Themed collection Contaminant remediation and fate

The reciprocity principle in mulch film deterioration and microplastic generation
Based on the reciprocity principle, this study evaluated the release and accumulation kinetics of microplastics from films, by developing an empirical model that linked the degradation performance of films under light with their molecular structure.
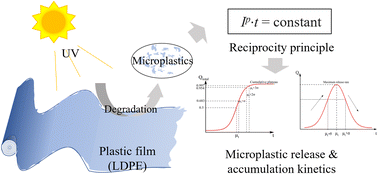
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 8-15
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00402C
Electrochemistry coupled with mass spectrometry for the prediction of the environmental fate and elucidation of the degradation mechanisms of pesticides: current status and future prospects
The state of the art of existing/published work in the prediction of environmental degradation of pesticides by EC-MS/EC-LC-MS coupling was reviewed. Ways to improve EC-MS techniques in the prediction of environmental degradation were proposed.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 340-350
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00451H
Towards improved characterization of the fate and impact of hydraulic fracturing chemicals to better secure regional water quality
New approaches to better characterize chemical contamination from hydraulic fracturing of shale and other permeable rock formations for improved risk-based management are presented.
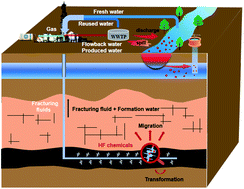
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 497-503
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00034B
Neonicotinoid insecticide sulfoxaflor in the environment: a critical review of environmental fate, degradation mechanism, and toxic effects
This paper focuses on the fate, degradation mechanisms and toxic effects of the neonicotinoid insecticide sulfentrazone in the environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 818-832
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00798K
Microcontaminants and microplastics in water from the textile sector: a review and a database of physicochemical properties, use in the textile process, and ecotoxicity data for detected chemicals
Microcontaminants and microplastics are released at every stage of production and use and end up in wastewater treatment plants and eventually in surface waters.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 297-319
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00639A
Photodegradation of typical psychotropic drugs in the aquatic environment: a critical review
An overview of the photodegradation of psychotropic drugs in the aquatic environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 320-354
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00669K
Current and emerging technologies for the remediation of difficult-to-measure radionuclides at nuclear sites
Effective remediation of a range of Difficult-to-Measure Radionuclides (DTMRs) in groundwater is needed to meet nuclear site end-state targets. This paper reviews recent developments in remediation of problem DTMRs, focusing on on-site application.
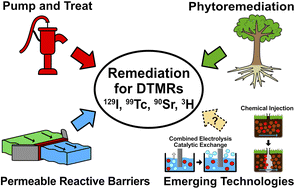
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1909-1925
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00190C
Photochemistry of oil in marine systems: developments since the Deepwater Horizon spill
Deepwater Horizon oil was exposed to sunlight in the Gulf of Mexico, changing its composition and behavior.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1878-1908
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00248A
SARS-CoV-2 airborne transmission: a review of risk factors and possible preventative measures using air purifiers
This critical review presents the best remedy to protect human health by efficient materials-based air filters that can be used to air-purify and kill the dangerous SARS-CoV-2 virus and remove the other air pollutants.
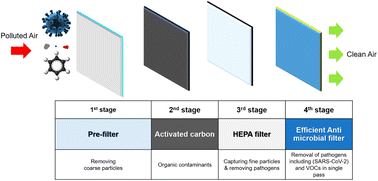
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2191-2216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00333C
Updated knowledge, partitioning and ecological risk of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in global aquatic environments
Distribution of PPCPs in the African, Asian, European, and North and South American continents is presented and discussed.
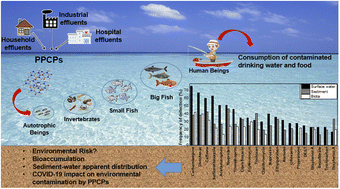
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1982-2008
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00132B
Influences of climate change on long-term time series of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in Arctic and Antarctic biota
Time series of contaminants in the Arctic are an important instrument to detect emerging issues and to monitor the effectiveness of chemicals regulation. Climate change can affect the link between primary emissions and concentrations in Arctic wildlife.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1643-1660
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00134A
Influence of climate change on persistent organic pollutants and chemicals of emerging concern in the Arctic: state of knowledge and recommendations for future research
Future climate change in the Arctic will lead to loss of ice, snow and permafrost, increasing human activity and development, and changes in wind and ocean circulation patterns, that could alter the pathways, distribution and fate of contaminants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 1530-1543
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00531F
Emerging investigator series: contributions of reactive nitrogen species to transformations of organic compounds in water: a critical review
Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) pose a potential risk to drinking water quality because they react with organic compounds to form toxic byproducts.
