Themed collection Polymer Chemistry Lectureship Winners

From plastic waste to new materials for energy storage
A perspective on using plastic waste as an alternative feedstock for the energy storage sector through upcycling. Materials for electrodes, electrolytes or binders could be obtained from both advanced combustion and depolymerization methods.
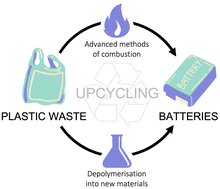
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 4222-4229
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00592A
Poly(hydroxy acids) derived from the self-condensation of hydroxy acids: from polymerization to end-of-life options
Poly(hydroxy acids) derived from the self-condensation of hydroxy acid are biodegradable and can be fully recycled in a Circular Economy approach.
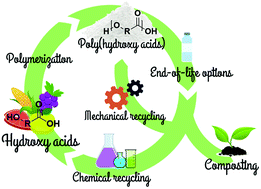
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 4861-4874
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00088D
Aziridines and azetidines: building blocks for polyamines by anionic and cationic ring-opening polymerization
The synthesis of aziridine and azetidine monomers and their ring-opening polymerization via different mechanisms is reviewed.
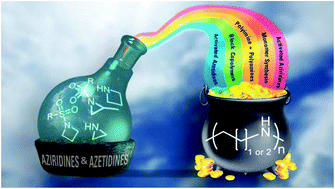
Polym. Chem., 2019,10, 3257-3283
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PY00278B
Organocatalysis for depolymerisation
Chemical recycling of plastics offers a green method to deal with plastic waste. In this review, we highlight the recent advances made by applying organocatalysts to chemically degrade polymers as a promising tool to reach a circular plastic economy.
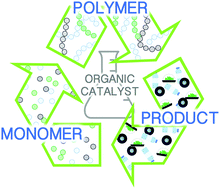
Polym. Chem., 2019,10, 172-186
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8PY01284A
Educational series: characterizing crosslinked polymer networks
Characterization of polymer networks presents unique challenges due to the insolubility of the materials, but this also enables characterization by new techniques that take advantage of the bulk network structure.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 219-247
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00914A
Educational series: turning monomers into crosslinked polymer networks
Multifunctional monomers enable the synthesis of polymer networks by adapting the polymerization methods used for conventional linear polymer synthesis.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 4503-4514
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00912B
Upcycling of BPA-PC into trimethylene carbonate by solvent assisted organocatalysed depolymerisation
This study describes the solvent-assisted organocatalysed depolymerisation of BPA-PC at low temperature for the selective formation of trimethylene carbonate. The key role of 1-methylimidazole as solvent and imidazole as catalyst is investigated.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 2299-2307
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00441D
Dual encryption of digital information in a tough fluorescent hydrogel
We report a photoresponsive hydrogel for dual information encryption including shape and pattern encryptions with adjustable mechanical properties and emissions.
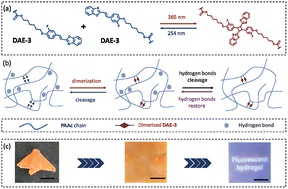
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 6255-6260
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY01295B
Macrocyclization efficiency for poly(2-oxazoline)s and poly(2-oxazine)s
Poly(2-oxazine)s show higher tendency to undergo macrocyclization compared to poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s, increasing scale-up potential and applicability of these cyclic polymers.
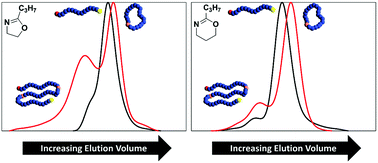
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 3975-3980
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00376G
Mechanism insights in controlling host–guest (de)complexation by thermoresponsive polymer phase transitions
The hydrophobic interactions involved in phase separation of LCST polymers are the critical factor inducing the BBox release from the BBox/naphthalene while the host-guest complexes remain stable during phase separation of UCST polymers upon cooling.
