accurate full-dimensional potential energy surface for the reaction OH + SO → H + SO2
An accurate full-dimensional PES for the OH + SO ↔ H + SO2 reaction is developed by the permutation invariant polynomial-neural network approach.
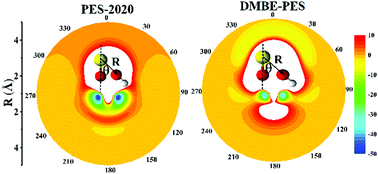
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021,23, 487-497
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP05206J
Deep learning enabled inorganic material generator
A machine learning framework that generates material compositions exhibiting properties desired by the user.
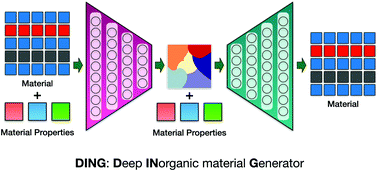
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 26935-26943
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03508D
DRACON: disconnected graph neural network for atom mapping in chemical reactions
We formulate a reaction prediction problem in terms of node-classification in a disconnected graph of source molecules and generalize a graph convolution neural network for disconnected graphs.
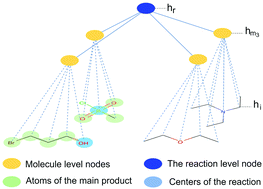
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 26478-26486
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04748A
An experimentally validated neural-network potential energy surface for H-atom on free-standing graphene in full dimensionality
We present a first principles-quality neural-network potential energy surface describing interactions for a hydrogen atom with free-standing graphene.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 26113-26120
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03462B
Artificial neural networks for the prediction of solvation energies based on experimental and computational data
We present a machine learning approach based on artificial neural networks for the prediction of ion pair solvation energies.
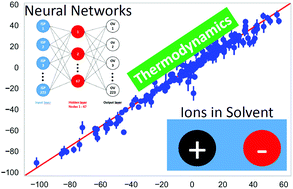
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 24359-24364
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03701J
Generating transition states of isomerization reactions with deep learning
We develop a deep learning architecture to predict 3D transition state geometries. The new method generates structures more rapidly than existing QM methods.
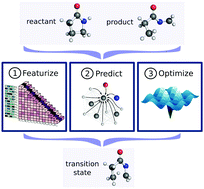
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 23618-23626
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04670A
Accurate predictions of aqueous solubility of drug molecules via the multilevel graph convolutional network (MGCN) and SchNet architectures
Deep learning based methods have been widely applied to predict various kinds of molecular properties in the pharmaceutical industry with increasingly more success.
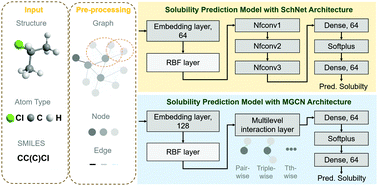
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 23766-23772
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03596C
Controlling the outcome of SN2 reactions in ionic liquids: from rational data set design to predictive linear regression models
An iterative, combined experimental and computational approach towards predicting reaction rate constants in ionic liquids is presented.
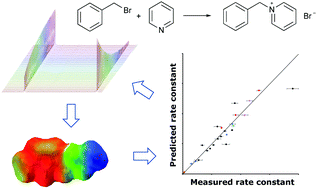
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 23009-23018
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04224B
Harnessing deep neural networks to solve inverse problems in quantum dynamics: machine-learned predictions of time-dependent optimal control fields
Deep neural networks are a cost-effective machine-learning approach for solving the inverse problem of constructing electromagnetic fields that enable desired transitions in quantum systems.
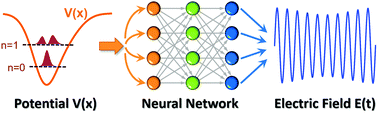
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 22889-22899
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03694C
Establishing the accuracy of density functional approaches for the description of noncovalent interactions in biomolecules
Biomolecules have complex structures, and noncovalent interactions are crucial to determine their conformations and functionalities.
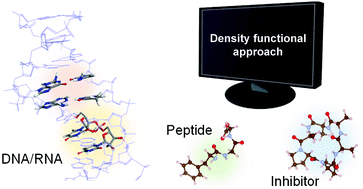
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 21685-21695
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP04137H
A machine-learning-assisted study of the permeability of small drug-like molecules across lipid membranes
Machine-learning models enable important substructure detection and property prediction for drug–membrane interactions.
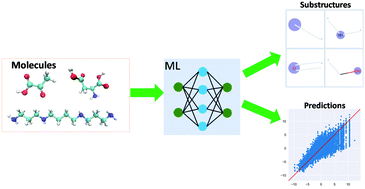
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 19687-19696
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03243C
A machine learning study of the two states model for lipid bilayer phase transitions
Machine learning algorithms can identify fluid and gel conformation states of individual lipid molecules.
