Themed collection Editors' collection: Environmental chemistry: Pollution control

Regeneration performance of clay-based adsorbents for the removal of industrial dyes: a review
The present review covers the regeneration capacity and adsorption efficiency of different adsorbents for the treatment of industrial dyes to control water pollution.
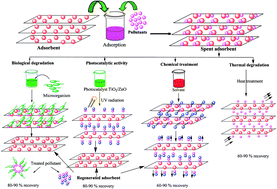
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 24571-24587
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA04290J
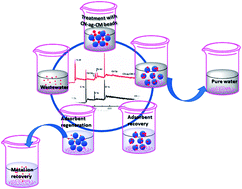
Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using layered double hydroxide derived adsorbents, a critical review
This paper provides a review of the currently available literature focusing on arsenic removal using LDHs.
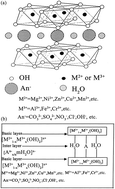
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 22694-22709
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03647K
Adsorptive environmental applications of MXene nanomaterials: a review
Due to their large specific surface area and abundant active surficial sites, MXenes can adsorb various environmental pollutants.
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 19895-19905
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03077D
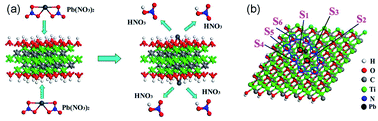
Synthesis and application of pillared clay heterogeneous catalysts for wastewater treatment: a review
The use of pillared interlayered clays (PILCs) as heterogenous catalysts in wastewater treatment technologies, particularly advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), is gaining popularity for the treatment of refractory wastewater effluents.
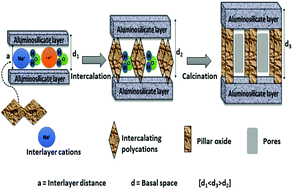
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 5197-5211
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA12924F
Investigation of novel nanomaterial for the removal of toxic substances from contaminated water
Preparation of novel nanosphere material for efficient capture of toxic substances. The nanosphere material was systematically investigated for the capture of a toxic substance. The material displayed high sensitivity with high adsorption efficiency.
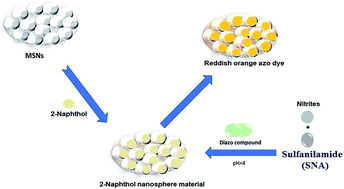
RSC Adv., 2019,9, 14167-14175
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00383E
Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from wastewater using arginine cross-linked chitosan–carboxymethyl cellulose beads as green adsorbent
Remediation of Pb(II) and Cd(II) containing wastewater by arginine crosslinked chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose beads.
RSC Adv., 2019,9, 7890-7902
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00356H
Parameter optimization and degradation mechanism for electrocatalytic degradation of 2,4-diclorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) herbicide by lead dioxide electrodes
Optimization of process parameters by the CCD method and electrocatalytic degradation and the electrochemical degradation mechanism of 2,4-D using modified electrode anodes were investigated.
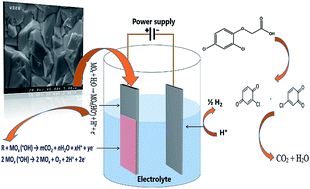
RSC Adv., 2019,9, 5064-5075
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA10105A
Development and application of novel bio-magnetic membrane capsules for the removal of the cationic dye malachite green in wastewater treatment
Novel bio-magnetic membrane capsules were prepared by a simple two-step titration-gel cross-linking method using a polyvinyl alcohol and sodium alginate matrix to control the disintegration of phytogenic magnetic nanoparticles in aqueous media.

RSC Adv., 2019,9, 3625-3646
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09275C
Functionalized biochar-supported magnetic MnFe2O4 nanocomposite for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
In this study, a novel magnetic biochar-MnFe2O4 nanocomposite (BC/FM) was prepared using low-cost corn straw and MnFe2O4 by sol–gel/pyrolyzing route using egg white, which has abundant functional groups (–NH2 and –COOH).
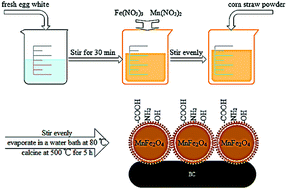
RSC Adv., 2019,9, 365-376
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09061K
Photocatalytic decontamination of phenol and petrochemical wastewater through ZnO/TiO2 decorated on reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite: influential operating factors, mechanism, and electrical energy consumption
ZnO/TiO2 anchored on a reduced graphene oxide (rGO) ternary nanocomposite heterojunction was synthesized via the multi-step method including hydrothermal, solvothermal and sol–gel methods.