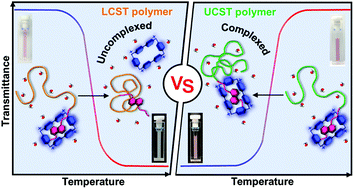
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 3742-3749
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00219A
A pillar[5]arene-based 3D polymer network for efficient iodine capture in aqueous solution
A pillar[5]arene-based 3D polymer network is constructed. It possesses good stability, recyclability and high efficiency in iodine capture in aqueous solution.
![Graphical abstract: A pillar[5]arene-based 3D polymer network for efficient iodine capture in aqueous solution](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D1PY00535A&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2021)
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 3517-3521
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00535A
Substituent effects in iniferter photopolymerization: can bond homolysis be enhanced by electronics?
Substituent effects on the dithiobenzoate moiety of RAFT iniferters are investigated. Donating groups accelerate the iniferter process, while withdrawing groups slow it. The unique efficiency of the methoxydithiobenzoate iniferter was uncovered.
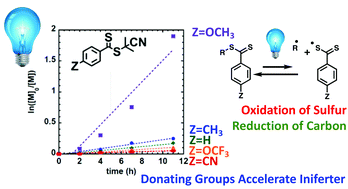
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 6129-6133
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01086C
Tailoring polymer dispersity by mixing chain transfer agents in PET-RAFT polymerization
Here we report a simple and versatile batch methodology to tailor polymer dispersity utilizing PET-RAFT polymerization.
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 4968-4972
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00823K
Aminolytic upcycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) wastes using a thermally-stable organocatalyst
We report the potential of thermally stable acid-base mixtures for the upcycling of PET in the presence of amines.
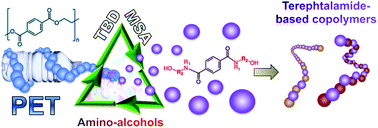
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 4875-4882
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00067A
3D printing of polymeric materials based on photo-RAFT polymerization
For the first time, we report 3D printing of RAFT-based formulations to fabricate functional objects in a layer-by-layer fashion.

Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 641-647
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PY01419E
Synthesis of defined high molar mass poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline)
In this communication, we report for the first time the synthesis of defined high molar mass poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline) (PMeOx), a water-soluble polymer with excellent anti-fouling properties.
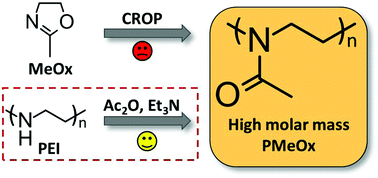
Polym. Chem., 2019,10, 1286-1290
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9PY00013E
Highly tunable polyurethanes: organocatalyzed polyaddition and subsequent post-polymerization modification of pentafluorophenyl ester sidechains
A facile method for the synthesis of high molecular weight functionalized polyurethanes from a novel pentafluorophenyl ester-containing diol precursor is described.
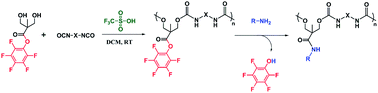
Polym. Chem., 2014,5, 3547-3550
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PY00262H
Synthesis of functionalized cyclic carbonate monomers using a versatile pentafluorophenyl carbonate intermediate
Functionalized cyclic carbonate monomers were synthesized via a two step route featuring a novel cyclic carbonate intermediate possessing a pendent activated pentafluorophenyl carbonate group (MTC-PFPC).

Polym. Chem., 2014,5, 327-329
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3PY01128C
Ring-opening polymerisation of alkyl-substituted ε-caprolactones: kinetic effects of substitution position
Alkyl-functional polycaprolactones were prepared via direct and well-controlled ring-opening polymerisation and the relationship between the substituent position and polymerisation rate was investigated.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 1227-1233
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY01380D
Biodegradable mPEG-b-poly(MDO-co-vinyl esters) block copolymers as a viable nanocarrier platform with tuneable disassembly
Xanthate-based copolymerisations of MDO and vinyl acetate-derivative monomers using a mPEG macroCTA created degradable amphiphilic block copolymers capable of self-assembly and crosslinking, where type of crosslinking influenced particle disassembly.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 1152-1165
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4PY00049H
Rate retardation trends in RAFT – an emerging monomer classification tool?
