Themed collection Biomaterials Science Emerging Investigator Series

Military regenerative medicine
Amid the rising toll of war-associated deaths and injuries and escalating conflicts between countries, there is a strong need to manage complex battlefield injuries by preventing further deterioration and accelerating the repair of damaged tissues.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 6562-6571
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM01098E
Non-viral mRNA delivery to the lungs
This review highlights emerging strategies for lung-targeted mRNA delivery using non-viral vehicles, describing advances in bioinspired design and nanoparticle engineering.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2871-2882
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00322A
The case for poly(ylides) as a class of charge-neutral, hydrophilic polymers with applications in biomaterials science
Hydrophilic polymers are essential components in biomaterials science. Recent research has highlighted the use of poly(ylides) as charge-neutral, hydrophilic polymers, advocating for their classification as a standalone class of polymers.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 5481-5490
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00928B
Liquid–liquid phase separation-inspired design of biomaterials
Biological liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) provides novel insights for the assembly of biomaterials with tailored structure and intrinsic functionality.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 1943-1949
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM02008H
Nanoparticle personalized biomolecular corona: implications of pre-existing conditions for immunomodulation and cancer
The nanoparticle biomolecular corona is affected by patients’ pre-existing conditions and it should be considered when developing novel immunotherapeutics.
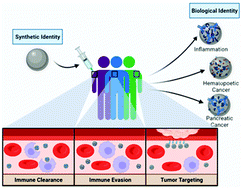
Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 2540-2549
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00315E
Advances in phenylboronic acid and phenylboronic ester-based responsive systems for precision medicine
PBA and PBE derived materials have played a crucial role in advanced healthcare technologies such as diagnostics, therapeutics and theranostics that can be useful for personalized therapies based on biomarkers of diseases.

Biomater. Sci., 2026, Advance Article
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM01624J
Fucoidan based hydrogel biomaterials for tissue engineering
This review outlines recent progress in developing fucoidan-based hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering. It summarizes structure, bioactivities and applications, and discusses key challenges and future prospects.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 6572-6597
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00676G
Current advancements in the investigation of mitochondria-targeting organic sensitizers in cancer immunotherapy
Schematic representation of the action of mitochondria-targeting organic sensitizers (MTOSs) for cancer immunotherapy by inducing multiple cell death modalities.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 5582-5604
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM01193K
Revisiting the biophysical aspects of extracellular-matrix-mimicking hydrogels: what cells see vs. what cells feel
This review revisits key properties of the extracellular matrix to be replicated in hydrogels for 3D cell culture and summarizes the interplay between hydrogel structural and mechanical properties, as well as their combined impact on cell function.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 5297-5324
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00210A
Engineered PD-L1 nanoregulators for enhanced tumor immunotherapy
This review discusses the recent developments of nanoscale regulators targeting the PD-L1 immune checkpoint pathway, highlighting innovative design strategies to boost antitumor immunity and overcome therapeutic resistance in cancer immunotherapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 4663-4680
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00748H
Multifunctional bilayer dressings: a next generation biomaterial for enhanced wound healing
Extracellular matrix mimicking bilayer wound dressings, combining hydrogels and electrospun nanofibers, offer a biomimetic approach for moisture retention, antibacterial activity, and pro-healing features for enhanced skin regeneration.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 4639-4662
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00095E
Indocyanine green-based nanomedicine for theranostic applications
This review summarizes the design strategies of ICG-based nanomedicines and explores their theranostic applications in multimodal imaging and therapy for tumors, inflammatory disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 4321-4357
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00670H
Nanomedicine in ophthalmology: conquering anatomical barriers and enhancing therapeutic efficacy
Nanocarriers enable various merits in ocular drug delivery. We review platforms like nanoparticles, micelles, suspensions, emulsions, wafers, and hydrogels, noting the need for long-term safety and clinical validation.

