Themed collection Hybrid Pores for CO2 Technologies

Introduction to hybrid pores for CO2 technologies
Petra Ágota Szilágyi, Jenny G. Vitillo and Gavin A. Craig introduce the Materials Advances themed collection on hybrid pores for CO2 technologies.

Mater. Adv., 2024,5, 5336-5338
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4MA90055C
Simulating excited states in metal organic frameworks: from light-absorption to photochemical CO2 reduction
Quantum chemical simulations have shed light on the complex photochemical processes occurring within metal–organic frameworks. This perspective explores the computational techniques used to describe the excited states of MOFs, considering molecular, periodic, and embedding models.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 5388-5419
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00518F
Connecting metal–organic cages (MOCs) for CO2 remediation
The connection of metal organic cages (MOCs) via coordination driven bonds, covalent bonds or mechanical bonds yields functional materials at the interface between solid and liquid states with potential applications in CO2 remediation.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 4333-4343
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00477E
Direct CO2 to methanol reduction on Zr6-MOF based composite catalysts: a critical review
The pressing problem of climate change on account of anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emissions underlines the necessity for carbon capture and utilisation technologies.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 5479-5495
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00345K
A critical review on emerging photocatalysts for syngas generation via CO2 reduction under aqueous media: a sustainable paradigm
A sustainable paradigm for syngas production via photocatalytic CO2 reduction.
Mater. Adv., 2022,3, 5274-5298
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2MA00334A
From metal–organic framework powders to shaped solids: recent developments and challenges
This review discusses the impact of shaping techniques on the physico-chemical properties of metal–organic frameworks.

Mater. Adv., 2021,2, 7139-7186
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00630D
The application of amine-based materials for carbon capture and utilisation: an overarching view
An account of the fundamental chemical and engineering principles of solid amine-based CO2 adsorbents and their industrial application, with discussion of the relevance of amine chemistry in CO2 utilisation technology.
Mater. Adv., 2021,2, 5843-5880
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00360G
Deep learning neural network potential for simulating gaseous adsorption in metal–organic frameworks
This study proposes ab initio neural network force fields with physically motivated features to offer superior accuracy in describing adsorbate–adsorbent interactions of nonpolar (CO2) and polar (H2O and CO) molecules in metal–organic frameworks with open-metal sites.

Mater. Adv., 2022,3, 5299-5303
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA01152A
Unusual adsorption-induced phase transitions in a pillared-layered copper ethylenediphosphonate with ultrasmall channels
The peculiar adsorption-induced phase transitions in an ultramicroporous copper phosphonate framework were investigated with a combination of experimental and computational methods.

Mater. Adv., 2024,5, 183-198
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00356F
Rapid microwave synthesis of sustainable magnetic framework composites of UTSA-16(Zn) with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient CO2 capture
A hydrothermal synthesis process has been developed to produce highly magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, which have been incorporated into metal-organic framework UTSA-16(Zn), facilitating efficient induction heating for thermal regeneration in CO2 capture applications.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 5838-5849
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00351E
Dicyano-functionalized indium framework as a heterogeneous catalyst for CO2 fixation in the absence of solvent and co-catalyst
MIL-68(In) modified with cyanide functional groups was synthesized and demonstrated appreciable catalytic results for the construction of five-membered cyclic carbonates via a cycloaddition reaction without any added solvent or co-catalyst.
Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 4921-4928
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00513E
Pore volume regulated CO2 adsorption in C–C bonded porous organic frameworks
Three C–C bonded porous organic polymers are assembled by reacting rigid monomers (triformylphenol, triformylphloroglucinol, triformylresorcinol) with pyrrole in a catalyst-free solvothermal reaction.

Mater. Adv., 2023,4, 3055-3060
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00218G
Tuning the switching pressure in square lattice coordination networks by metal cation substitution
Coordination networks that undergo guest-induced switching between nonporous and porous phases are of increasing interest as the resulting stepped sorption isotherms can offer exceptional working capacities for gas storage applications.
Mater. Adv., 2022,3, 1240-1247
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00785H
Elucidating the role of non-covalent interactions in unexpectedly high and selective CO2 uptake and catalytic conversion of porphyrin-based ionic organic polymers
Here, we present viologen-porphyrin based ionic covalent organic polymers (H2-ICOP and Zn-ICOP) with multiple CO2-philic sites.
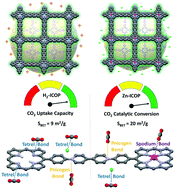
Mater. Adv., 2021,2, 3685-3694
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00217A
Rapid fabrication of MOF-based mixed matrix membranes through digital light processing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing technology, has greatly expanded across multiple sectors of technology replacing classical manufacturing methods by combining processing speed and high precision.
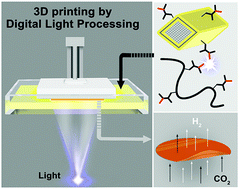
Mater. Adv., 2021,2, 2739-2749
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00023C
Tuneable CO2 binding enthalpies by redox modulation of an electroactive MOF-74 framework
Chemical reduction of an electroactive metal–organic framework based on napthalenediimide modulates carbon dioxide uptake and heat of adsorption.

Mater. Adv., 2021,2, 2112-2119
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00503G
A microporous, amino acid functionalized Zn(II)-organic framework nanoflower for selective CO2 capture and solvent encapsulation
A robust Zn-CBS nanoflower is utilized for selective sorption of CO2 and encapsulation of solvents.

Mater. Adv., 2020,1, 1455-1463
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00481B
Revealing the effect of structure curations on the simulated CO2 separation performances of MOFs
The CO2 separation performances of MOFs significantly change depending on the structure curation used in computation-ready databases.
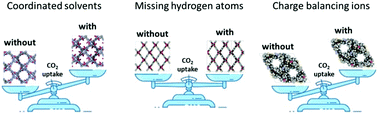
Mater. Adv., 2020,1, 341-353
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0MA00039F
About this collection
Guest Edited by Petra Ágota Szilágyi (University of Oslo), Jenny G. Vitillo (Università degli Studi dell'Insubria), and Gavin A. Craig (University of Strathclyde).
This themed collection is focused on inorganic-organic porous materials that enable the capture, storage, sensing, and conversion of CO2. It offers a summary of the state of the art in experimental and in silico approaches to tuning the interaction between CO2 and host materials such as metal-organic frameworks and metal-organic polyhedra/metal-organic cages. The themed collection also explores current trends in the development and processing of these porous materials for the realisation of Global Net Zero commitments.