The RAFT rate retardation effect is used to classify monomers according to their reactivity. The stability of the radical correlates inversely with the extent of retardation allowing a framework for classifying monomer reactivity to be established.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 1052-1061
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY01332D
Exploring high molecular weight vinyl ester polymers made by PET-RAFT
Polyvinyl esters are used in many applications, however, high molecular weight polyvinyl esters have many challenges, with strategies for the synthesis of these polymers being the focus of this work.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 868-877
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4PY00065J
A combined computational and experimental study of metathesis and nucleophile-mediated exchange mechanisms in boronic ester-containing vitrimers
The mechanism of bond exchange in boronic-ester containing vitrimers is shown to occur by either direct metathesis or a nucleophile mediated mechanism, which can be used advantageously to give orders of magnitude increase in exchange dynamics.

Polym. Chem., 2024,15, 181-192
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY01047C
Controlled photodegradation of phenyl vinyl ketone polymers by reinforcement with softer networks
Polymer networks based on phenyl vinyl ketone were synthesized. The introduction of a second network enhanced the control over the material's photodegradation, as well as modulating the mechanical properties.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 4160-4168
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00217A
Preparation and structure–property relationship of flexible aramid films with enhanced strength by introducing asymmetric and symmetric aromatic ether bond structures
The flexible molecular segments and aggregated structures of MAPB–PMIA and PAPB–PMIA endow polymers with soft properties with high extension and low modulus.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 3906-3915
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00525A
Polyhydroxyurethane covalent adaptable networks: looking for suitable catalysts
Various bases (DMAP, DBU, TBD, t-BuOK), acid (p-TSA), thiourea (TU) and organometallic Lewis acid (DBTDL) were investigated as potential catalysts for the preparation of polyhydroxyurethane covalent adaptable networks.
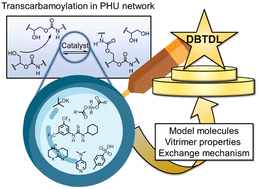
Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 3610-3620
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00579H
Insights into the interaction between bis(aryloxide)alkylaluminum and N-heterocyclic carbene: from an abnormal Lewis adduct to a frustrated Lewis pair for efficient polymerizations of biomass-derived acrylic monomers
This contribution reports the development of a new and stable frustrated Lewis pair catalyst which is general for efficient/controlled polymerizations of inert biomass-derived acrylic monomers.
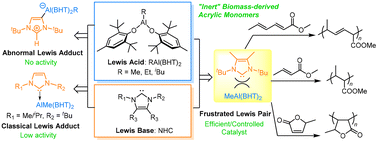
Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 3286-3293
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00546A
Amidation of methyl ester-functionalised poly(2-oxazoline)s as a powerful tool to create dual pH- and temperature-responsive polymers as potential drug delivery systems
We present the synthesis of different amine-functionalised poly(2-oxazoline)s, their dual pH and temperature response as well as their capability to as promising stimuli responsive drug delivery vectors.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 2034-2044
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00050H
Degradable vinyl polymer particles by radical aqueous emulsion copolymerization of methyl methacrylate and 5,6-benzo-2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane
Aqueous emulsion copolymerization of methyl methacrylate (MMA) and 5,6-benzo-2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane (BMDO) leads to stable particles of PMMA bearing in-chain ester units that can be cleaved under basic conditions.