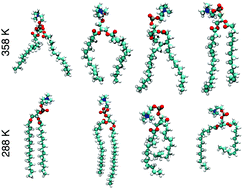
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 19147-19154
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02058C
Neural network assisted analysis of bimetallic nanocatalysts using X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy
Trained neural networks are used to extract the first partial coordination numbers from XANES spectra. In bimetallic nanoparticles, the four local structure descriptors provide rich information on structural motifs.
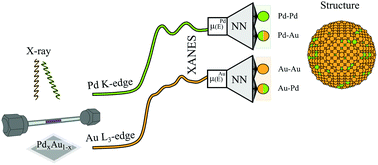
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 18902-18910
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02098B
Machine-guided representation for accurate graph-based molecular machine learning
Based on the deep metric learning, a machine-guided representation is automatically optimized for any given dataset of molecular properties.
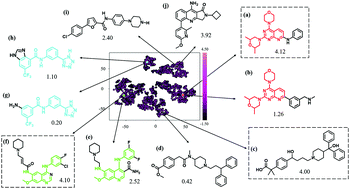
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 18526-18535
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02709J
Development of interatomic potential for Al–Tb alloys using a deep neural network learning method
The developed deep neural network (DNN) potential can describe the structural properties of the Al90Tb10 liquid and the formation energies of Al–Tb crystals with the accuracy of ab initio calculations.
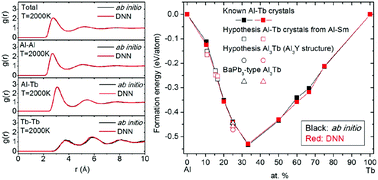
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 18467-18479
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01689F
Graph convolutional neural networks with global attention for improved materials property prediction
Graph neural networks with local and global attention mechanisms help to extract better features for materials property prediction.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 18141-18148
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01474E
Quasi-classical trajectory analysis with isometric feature mapping and locally linear embedding: deep insights into the multichannel reaction on an NH3+(4A) potential energy surface
Two manifold learning methods, isometric feature mapping and locally linear embedding, are applied to the analysis of quasi-classical trajectories for multi-channel reaction NH+ + H2 → N + H3+/NH2+ + H.
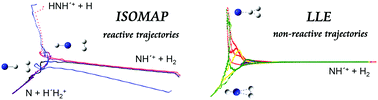
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 17460-17471
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01941K
Non-adiabatic dynamics studies of the K(4p2P) + H2(X1Σ+g) reaction based on new diabatic potential energy surfaces
The reaction and quenching processes of the K(4p2P) + H2 reaction are studied based on new diabatic PESs.
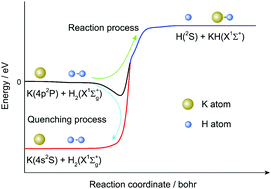
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 16203-16214
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02859B
Unified and transferable description of dynamics of H2 dissociative adsorption on multiple copper surfaces via machine learning
Schematic of the developed neural network potential energy surface enabling a unified and transferable description of dynamics of H2 dissociative adsorption on multiple copper surfaces.
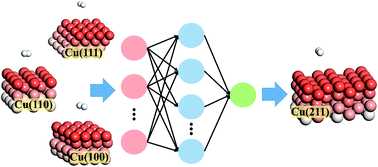
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 13958-13964
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02291H
Powerful, transferable representations for molecules through intelligent task selection in deep multitask networks
We develop and test a framework for selecting appropriate chemical datasets to create molecular representations tailored for specific tasks.