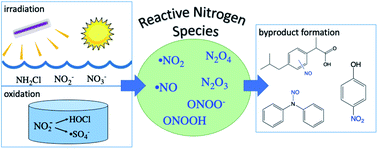
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 851-869
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00102K
Emerging investigator series: microplastic sources, fate, toxicity, detection, and interactions with micropollutants in aquatic ecosystems – a review of reviews
Hundreds of review studies have been published focusing on microplastics (MPs) and their environmental impacts.
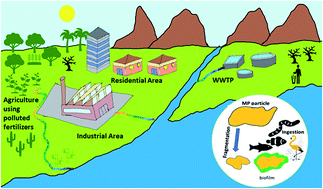
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 172-195
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00443C
PFAS surveillance within a highly militarized island: a case study of Okinawa, Japan
Comprehensive monitoring of 31 PFAS on a highly militarized island. ∑PFAS measured for 15 individual PFAS analogues. Varying PFAS fingerprints found at different geographical locations on the island.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 46-51
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00508B
PFAS occurrence and distribution in yard waste compost indicate potential volatile loss, downward migration, and transformation
This novel investigation revealed substantial PFAS contamination and plastic-PFAS co-occurrence in yard waste compost. Insights gained from the distribution of PFAS in compost are valuable for improving its management and application.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 657-666
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00538K
Use and release of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in consumer food packaging in U.S. and Canada
PFASs used in food packaging have the potential to contaminate the environment and numerous parts of the waste stream.
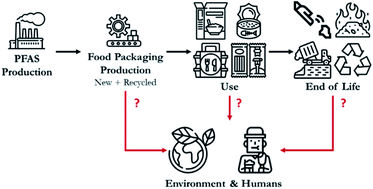
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 2032-2042
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00166G
Nitrogen fixing bacteria facilitate microbial biodegradation of a bio-based and biodegradable plastic in soils under ambient and future climatic conditions
We discovered a biological mechanism supporting microbial degradation of bio-based poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) plastic in soils under ambient and future climates.
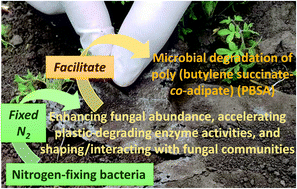
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 233-241
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00426C
Longevity of size-dependent particle removal performance of do-it-yourself box fan air filters
Filtration performance of do-it-yourself (DIY) box fan air filters deployed across a university campus was assessed over an academic year.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1629-1639
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00406J
Indoor air concentrations of PM2.5 quartz fiber filter-collected ionic PFAS and emissions to outdoor air: findings from the IPA campaign
Indoor concentrations of total PFAS were ∼3.4 times higher than outdoor concentrations and indoor-to-outdoor emission rates suggest home emissions may contribute to ambient concentrations of some PFAS away from major point sources.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1603-1618
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00359D
Elucidation of the mechanism by which the foliar application of triacontanol enhances Cd enrichment in Tagetes patula L. through morphological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses
The effect of triacontanol on Cd enrichment and tolerance in T. patula and the mechanism of action are investigated using a multi-omics approach, with a focus on the leaves and roots.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 1041-1053
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00736K
Identification of novel tetrabromobisphenol A byproducts in industrial chemicals and the environment near a manufacturing site: an overlooked source of novel pollutants
Fourteen byproducts were found in industrial-grade TBBPA chemicals and the environment near a manufacturing site, indicating the environmental effects of TBBPA transformation/degradation products and byproducts should be independently estimated.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 950-959
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00030K
Sorption kinetics of metallic and organic contaminants on micro- and nanoplastics: remarkable dependence of the intraparticulate contaminant diffusion coefficient on the particle size and potential role of polymer crystallinity
We developed a mechanistic diffusion model to describe the sorption kinetics of metallic and organic contaminants on nano- and micro-plastics.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 634-648
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00744A
Distribution and risk assessment of antibiotic resistance genes in swine farm wastewater and its surrounding environments: from soil to water
A significant correlation between the relative abundances of ARGs and MGEs in a swine farm and its surrounding environments was found.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 741-751
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00687A
Enantiomeric fraction evaluation for assessing septic tanks as a pathway for chiral pharmaceuticals entering rivers
Septic tanks (STs) are an important pathway for pharmaceuticals entering rivers.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 779-793
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00715H
Arsenic source-sink dynamics under phosphorus competition in sediments from river–lake connected systems
Multiple factors in the river–lake connected system can affect the transport and transformation of arsenic (As) in sediments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 706-717
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00707G
Characterization of the binding process between gallic acid and trivalent chromium in tannery wastewater: a spectroscopic perspective
UV and FTIR spectroscopy combined with 2DCOS reveal that the binding sequence of GA with Cr3+ is meta-hydroxyl groups → carboxyl groups → para-hydroxyl groups.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 453-462
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00621F
Environmental drivers of monomethylmercury photodegradation along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum
Monomethylmercury (MMHg) photodegradation along the land-to-ocean aquatic continuum is affected by dissolved organic matter (DOM) composition, concentration, and salinity.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 401-411
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00636D
Preliminary insight into the intracellular behaviour of rare earths and other technology-critical elements (TCEs) in northern pike liver: study of TCE-binding biomolecules via size-exclusion HPLC-ICP-MS