Polym. Chem., 2023,14, 1224-1231
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3PY00040K
Moisture tolerant cationic RAFT polymerization of vinyl ethers
Cationic RAFT of vinyl ethers was performed without reagent purification and under ambient conditions by utilizing a PCCP acid initiator with a HBD catalyst. Despite inherent nucleophiles, the system retained high chain end fidelity and modularity.
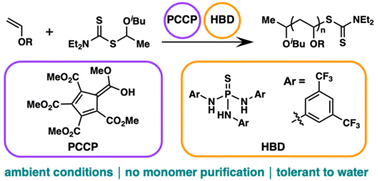
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 5974-5979
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00780K
A dual initiator approach for oxygen tolerant RAFT polymerization
A broadly applicable approach to oxygen tolerant RAFT polymerization is reported by leveraging the synergistic combination of two radical initiators to provide temporal control over radical flux during polymerization.
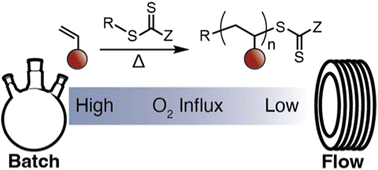
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 4798-4808
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00603K
Network polymers incorporating lipid-bilayer disrupting polymers: towards antiviral functionality
Polymer based solid-state materials capable of disrupting lipid-bilayers are developed. The materials are mechanically robust and capable of outperforming a 10% small-molecule surfactant and modify filter materials.
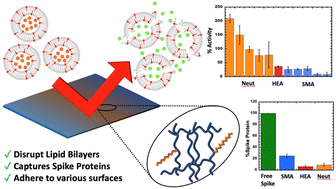
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 4547-4556
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00602B
Stimuli-responsive and core cross-linked micelles developed by NiCCo-PISA of helical poly(aryl isocyanide)s
Spherical micelles with a helical core synthesised by NiCCo-PISA are functionalised with different cross-linkers to make stimulus-sensitive nanostructures.

Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 4047-4053
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00397J
Interpenetrated triple network polymers: synergies of three different dynamic bonds
Triply interpenetrated networks were made with a unique dynamic linker in each network. The linkers were hydrogen bonds, boronic esters and Diels–Alder adducts. Triply dynamic materials had superior properties compared to doubly dynamic analogues.
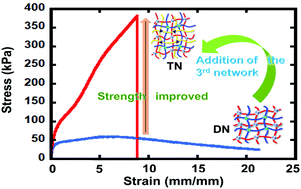
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 3705-3712
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00575A
Design of selective divalent chain transfer agents for coordinative chain transfer polymerization of ethylene and its copolymerization with butadiene
A selective divalent chain transfer agent is designed to exclusively lead to polyolefin chain growth on a divalent pentanediyl moiety via coordinative chain transfer polymerization (CCTP).

Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 1970-1977
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2PY00155A
A unified kinetic Monte Carlo approach to evaluate (a)symmetric block and gradient copolymers with linear and branched chains illustrated for poly(2-oxazoline)s
Kinetic modeling is used to verify if PAOx synthesis routes can deliver ideal products such as (a)symmetric (block-)gradients and block copolymers. It is shown that a variation in chain length and topology affects the overall compositional deviation.
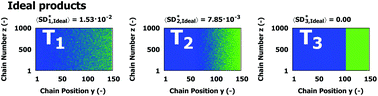
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 1559-1575
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01391B
A general model for the ideal chain length distributions of polymers made with reversible deactivation
A general model is developed for the distribution of polymers made with reversible deactivation. The model is applied to a range of experimental systems including RAFT, cationic and ATRP.
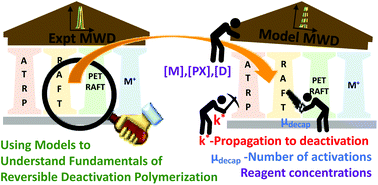
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 898-913
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01331A
Differences and similarities between mono-, bi- or tetrafunctional initiated cationic ring-opening polymerization of 2-oxazolines
Cationic ring-opening polymerization (CROP) is an interesting synthesis technique to obtain well-defined polymers with narrow molar mass distribution (MMD).