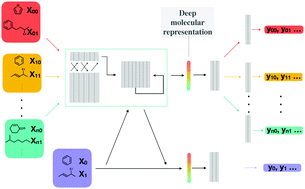
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 13041-13048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02319A
Predicting the phase diagram of titanium dioxide with random search and pattern recognition
Predicting phase stabilities of crystal polymorphs is central to computational materials science and chemistry.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 12697-12705
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP02513E
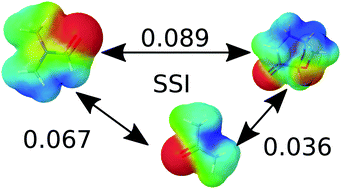
Solvent similarity index
The Solvent Similarity Index (SSI) is a quantitative parameter we introduce for the comparison of the solvation properties of any solvent or solvent mixture.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 11967-11975
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01570A
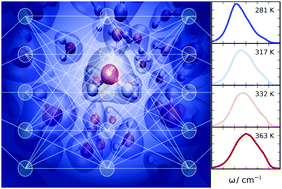
Raman spectrum and polarizability of liquid water from deep neural networks
Using deep neural networks to model the polarizability and potential energy surfaces, we compute the Raman spectrum of liquid water at several temperatures with ab initio molecular dynamics accuracy.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 10592-10602
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01893G
Quantitative structure–property relationship of the photoelectrochemical oxidation of phenolic pollutants at modified nanoporous titanium oxide using supervised machine learning
The effects of intrinsic structural properties on the photoelectrochemical oxidation of phenolic pollutants at nanoporous TiO2 are systemically studied.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8878-8888
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01518K
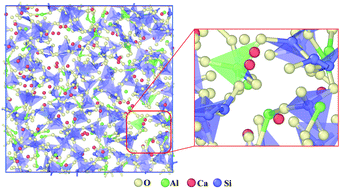
Effects of temperature on the thermal conductivity of amorphous CaO–SiO2–Al2O3 slags: a computational insight
Amorphous CaO–SiO2–Al2O3 (CSA) slags are widely used in the glass, ceramic, cement and metallurgy industries.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8808-8816
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00382D
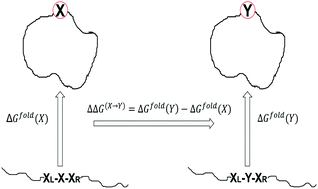
A method for efficient calculation of thermal stability of proteins upon point mutations
Illustration of the calculation process to predict the relative stability of a protein upon point mutation from residue X to Y.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8461-8466
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00835D
Thermal activation of methane by MgO+: temperature dependent kinetics, reactive molecular dynamics simulations and statistical modeling
The kinetics methane activation (MgO+ + CH4) was studied experimentally and computationally by running and analyzing reactive atomistic simulations.
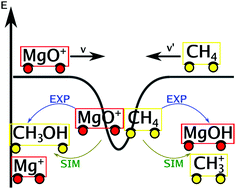
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8913-8923
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00668H
Are 2D fingerprints still valuable for drug discovery?
Recently, low-dimensional mathematical representations have overshadowed other methods in drug discovery. This work reassesses eight 2D fingerprints on 23 molecular datasets and reveals that they can perform as well as mathematical representations in tasks involving only small molecules.
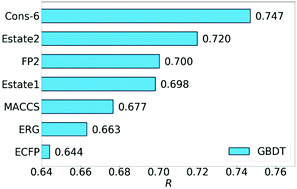
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8373-8390
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00305K
A global ab initio potential energy surface and dynamics of the proton-transfer reaction: OH− + D2 → HOD + D−
The reaction mechanisms of OH− + D2 → HOD + D− were first revealed by theory, based on an accurate full-dimensional PES.
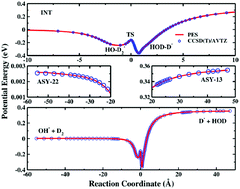
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 8203-8211
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP00107D
Equation of state of water based on the SCAN meta-GGA density functional
By ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, the newly developed SCAN meta-GGA functional is proved better than the widely used PBE-GGA functional in describing the equation of state of water.
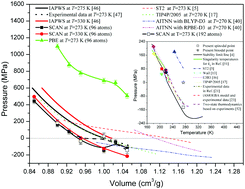
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 4626-4631
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP06362E
Biomimetic ultra-broadband perfect absorbers optimised with reinforcement learning
The reinforcement learning method of double deep-Q learning is used to design moth-eye structure-based ultra-broadband perfect absorbers with a variety of transition metals, using transfer learning to share knowledge between different environments.
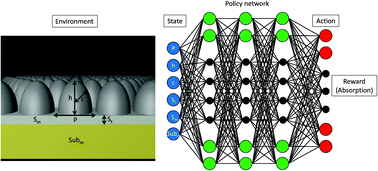
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 2337-2342
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP05621A
Automatic classification of single-molecule charge transport data with an unsupervised machine-learning algorithm
Based on unsupervised deep learning algorithms, an automatic data analysis method for single-molecule charge transport data is developed, which offers an opportunity to reveal more physical and chemical phenomena at the single-molecule level.
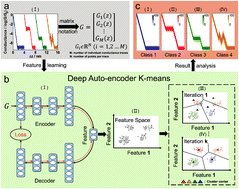
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 1674-1681
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP04496E
An accurate potential energy surface and ring polymer molecular dynamics study of the Cl + CH4 → HCl + CH3 reaction
Thermal rate coefficients for the Cl + CH4/CD4 reactions were studied on a new full-dimensional accurate potential energy surface with the spin–orbit corrections considered in the entrance channel.
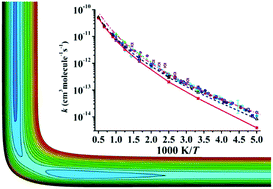
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020,22, 344-353
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP05693A