Biomater. Sci., 2026, Advance Article
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00325C
Ultrasound-activated inorganic nanomaterials to generate ROS for antibacterial applications
This review discusses recent progress in inorganic nanomaterials that respond to ultrasound to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) for antimicrobial applications, with the aim of inspiring the design of future novel antimicrobial agents.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2628-2641
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00121H
Micro/nanomotors for active inflammatory disease therapy
We mainly discuss the advancements of micro/nanomotors for the active therapy of a variety of inflammatory diseases, including gastrointestinal inflammation, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular inflammation, arthritis, diabetic wounds, and others.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2541-2555
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00052A
Recent advances in functional polyurethane elastomers: from structural design to biomedical applications
This review highlights the strategies for tuning the mechanical properties, self-healing capacity, and biodegradable performance of PU elastomers, as well as their latest applications in biomedicine, and looking forward to their future prospects.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2526-2540
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00122F
Electrical hydrogel: electrophysiological-based strategy for wound healing
The applications of electrical hydrogels in the healing of various types of wounds, including acute traumatic wounds, chronic infected wounds, chronic diabetic wounds, and chronic burn wounds.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2274-2296
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01734J
Polydopamine as a versatile optical indicator for colorimetric and fluorescence-based biosensing
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the advancements in the use of polydopamine-based materials for colorimetric and fluorescence-based biosensing.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2261-2273
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00084J
Membrane-intercalating conjugated oligoelectrolytes for lipid membrane imaging
Membrane-intercalating conjugated oligoelectrolytes (MICOEs), which can spontaneously integrate into lipid bilayers, are potent candidates for the next generation of biological membrane imaging probes.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1923-1938
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00028A
Extracellular vesicles as drug and gene delivery vehicles in central nervous system diseases
This review summarizes naïve extracellular vesicles (EVs) in clinical trials for central nervous system (CNS) diseases and updates recent translational preclinical research on EV-loaded drugs or genes for CNS treatments.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1161-1178
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01394H
Engineering considerations in the design of tissue specific bioink for 3D bioprinting applications
Designing tissue-specific bioinks to replicate actual tissue environments and desired biomechanical properties.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 93-129
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01192A
Design considerations and biomaterials selection in embedded extrusion 3D bioprinting
In embedded extrusion 3D bioprinting, a temporary matrix preserves a paste-like filament ejecting from a narrow nozzle.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 4506-4518
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00550C
Splittable systems in biomedical applications
Splittable systems divide active molecules into inactive parts that recombine under specific conditions for versatile biomedical uses. Applications include immunotherapy, gene editing, prodrug activation, synthetic biology, and biosensing.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 4103-4116
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00709C
Advances in 3D tissue models for neural engineering: self-assembled versus engineered tissue models
Self-assembled models offer advantages in studying neural development, but standardisation, control, and scalability are limited. Engineering hydrogel-based models to mimic native tissue structures shows promise in overcoming these challenges.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 3522-3549
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00317A
Non-viral vector-based genome editing for cancer immunotherapy
Non-viral vector-based CRISPR-Cas-mediated immunoengineering in tumor cells and immune cells for cancer immunotherapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 3068-3085
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00286E
Machine learning in nanozymes: from design to application
Nanozymes, a distinctive class of nanomaterials with enzyme-like activity and kinetics akin to enzyme-catalysed reactions, present several advantages over natural enzymes, including cost-effectiveness, heightened stability, and adjustable activity.
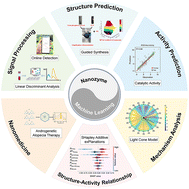
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2229-2243
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00169A
Emerging nanoparticle platforms for CpG oligonucleotide delivery
In this review, we provide a comprehensive summary of the nanoparticle-based CpG delivery systems developed to improve the efficacy of CpG-mediated immune responses.
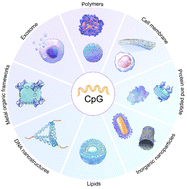
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 2203-2228
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM01970E
Research progress and perspective of metallic implant biomaterials for craniomaxillofacial surgeries
Craniomaxillofacial bone serves a variety of functions.