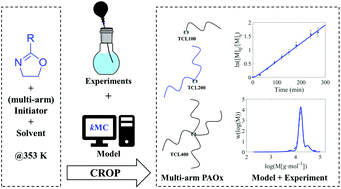
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 861-876
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01471D
Hybrid copolymerization of acrylate and thiirane monomers mediated by trithiocarbonate
The composition and structure of polymers have great influence on their performances.

Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 402-410
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01031J
Electroactive 3D printable poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-graft-poly(ε-caprolactone) copolymers as scaffolds for muscle cell alignment
Graft copolymers between conducting PEDOT and biodegradable PCL were synthesized and investigated for 3D printing scaffolds for patterning of muscle cells.
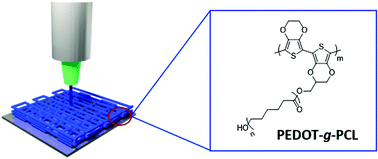
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 109-120
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01185E
Controlling mechanical properties of 3D printed polymer composites through photoinduced reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) polymerization has been exploited to design silica-nanoparticle-incorporated photocurable resins for 3D printing of materials with enhanced mechanical properties and complex structures.
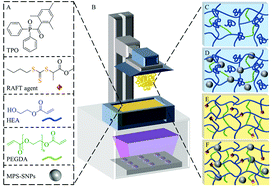
Polym. Chem., 2022,13, 44-57
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01283E
Releasable antimicrobial polymer-silk coatings for combating multidrug-resistant bacteria
Controlled release of synthetic cationic antimicrobial polymers from silk-based coating for preventing bacterial biofilm formation on the surface and for killing planktonic bacteria cells.
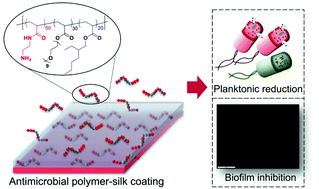
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 7038-7047
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01219C
PNIPAM-immobilized gold-nanoparticles with colorimetric temperature-sensing and reusable temperature-switchable catalysis properties
The temperature-responsive core–shell hybrid nanoparticles PNIPAMs-AuNP have dual-functional applications as colorimetric temperature-sensors and reusable temperature-switchable catalysts.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6903-6913
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01180D
Effect of heterogeneous and homogeneous polymerisation on the structure of pNIPAm nanogels
The choice of the polymerisation temperature and initiator in the synthesis of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based nanogels can significantly influence their structure, morphology and thermoresponsive properties.
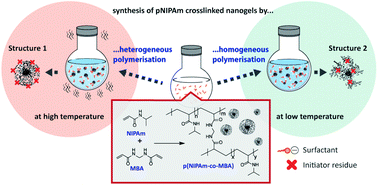
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6854-6864
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01333E
Tuning the molecular weight distributions of vinylketone-based polymers using RAFT photopolymerization and UV photodegradation
The choice and mixture of chain transfer agent in reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer polymerization has been used to modulate the dispersity and architecture of vinyl ketone polymers and their copolymers.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6761-6770
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01129D
Screening RAFT agents and photocatalysts to mediate PET-RAFT polymerization using a high throughput approach
We report a high throughput approach for the screening of RAFT agents and photocatalysts to mediate photoinduced electron/energy transfer-reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (PET-RAFT) polymerization.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6548-6560
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01258D
High-performance polyamides with engineered disorder
Introducing molecular scale defects into semiaromatic polyamides by high-temperature melt compounding with aliphatic polyamides provides a simple means of tailoring the balance of microstructural order and disorder in these materials and achieving unusual property profiles.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6426-6435
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01225H
Development of physical, mechanical, antibacterial and cell growth properties of poly(glycerol sebacate urethane) (PGSU) with helping of curcumin and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles
Biocompatible and antimicrobial elastomers with controlled hydrophilicity and degradation rate, as well as appropriate stiffness and elasticity, are interesting for biomedical applications, such as regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
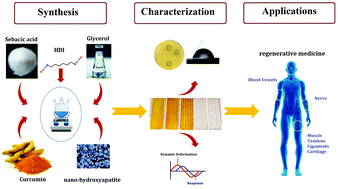
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 6263-6282
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01040A
Effect of hydrophilic groups on the bioactivity of antimicrobial polymers
Antimicrobial polymers have recently been investigated as potential treatments to combat multidrug-resistant pathogens.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 5689-5703
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY01075A
Thermoresponsive properties of polyacrylamides in physiological solutions
We show that the cloud point temperature (TCP) of thermoresponsive polyacrylamides is considerably lower in physiologically relevant solvents (phosphate-buffered saline, serum) than in pure water. This decrease of TCP may be critical for some biomedical applications.
