Themed collection Biomaterials Science Lectureship Winners

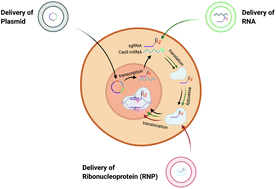
Harnessing lipid nanoparticles for efficient CRISPR delivery
Lipid-based nanomaterials have shown to mediate specific and effective CRISPR delivery in vivo for the treatment of various diseases, including cancers, genetic disorders and infectious diseases.
Biomater. Sci., 2021,9, 6001-6011
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1BM00537E
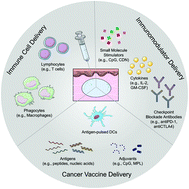
Surgery-free injectable macroscale biomaterials for local cancer immunotherapy
Up-to-date review and perspective on injectable macroscale biomaterials for local cancer immunotherapy.
Biomater. Sci., 2019,7, 733-749
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM01470A
Engineering DNA scaffolds for delivery of anticancer therapeutics
DNA scaffolds with programmability in size, shape and surface chemistry have been engineered for the delivery of various anticancer therapeutics.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1018-1024
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00459K
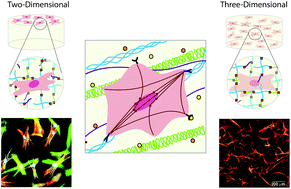
Hydrogel scaffolds as in vitro models to study fibroblast activation in wound healing and disease
Hydrogels offer controllable and well-defined in vitro platforms to study the role of the fibroblast in wound healing and fibrosis.
Biomater. Sci., 2014,2, 634-650
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3BM60319A
Recent progress in the development of near-infrared organic photothermal and photodynamic nanotherapeutics
Phototherapies including photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) have gained considerable attention due to their high tumor ablation efficiency, excellent spatial resolution and minimal side effects on normal tissue.
Biomater. Sci., 2018,6, 746-765
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7BM01210A
Supramolecular polymeric biomaterials
This review highlights how the dynamic chemistry of supramolecular polymeric hydrogels affords macroscopic properties implemented in emerging biomaterials.
Biomater. Sci., 2018,6, 10-37
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7BM00780A
Hierarchically structured hydrogels utilizing multifunctional assembling peptides for 3D cell culture
Synthetic multifunctional assembling peptides were designed to mimic the structure of collagen and allow independent control of hydrogel mechanical and biochemical properties through covalent crosslinking, enabling long-term in vitro 3D cell culture.
Biomater. Sci., 2020,8, 1256-1269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9BM01894H
Poly(glycoamidoamine) brush nanomaterials for systemic siRNA delivery in vivo
Delivery is the key challenge for siRNA based therapeutics.

Biomater. Sci., 2017,5, 38-40
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6BM00683C
MMP9-sensitive polymers mediate environmentally-responsive bivalirudin release and thrombin inhibition
Enzymatically-responsive bivalirudin polymers loaded in thermoresponsive hydrogels mediate localized therapeutic peptide delivery in spinal cord injuries. These materials respond to upregulated remodelling enzymes to release therapeutic peptide into injured tissue.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 41-45
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00259H
Subcutaneous delivery of an antibody against SARS-CoV-2 from a supramolecular hydrogel depot
Prolonged maintenance of therapeutically-relevant levels of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) is necessary to enable passive immunization against infectious disease.
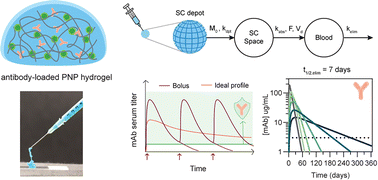
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 2065-2079
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM00819J
Development and optimization of an ocular hydrogel adhesive patch using definitive screening design (DSD)
Bioadhesive hydrogel patches based on chemically modified photocrosslinkable polymers with specific physicochemical properties for sealing and repair of ocular injuries.
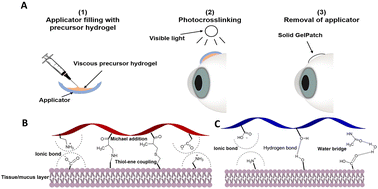
Biomater. Sci., 2023,11, 1318-1334
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2BM01013E
Ciprofloxacin-loaded bioadhesive hydrogels for ocular applications
Micelles loaded in a photocrosslinkable gelatin based hydrogel as a non-invasive suture-free approach for corneal tissue regeneration after injury with infection.