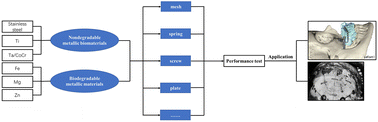
Biomater. Sci., 2024,12, 252-269
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01414A
Magnetically anisotropic hydrogels for tissue engineering
The magnetically anisotropic structure confers unique properties and promising application prospects to hydrogels in tissue engineering.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 6384-6402
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00744H
Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles for drug delivery
This review summarizes the biological function of PEVs, introduces recent applications of PEVs in targeted drug delivery and makes an outlook for the further development of utilizing PEVs for drug delivery.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5758-5768
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00893B
Microneedle-based glucose monitoring: a review from sampling methods to wearable biosensors
Microneedles are designed to mediate biofluid extraction and achieve transdermal biosensing and diagnosis.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5727-5757
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00409K
Development of organic photosensitizers for antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
This review mainly summarises the recent progress in the development of organic photosensitizers, including porphyrins, chlorophyll, phenothiazines, xanthenes and aggregation-induced emission photosensitizers, for antimicrobial photodynamic therapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 5108-5128
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00730H
Cellular modifications and biomaterial design to improve mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
Cell delivery is a major determinant of success in mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapies. Cellular modifications and biomaterial-assisted approaches can enhance the engraftment, retention, and survival of implanted cells for improved tissue repair.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 4752-4773
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00376K
Structural and componential design: new strategies regulating the behavior of lipid-based nanoparticles in vivo
This review aims to highlight the new strategies regulating the tissue distribution, cell internalization, and drug release of lipid-based nanoparticles in vivo, focusing on ways to improve their structural and componential design.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 4774-4788
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00387F
Nano-based ocular drug delivery systems: an insight into the preclinical/clinical studies and their potential in the treatment of posterior ocular diseases
A snapshot of nano-based drug delivery systems for ocular diseases in the preclinical/clinical studies and examples of novel nano-based eye drops for the treatment of posterior segment of the eye.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 4490-4507
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00505D
Modulating tumor mechanics with nanomedicine for cancer therapy
In this review, we discuss the nanomedicines that can regulate mechanical stiffness, solid stress, and IFP, with a focus on how nanomedicines change abnormal mechanical properties and facilitate drug delivery.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 4471-4489
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3BM00363A
Transferrin receptor 1 targeted nanomedicine for brain tumor therapy
This review summarizes the latest advances in TfR1-targeted nanomedicine for brain tumor therapy.
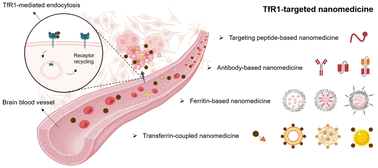
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 3394-3413
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM02152H
Glutathione peroxidase-like nanozymes: mechanism, classification, and bioapplication
This is the first comprehensive review of glutathione peroxidase-like nanozymes which discusses their mechanism, classification, and bioapplication to further develop this field.
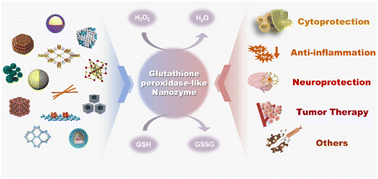
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 2292-2316
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01915A
Cellular metabolism: a link connecting cellular behaviour with the physiochemical properties of biomaterials for bone tissue engineering
This review highlights the importance of cell metabolism as a missing link connecting the cellular behavior and physicochemical properties of biomaterials and serves as a guiding principle for designing scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.
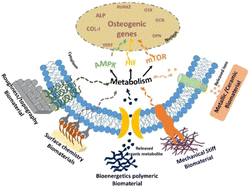
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 2277-2291
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01410F
Polymeric nanomaterial strategies to encapsulate and deliver biological drugs: points to consider between methods
Different techniques developed for the encapsulation of biological drugs within polymeric nanoparticles.

Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 1923-1947
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01594C
Current knowledge on the tissue distribution of mRNA nanocarriers for therapeutic protein expression
Review on the biodistribution of mRNA-nanocarrier in primary organs highlighting key parameters for optimal protein expression.
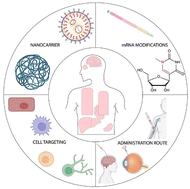
Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 6077-6115
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00859A
Surface-modified nanotherapeutics targeting atherosclerosis
Modified nanoparticles for targeting atherosclerotic overexpressed receptors.

Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 5459-5471
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00660J
Membrane-wrapped nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery
This review summarizes recent progress in the development of biomimetic, membrane-wrapped nanoparticles for targeted delivery of nucleic acids (including siRNA, pDNA, and CpG ODNs) to manage cancer.