Due to their binding to possibly important high/medium-molecular mass intracellular proteins, technology-critical elements, actinides and other nonessential metals could pose a risk for aquatic organisms in highly contaminated aquatic environments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 262-276
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00674G
Emerging investigator series: open dumping and burning: an overlooked source of terrestrial microplastics in underserved communities
Open dumping and burning of solid waste are widely practiced in underserved communities lacking access to solid waste management facilities. The generation of microplastics from these sites has been overlooked.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 52-62
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00439F
Sorption of metal ions onto PET-derived microplastic fibres
Retention of metal ions onto PET microplastic fibres is expected during sewage treatment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2309-2319
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00373J
Fluorinated aromatic PBCTF and 6:2 diPAP in bridge and traffic paints
This study takes a multifaceted approach toward characterizing total fluorine and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in traffic and bridge paints.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2158-2165
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00546E
Degradation of norfloxacin by the synergistic effect of micro–nano bubbles and sodium hypochlorite: kinetics, influencing factors and pathways
The degradation reaction process and influencing factors of norfloxacin in the sodium hypochlorite and micro–nano bubble composite system.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2189-2202
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00490F
Leachability of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances from contaminated concrete
This study examines PFAS leaching behavior from concrete contaminated by the historical use of aqueous film-forming foams at an Australian Defence site, highlighting the long-term environmental implications of contaminated infrastructure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2227-2239
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00482E
Systematic characterization of selenium speciation in coal fly ash
A survey study of Se speciation in coal fly ash samples representative of coal source and combustion conditions.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2240-2249
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00398E
More than just sweet: current insights into microplastics in honey products and a case study of Melipona quadrifasciata honey
The presence of microplastics in honey samples from a native Brazilian bee varied from 0.1 to 2.6 particles per mL across urban and vegetated areas.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2132-2144
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00262H
Exploring the interactions of glyphosate in soil: the sorption scenario upon soil depletion and effect on waterleaf (Talinum triangulare) growth
Glyphosate translocation in soil and plants, and its effect on waterleaf growth.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2051-2061
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00433G
Impact of particle size separation on the stabilisation efficiency of heavy-metal-contaminated soil: a meta-analysis
The meta-method was used to analyze the impact of soil sieving particle size on the unit stabilisation efficiency of heavy metals.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1821-1835
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00308J
Microplastics are effective carriers of bisphenol A and facilitate its escape from wastewater treatment systems
Microplastics (MPs) pollution is a major issue in aquatic environments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1811-1820
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00297K
Fungal diversity and key functional gene abundance in Iowa bioretention cells: implications for stormwater remediation potential
Fungal communities within bioretention cells were diverse, including taxa capable of biodegrading recalcitrant contaminants, and influenced by plant type. Fungal functional genes demonstrate bioremediation potential in stormwater infrastructure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1796-1810
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00275J
Emerging investigator series: in-depth chemical profiling of tire and artificial turf crumb rubber: aging, transformation products, and transport pathways
Chemical profiling of artificial turf crumb rubber reveals time-based trends in transformation products and transport pathways.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1703-1715
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00326H
Photodegradation of the main synthetic musk (HHCB) in water: kinetic study and influencing factors
Galaxolide (HHCB) is the most common synthetic musk compound detected in numerous daily products.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1571-1587
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00351A
Molecular composition of fresh and aged aerosols from residential wood combustion and gasoline car with modern emission mitigation technology
Atmospheric aging enhances levels of fine particulate matter from road traffic and residential heating of current exhaust emission standards.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1295-1309
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00106K
Assessing the aging and environmental implications of polyethylene mulch films in agricultural land
Polyethylene mulch films (MFs) are widely employed in agricultural land to enhance crop yield and quality, but the MF residue causes significant environmental concerns.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1310-1321
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00102H
Effects of burning and photochemical degradation of Macondo surrogate oil on its composition and toxicity
When water accommodated fractions made from burned and unburned oil were exposed to light, burning of crude oil removes some, but not all toxic compounds, leaving behind compounds of considerable toxicity.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1205-1215
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00023D
Microplastics encapsulation in aragonite: efficiency, detection and insight into potential environmental impacts
This study confirms encapsulation of nontreated and humic acid treated polystyrene and polyethylene microplastics into aragonite, main building block of coral skeleton.