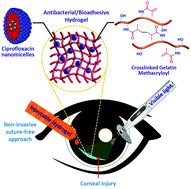
Biomater. Sci., 2020,8, 5196-5209
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0BM00935K
Biomimetic proteoglycan nanoparticles for growth factor immobilization and delivery
Growth factor delivery is often challenging due to their short half-life, low stability, and rapid deactivation. Here, we engineered novel biomimetic proteoglycan nanocarriers for the immobilization and controlled release of growth factors.
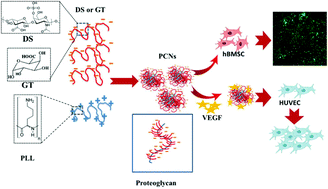
Biomater. Sci., 2020,8, 1127-1136
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9BM00668K
Redox-responsive interleukin-2 nanogel specifically and safely promotes the proliferation and memory precursor differentiation of tumor-reactive T-cells
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a potent T-cell mitogen that can adjuvant anti-cancer adoptive T-cell transfer (ACT) immunotherapy by promoting T-cell engraftment.

Biomater. Sci., 2019,7, 1345-1357
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM01556B
Interpenetrating network gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) and pectin-g-PCL hydrogels with tunable properties for tissue engineering
The design of new hydrogel-based biomaterials with tunable physical and biological properties is essential for the advancement of applications related to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
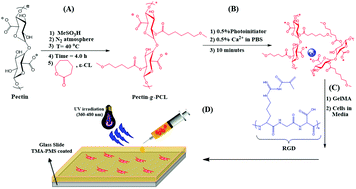
Biomater. Sci., 2018,6, 2938-2950
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM00474A
Designing well-defined photopolymerized synthetic matrices for three-dimensional culture and differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells
In this work, we establish an approach for the three-dimensional (3D) culture and differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) within well-defined synthetic matrices using light-based chemistries of relevance for the study of both disease and regeneration.
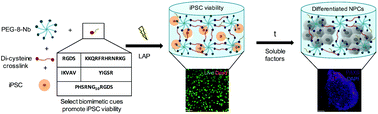
Biomater. Sci., 2018,6, 1358-1370
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM00099A
Albumin as a “Trojan Horse” for polymeric nanoconjugate transendothelial transport across tumor vasculatures for improved cancer targeting
An albumin-functionalized polymeric NC (Alb-NC) capable of crossing the endothelium barrier through a caveolaemediated transcytosis pathway to better target cancer is reported.
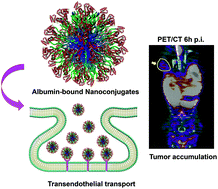
Biomater. Sci., 2018,6, 1189-1200
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM00149A
In vitro and in vivo analysis of visible light crosslinkable gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels
Engineering visible light crosslinked GelMA hydrogels with tunable physical properties.
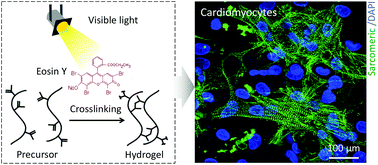
Biomater. Sci., 2017,5, 2093-2105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7BM00110J
Iodine-131-labeled, transferrin-capped polypyrrole nanoparticles for tumor-targeted synergistic photothermal-radioisotope therapy
Tumor-targeting nanoparticles based on transferrin-capped polypyrrole are fabricated by a one-step approach for combination cancer therapy with a remarkable synergistic therapeutic effect.

Biomater. Sci., 2017,5, 1828-1835
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7BM00409E
Effects of the poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel crosslinking mechanism on protein release
Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel crosslinking mechanism has a differential effect on controlling protein release.
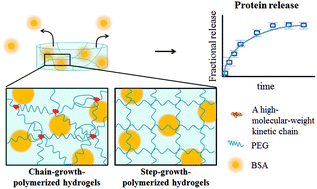
Biomater. Sci., 2016,4, 405-411
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00256G
Reducible, dibromomaleimide-linked polymers for gene delivery
Reducible, dibromomaleimide-linked polycations exhibit reduced cytotoxicity compared to their non-degradable analogs and can be site-specifically functionalized.