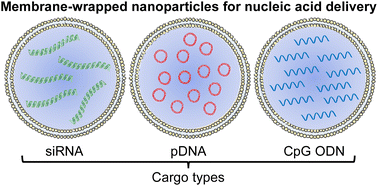
Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 4378-4391
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00447J
Antimicrobial mechanisms of biomaterials: from macro to nano
This review provides a comprehensive understanding about how different classes of biomaterials, starting from macroscale to nanoscale, interact with bacteria and viruses to exert their antimicrobial properties through diverse mechanisms of action.

Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 4392-4423
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00472K
Evaluating green solvents for sustainable PLGA nanoparticle synthesis
In this study, the use of green solvents for PLGA nanoparticle synthesis is explored as a safer and more sustainable alternative to the use of traditional solvents.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2883-2890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00374A
Laser-responsive sequential delivery of multiple antimicrobials using nanocomposite hydrogels
Precise control of antimicrobial delivery can prevent the adverse effects of antibiotics.
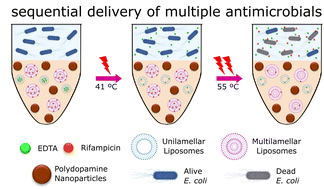
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 2330-2335
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01471H
Short term, low dose alpha-ketoglutarate based polymeric nanoparticles with methotrexate reverse rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in mice and modulate T helper cell responses
Suppressive T cells induce anti-inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) which then reverse inflammation of the joints.
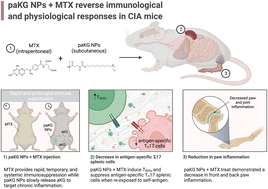
Biomater. Sci., 2022,10, 6688-6697
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00415A
On demand synthesis of calcium phosphate crystals in droplet micro-reactors of continuous operation
Biomater. Sci., 2025, Accepted Manuscript
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM01425E
The evaluation of platelet lysate incorporation into the microfracture clot in a pig model
Schematic illustration of platelet lysate incorporation, evaluated both within in vitro fibrin gels and in vivo microfracture clots.

Biomater. Sci., 2026, Advance Article
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00372E
Gelatin methacryloyl granular hydrogel scaffolds for skin wound healing
Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) granular hydrogel scaffolds (GHS) enhance cell infiltration, modulate inflammation, and improve the quality of skin tissue repair. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of GelMA GHS for wound healing.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 6013-6023
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01062K
Lung-targeting lipid nanoparticle-mediated sparstolonin B delivery improves acute lung injury
A lung-targeted sulfonium lipid nanoparticle (sLNP) formulation of sparstolonin B (SsnB) effectively inhibited inflammation and tissue injury in a murine model of LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) following intravenous administration.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 5429-5441
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00590F
Seeing deep to map cell–biomaterial interactions via whole mount light sheet imaging and automated analytics in decellularized extracellular matrix models
An optical clearing, light sheet microscopy and analysis pipeline was created for decellularized ECM (dECM)-based in vitro models. Our approach quantifies cell invasion in colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) models engineered with dECM.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 5442-5459
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00630A
Silk-based double-sided magnetic microneedles for enhanced targeted retention in the gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal-retentive drug delivery devices represent a novel oral drug delivery approach capable of significantly enhancing patient compliance and improving local drug delivery efficiency compared to conventional oral formulations.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 5460-5474
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00125K
Rapid in situ forming PEG hydrogels for mucosal drug delivery
A rapid in situ-forming, mucoadhesive PEG hydrogel was developed, offering prolonged retention in the nasal cavity and potentially other mucosal sites for drug delivery applications.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 4390-4399
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01101E
Engineering blood–brain barrier microphysiological systems to model Alzheimer's disease monocyte penetration and infiltration
We report the development of engineered human stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier microphysiological systems for modeling neuroinflammation in Alzheimers' disease.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 3650-3661
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00204D
Injectable and self-healable supramolecular hydrogels assembled by quaternised chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complexation for sustained drug delivery and cell encapsulation
Supramolecular hydrogels based on water-soluble quaternised chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complexes showed self-healing and injectable properties, a sustained release of bovine serum albumin, and enabled cell encapsulation at physiological pH.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 3617-3632
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00072F
Development of a bioactive hyaluronic acid hydrogel functionalised with antimicrobial peptides for the treatment of chronic wounds