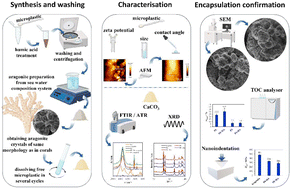
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1116-1129
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00004H
Determining wavelength-dependent quantum yields of photodegradation: importance of experimental setup and reference values for actinometers
Wavelength-dependent Φλ of uridine, atrazine, PNA, sulfamethoxazole, and diclofenac were determined, which can be used to characterize and model the photodegradation of chemicals of interest.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1052-1063
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00084F
Characteristics and adsorption behavior of typical microplastics in long-term accelerated weathering simulation
Adsorption of different organic pollutants by three microplastics before and after weathering.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 882-890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00062E
Co-exposure to tire wear particles and nickel inhibits mung bean yield by reducing nutrient uptake
Tire wear particles and nickel have detrimental effects on plant health by causing blockage and altering nutrient hemotasis, ultimately reducing plant yield.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 832-842
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00070F
Wildland–urban interface wildfire increases metal contributions to stormwater runoff in Paradise, California
Runoff from a destroyed town following a large wildland-urban interface wildfire transported metals into adjacent watersheds.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 667-685
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00298E
Distribution, sources, and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from rural communities around gas flaring points in the Niger Delta of Nigeria
This study investigates the concentrations, sources, and ecological and human health risks from exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils of rural communities around gas flaring points in Delta State, Nigeria.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 721-733
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00067B
Synergistic inhibition of green rust crystallization by co-existing arsenic and silica
Co-existing silica prolongs the stability of mixed valence iron minerals like green rust and magnetite, effectively immobilizing arsenic in anoxic environments.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 632-643
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00458A
Speeding it up: dual effects of biostimulants and iron on the biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) at mesophilic conditions
Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) in compost environment enriched with iron, and gelatin significantly enhanced microbial enzymatic activity, thus accelerating PLA degradation at mesophilic conditions (home/backyard composting setting).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 530-539
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00534H
Nano-mineral assemblages in mercury- and silver-contaminated soils: records of sequestration, transformation, and release of mercury- and silver-bearing nanoparticles
In mercury-contaminated soils, mercury sulfides (HgS) occur as nanoparticles in mineral surface coatings. The coatings are composed of ferrihydrite and its replacement by goethite results in the release of the HgS nanoparticles.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 483-498
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00302G
Heterogeneous interactions and transformations of dibasic esters with indoor relevant surfaces
Dibasic esters, indoor air pollutants emitted from furniture coatings, readily adsorb to surfaces thus initially decreasing their gas phase concentrations but then slowly desorb leading to possible long term exposure.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 582-594
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00542A
Isotopes and otolith chemistry provide insight into the biogeochemical history of mercury in southern flounder across a salinity gradient
Methylmercury (MeHg) continues to pose a significant global health risk to wildlife and humans through fish consumption.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 233-246
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00482A
Adsorption of copper by naturally and artificially aged polystyrene microplastics and subsequent release in simulated gastrointestinal fluid
Microplastics, especially aged microplastics can become vectors of metals from environment to organisms with potential negative effects on food chain.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 411-420
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00354J
Characteristics and ecological risks of microplastic pollution in a tropical drinking water source reservoir in Hainan province, China
The overall abundance of microplastics in water was 3.05 ± 1.16 items per L and in sediment was 0.15 ± 0.06 items per g dw. The pollution load index and the potential ecological hazards of microplastics in most sites are at a low level.