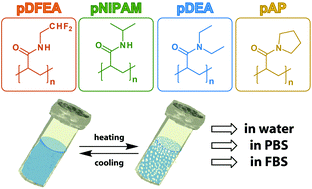
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 5077-5084
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00843A
Achieving molecular weight distribution shape control and broad dispersities using RAFT polymerizations
Metered additions of chain transfer agents are used to control molecular weight distribution (MWD) features in reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer polymerizations, giving polymers with tailored MWD shapes and dispersities as high as 6.2.
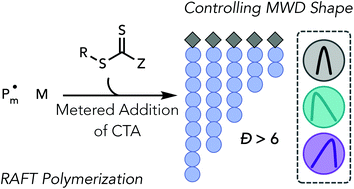
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 4910-4915
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00399B
Synthetic lignin-like and degradable nanocarriers
Bio-based lignin-like building blocks were synthesized and transformed into polyurethane nanocarriers by interfacial polymerization in a miniemulsion. The nanocarriers were degradable by fungal enzymes and might be used for agrochemical delivery.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 4661-4667
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00818H
Novel imino- and aryl-sulfonate based photoacid generators for the cationic ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactone
The use of photoacid generators for the ring opening polymerization of cyclic esters is investigated.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 4035-4042
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00734C
Methionine-based carbon monoxide releasing polymer for the prevention of biofilm formation
A new water-soluble methionine-based CO releasing polymer shows slow and spontaneous release of CO with sustained-release kinetics, preventing biofilm formation against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
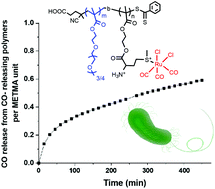
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 3968-3975
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00546D
Molecular tailoring of trifluoromethyl-substituted conjugated polymers for efficient organic solar cells
This work reports a series of novel trifluoromethylated polymers as efficient donor materials for high-performance OSCs.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 3346-3351
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00177A
Polymer defect engineering – conductive 2D organic platelets from precise thiophene-doped polyethylene
Synthesis and crystallization of polyethylene with precisely positioned thiophene groups were used to produce polymer crystals with a conductive surface.
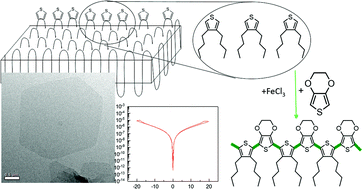
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 2045-2053
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00117E
Dynamic covalent chemistry for architecture changing interpenetrated and single networks
Dynamic single and interpenetrated materials were developed, with post polymerization network exchange enhancing the material properties.
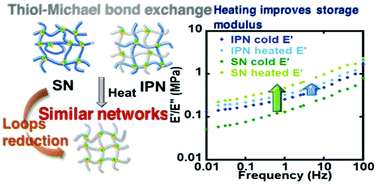
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 1975-1982
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1PY00198A
Controlling the crystallinity and solubility of functional PCL with efficient post-polymerisation modification
Varying the size of an alkyl side-chain group, installed by thiol–ene addition of alkylthiols to poly(ε-allyl caprolactone), the semi-crystallinity and lipophilicity of functional PCLs could be modulated to achieve divergent physico-chemical properties.