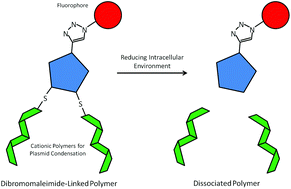
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 112-120
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00240G
Design of thiol–ene photoclick hydrogels using facile techniques for cell culture applications
Thiol–ene photoclick hydrogels with tunable biomechanical and biochemical properties for biological applications, including controlled cell culture, regenerative medicine, and drug delivery.
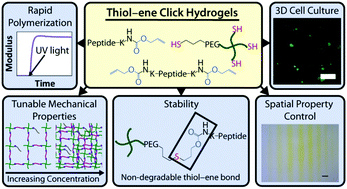
Biomater. Sci., 2014,2, 1612-1626
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00187G
Controllably degradable β-sheet nanofibers and gels from self-assembling depsipeptides
Inserting an ester bond into self-assembling peptides generated controllably degradable nanofibers and hydrogels for 3D cell culture.
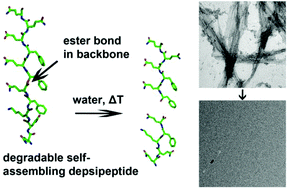
Biomater. Sci., 2013,1, 1037-1045
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3BM60161G
Comparative study of guanidine-based and lysine-based brush copolymers for plasmid delivery
Guanidinylated HPMA-co-oligolysine copolymers exhibit higher transfection efficiency to cultured cells than analogous lysine-based polymers for nucleic acid delivery.
Biomater. Sci., 2013,1, 736-744
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3BM60079C
Synthetic hydrogel platform for three-dimensional culture of embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons
Presented is an engineered PEG hydrogel capable of supporting the viability and subsequent axon extension of encapsulated mouse embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons in 3D.
Biomater. Sci., 2013,1, 460-469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3BM00166K
About this collection
This collection highlights winners of the Biomaterials Science Lectureship. This annual award was established in 2014 to honour an early-stage career scientist who has made a significant contribution to the biomaterials field.
The 2025 Biomaterials Science Lectureship was awarded to Li Tang (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne, Switzerland)
Li Tang received his B.S. in Chemistry from Peking University, China, in 2007, and Ph.D. in Materials Science and Engineering from University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, in 2012, under the supervision of Prof. Jianjun Cheng. He was a CRI Irvington Postdoctoral Fellow in the laboratory of Prof. Darrell Irvine at Massachusetts Institute of Technology during 2013-2016. He joined the faculty of Institute of Bioengineering, and Institute of Materials Science & Engineering, at École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland, as a Tenure-Track Assistant Professor in 2016, and promoted to Associate Professor with tenure in 2022. He is also the Vice Dean for Innovation, and Director of Innovate4Life program at School of Life Sciences, EPFL.
His research focuses on developing multidimensional immunoengineering approaches for enhanced cancer immunotherapies. Dr. Tang is the recipient of Friedrich Miescher Award (2025) from Life Sciences Switzerland (LS2), Leenaards Prize for Translational Medical Research (2025), Biomaterials Science Lectureship (2025), CAB Mid-Career Investigator Award (2024), Biomaterials Award for Young Investigators (2024), Cancer Research Institute CLIP Award (2021), Anna Fuller Award (2021 and 2022), European Research Council (ERC) Starting Grant Award (2018), and named in the MIT Technology Review’s "Top 35 Innovators under Age 35" list of China region (2020).
This collection features articles published in Biomaterials Science from Li Tang as well as the previous lectureship winners:
2023- Eric Appel, Stanford University, USA
2022- Yizhou Dong, The Ohio State University, USA
2021- Nasim Annabi, University of California, USA
2020 – Kanyi Pu, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
2019 - April Kloxin, University of Delaware, USA
2018 - Zhen Gu, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill & North Carolina State University, USA
2017 - Zhuang Liu, Foochow University, China
2016 – Fan Yang, Stanford University, USA
2015 – Joel Collier, Duke University, USA
2014 – Suzie Pun, University of Washington, USA