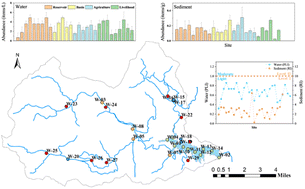
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 451-460
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00528C
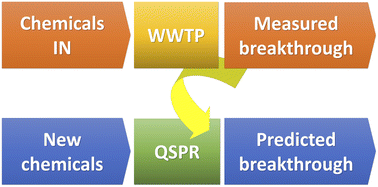
In silico approaches for the prediction of the breakthrough of organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plants
Quantitative structure–property relationships (QSPRs) can be used for the prediction of breakthrough of chemicals from wastewater treatment plants. These QSPRs are simple, interpretable, and checked both for overfitting and chance relationships.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 400-410
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00267E
Characterization and dermal bioaccessibility of residual- and listed PFAS ingredients in cosmetic products
Estimation of dermal bioaccessibility and characterization of listed-ingredient and residual per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetic products.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 259-268
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00461A
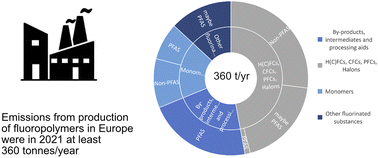
Emission inventory of PFASs and other fluorinated organic substances for the fluoropolymer production industry in Europe
This study assesses the environmental impact of the fluoropolymer industry in Europe by making an inventory of their emissions of PFASs and other fluorinated organic substances.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 269-287
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00426K
Isolation of aqueous pesticides on surface-functionalized SBA-15: glyphosate kinetics and detailed empirical insights for atrazine
Removal of atrazine and glyphosate from aqueous medium.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 323-333
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00425B
Spatial and temporal variability of micropollutants within a wastewater catchment system
Treated wastewater effluent is a major contributor to concentrations of many anthropogenic chemicals in the environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 357-367
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00361B
Understanding the importance of atmospheric transformation in assessing the hazards of liquid crystal monomers
The results suggest that atmospheric transformation can significantly change the hazard properties of LCMs, emphasizing the importance of atmospheric transformation when evaluating the hazards of LCMs.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 94-104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00424D
Temperature and particles interact to affect human norovirus and MS2 persistence in surface water
To our knowledge, this study is the first to assess the effects of surface water particle content on human norovirus decay rate constants, which will be useful parameters in fate and transport models.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 71-81
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00357D
Cyanobacterial extracellular antibacterial substances could promote the spread of antibiotic resistance: impacts and reasons
Cyanobacterial extracellular substances (CES) could promote the development of ARGs. CES could change the structure of a bacterial community and enrich ARB.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 2139-2147
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00306J
Limited effects of different real groundwaters from three coastal cities in China on the transport of low-concentration nanoplastics in quartz sand
Nanoplastics (NPs) have been widely detected in soil–groundwater systems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 2148-2156
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00388D
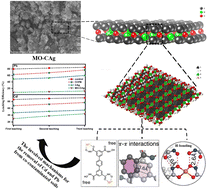
Towards engineering mitigation of leaching of Cd and Pb in co-contaminated soils using metal oxide-based aerogel composites and biochar
The remediation of heavy metal contaminated environments and related mechanisms in a comprehensive manner using metal-based nanomaterials can provide a useful resource for academic as well as industrial researchers.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 2110-2124
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00284E
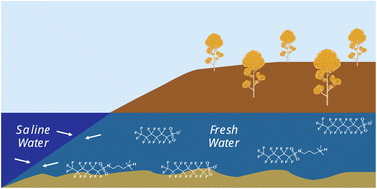
Enhanced aggregation and interfacial adsorption of an aqueous film forming foam (AFFF) in high salinity matrices
Saline water increases aggregation and interfacial accumulation of PFAS found in AFFF mixtures, having the potential to affect retention during transport at or near coastal contamination sites.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 2181-2188
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00247K
Feedstock nitrogen content mediates maximum possible Pb sorption capacity of biochars
It is possible that cation–π interactions with heterocyclic N structures is the primary mechanism for the sorption of Pb to biochar, highlighting the importance of feedstock nitrogen content to create biochars with a high Pb sorption capacity.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 2102-2109
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00246B
About this collection
This web collection features research articles published in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts focussed on the environmental fate of contaminants, and contaminant remediation.