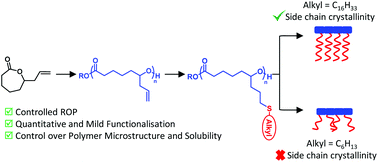
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 1983-1990
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01535K
Organocatalyzed closed-loop chemical recycling of thermo-compressed films of poly(ethylene furanoate)
Poly(ethylene furanoate) (PEF) films were first produced using thermo-compression. Thereafter, the chemical recyclability was demonstrated in the presence of a thermally stable organocatalyst followed by its repolymerization.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 1571-1580
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01623C
Sustainable thermoplastic elastomers produced via cationic RAFT polymerization
Cationic polymerization enables production of sustainable thermoplastic elastomers constructed from renewable vinyl ethers and -p-methoxystyrene with properties consistent with their petroleum-derived counterparts.
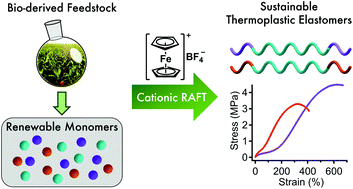
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 1097-1104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01640C
Self-healing hydrophobic POSS-functionalized fluorinated copolymers via RAFT polymerization and dynamic Diels–Alder reaction
Development of self-healing hydrophobic POSS-functionalized fluorinated copolymethacrylate(s) via RAFT Polymerization and dynamic Diels–Alder Reaction.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 876-884
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01522A
Towards nanoparticles with site-specific degradability by ring-opening copolymerization induced self-assembly in organic medium
Radical ring-opening copolymerization-induced self-assembly (rROPISA) was successfully applied to the synthesis of core-, surface- or surface plus core-degradable nanoparticles in heptane, leading to site-specific degradability by rROPISA.
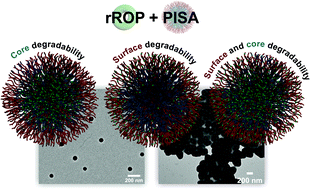
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 594-607
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01425G
Reversible covalent locking of a supramolecular hydrogel via UV-controlled anthracene dimerization
The formation of supramolecular hydrogels is demonstrated based on ternary complexes between anthracene side-chain functionalized polymers and macrocyclic hosts. Photo-induced reversible dimerization enables switching between supramolecular and covalent hydrogels.
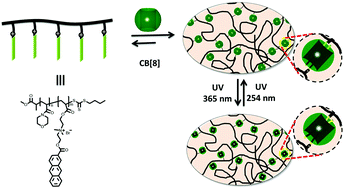
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 307-315
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01283A
Functional nanostructures by NiCCo-PISA of helical poly(aryl isocyanide) copolymers
Nickel-catalysed coordination polymerisation-induced self-assembly (NiCCo-PISA) as a straightforward and versatile methodology to achieve functional helix-containing polymeric nano-objects.

Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 105-112
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00791A
Forced gradient copolymerisation: a simplified approach for polymerisation-induced self-assembly
In this work, a novel and versatile gradient copolymerisation approach to simplify polymeric nanoparticle synthesis through polymerisation-induced self-assembly (PISA) is reported.
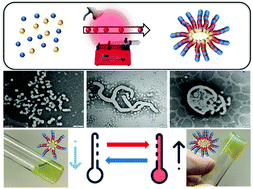
Polym. Chem., 2021,12, 57-68
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00889C
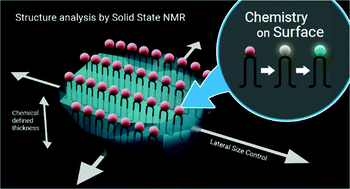
Defect engineering of polyethylene-like polyphosphoesters: solid-state NMR characterization and surface chemistry of anisotropic polymer nanoplatelets
Polyethylene-like polyphosphoesters crystallized from dilute solution into anisotropic nanoplatelets. As proven by solid-state NMR, the phosphate groups are expelled to the surface and on-surface chemistry was conducted leaving the crystals intact.