A bioactive hyaluronic acid hydrogel is developed by conjugation of gelatin and antimicrobial peptides.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 3561-3575
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00567A
Theragenerative injectable bone-adhesive hydrogels for combined photothermal osteosarcoma therapy and bone repair
Injectable hydrogels with self-healing properties, tissue adhesion, biocompatibility, and cancer therapeutic capabilities offer a promising solution for addressing bone loss and residual tumor cells following surgical resection of osteosarcoma.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 3544-3560
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00559K
Functionalization of viscoelastic gels with decellularized extracellular matrix microparticles enhances tissue adhesion, cell spreading, and tissue regeneration
Viscoelastic gels are functionalized with decellularized ECM microparticles for tissue regeneration. This approach would be a powerful method because functional scaffolds with sufficient mechanical and biological properties facilitate tissue regeneration.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 3576-3584
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00394F
Machine-learning-guided identification of protein secondary structures using spectral and structural descriptors
We demonstrated the implementation of a machine-learning-mediated approach to identify the secondary structures of proteins based on different spectral and structural descriptors.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2973-2982
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00153F
A hypoxia-activated and tumor microenvironment-remodeling nanoplatform for augmenting sonodynamic–chemodynamic-chemotherapy of breast cancer
A hypoxia-activated and tumor microenvironment-remodeling nanoplatform is reported for effective breast cancer therapy via augmenting sonodynamic–chemodynamic-chemotherapy.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2983-2993
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00060B
Leveraging microtopography to pattern multi-oriented muscle actuators
Simple templating of actuators via micro-topographical patterning (STAMP) enables precisely patterning muscle fibers within engineered tissues, enabling fabrication of complex multi-oriented architectures such as a biomimetic iris.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2891-2907
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01017E
Gradually-frozen aligned bacterial nanocellulose membranes loaded with gallic acid exhibit enhanced mechanical and dual antithrombotic-antimicrobial properties
Microstructurally aligned gradually-frozen bacterial nanocellulose is promising for biomedical applications. While BNC lacks antibacterial or antithrombotic activity, incorporating gallic acid and glycerol results in dual antifouling properties.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2673-2689
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00176E
Controlling stimulus sensitivity by tailoring nanoparticle core hydrophobicity
This study introduces a novel and efficient approach for constructing stimulus-responsive polycarbonates with tunable stimulus sensitivity by tailoring nanoparticle core hydrophobicity.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 2332-2339
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5BM00163C
Oxidation-responsive, settable bone substitute composites for regenerating critically-sized bone defects
Traditionally used bone substitutes do not yield desired bone regeneration outcomes in critically-sized bone defects. Oxidation sensitive bone substitutes are an alternative that produce improved regeneration in large-scale bone defects.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1975-1992
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01345J
Overcoming drug delivery challenges with lipid-based nanofibers for enhanced wound repair
Wound healing is a dynamic, multi-phase process that includes haemostasis, tissue regeneration, cellular proliferation, and matrix modification.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1960-1974
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01536C
Recyclable 3D printable single network granular hydrogels
Spherical microgels can be conveniently direct ink written into granular hydrogels because of their rheological properties when jammed.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1426-1433
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00871E
Aliphatic polycarbonates with acid degradable ketal side groups as multi-pH-responsive immunodrug nanocarriers
Controled release of immunodrugs from a nanocarriers enhances their efficiacy and improves pharmacokinetics and biodistributions.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1414-1425
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM00949E
Optical fibre long-period grating sensors modified with antifouling bio-functional nano-brushes
Our study pioneers a post-modification strategy using antifouling terpolymer nano-brushes grafted onto long-period grating fibres, achieving excellent antifouling and biorecognition performance.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1199-1208
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01447B
Dimethysiloxane polymer for the effective transdermal delivery of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease treatment
We disclosed a novel transdermal donepezil delivery system using a siloxane-based polymer for Alzheimer's disease treatment.

Biomater. Sci., 2025,13, 1189-1198
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4BM01368A