RSC Adv., 2018,8, 40035-40053
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA07936F
Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet dye and electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid using a BiVO4/FeVO4 heterojunction composite
A highly pure BiVO4/FeVO4 heterojunction nanocomposite photocatalyst was synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. The simple and economical manufacturing process allows easier industrial scale-up and the results contribute to the design of more effective photocatalysts.
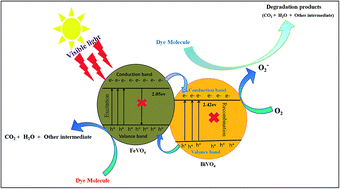
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 23489-23498
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03890B
Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by cattle manure-derived low temperature biochar
Biochar is a kind of low cost and renewable adsorbents which can be used to remove dye from wastewater. The mechanism between MB and CMB involved cation exchange, electrostatic interaction, hydrogen bonding, physical function and others.

RSC Adv., 2018,8, 19917-19929
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA03018A
Comparative photocatalytic activity of sol–gel derived rare earth metal (La, Nd, Sm and Dy)-doped ZnO photocatalysts for degradation of dyes
In this study, we compared the photocatalytic activity of sol–gel derived rare earth metal (La, Nd, Sm and Dy)-doped ZnO photocatalysts by studying the degradation of MB and RhB under UV light irradiation.
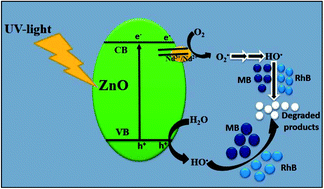
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 17582-17594
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01638K
Efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from water by an adsorption–reduction mechanism with sandwiched nanocomposites
A sandwiched nanocomposite has been developed to remove hexavalent chromium ion Cr(VI) from water by an adsorption–reduction mechanism.

RSC Adv., 2018,8, 15087-15093
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01805G
Polysulfides made from re-purposed waste are sustainable materials for removing iron from water
A polymer prepared by co-polymerisation of sulfur and canola oil removed Fe3+ from water. Microwave irradiation was convenient in promoting the polymerisation.
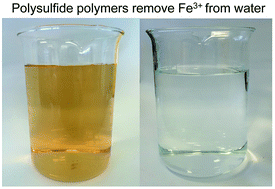
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 1232-1236
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA11999B
Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue by reduced CuFe2O4
CuFe2O4 was reduced for activation of hydrogen peroxide and the reduced CuFe2O4 showed a relatively higher catalytic activity.
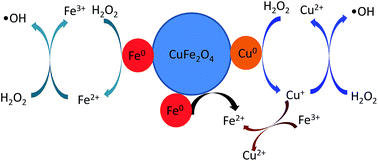
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 1071-1077
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA12488K
Highly improved visible-light-induced photocatalytic performance over BiOI/Ag2CO3 heterojunctions
The heterojunctions between BiOI and Ag2CO3 obviously improved visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity compared with separate BiOI and Ag2CO3 particles.
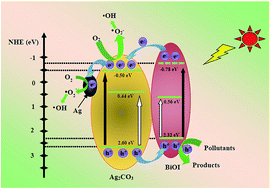
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 537-546
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA10423E
Schiff base-functionalized mesoporous silicas (MCM-41, HMS) as Pb(II) adsorbents
MCM-41@salen, HMS-C12@salen and HMS-C16@salen sorbents present high sorption capacities for Pb(II) and are suitable materials for the removal of Pb(II).
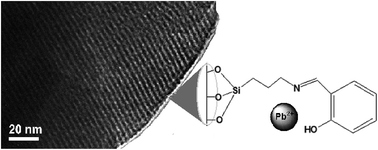
RSC Adv., 2018,8, 176-189
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA12310H
About this collection
This collection, guest-edited by RSC Advances Associate Editor Professor Feng Zhao (Institute of Urban Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences) features articles on the theme 'pollution control', illustrating the notability, quality and variety of publications in RSC Advances. These articles are already among the most highly cited research articles in the journal, illustrating their impact. Subject areas include absorptive materials, photocatalytic materials, bio-magnetic membranes and method development.