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 7235-7243
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01352H
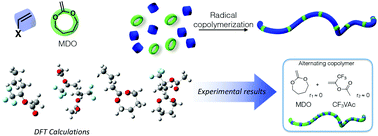
DFT-calculation-assisted prediction of the copolymerization between cyclic ketene acetals and traditional vinyl monomers
The ring-opening polymerization of cyclic ketene acetals (CKAs) and vinyl monomers is an elegant method to produce degradable copolymers. Owing to DFT calculations, we are now able to better understand the reactivity of CKAs & common vinyl monomers.
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 7159-7169
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01179G
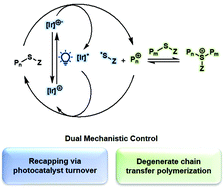
Photocontrolled cationic degenerate chain transfer polymerizations via thioacetal initiators
Photocontrolled cationic polymerizations controlled through a degenerate chain transfer process and photocatalyst turnover to recap propagating chains.
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 6499-6504
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01100B
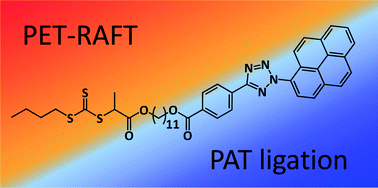
Two colours of light drive PET–RAFT photoligation
By fusing the realms of photopolymerisation and photoligation, our contribution exploits two orthogonal wavelengths of visible light to readily synthesise and functionalise well defined polymers from a unique dual functionality RAFT agent.
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 6453-6462
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY01078B
Dynamic polyurethane thermosets: tuning associative/dissociative behavior by catalyst selection
Catalyst selection can tune the associative/dissociative dynamic behaviour of polyurethane themosets.
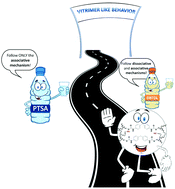
Polym. Chem., 2020,11, 5386-5396
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0PY00842G
About this collection
This collection highlights winners of the Polymer Chemistry Lectureship. This annual award was established in 2015 to honour an early-stage career scientist who has made a significant contribution to the polymer chemistry field.
The 2025 Polymer Chemistry Lectureship was awarded to Frank Leibfarth (University of North Carolina, USA).
Frank Leibfarth attended the University of South Dakota, where he was a Goldwater Scholar and graduated in 2008 with degrees in Chemistry and Physics. In that same year, he began a Ph.D. program in chemistry at the University of California Santa Barbara under the direction of Professor Craig J. Hawker. In 2013, Frank began his postdoctoral studies at MIT under the direction of Professor Timothy F. Jamison as an NSF Fellow. He began his independent career in 2016 at the University of North Carolina, where he is an Associate Professor in the Chemistry Department. The overarching goal of the Leibfarth group is to develop synthetic methods that transform readily available starting materials into functional and sustainable thermoplastics with molecular-level precision.
To accomplish these goals, his group leverages polymer chemistry, organic chemistry, and continuous flow chemistry to provide potentially useful solutions to challenges in sustainability and human health. The work of Professor Leibfarth’s group has been recognized by the Beckman Young Investigator award, the Popular Science Brilliant Ten recognition, the Presidential Early Career Award in Science & Engineering, and the Sloan Research Fellowship, among others. At UNC, Prof. Leibfarth has been recognized by the Tanner Award for Excellence in Undergraduate Teaching and as the Winter 2021 commencement speaker.
This collection features articles published in Polymer Chemistry from Frank Leibfarth, as well as the previous lectureship winners: