Themed collection SDG13: Climate Action- chemistry of greenhouse gases, 2022

Secondary organic aerosol formation from monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: insights from laboratory studies
This review summarizes in detail the current knowledge in the chemical compositions, formation mechanisms, and physicochemical properties of secondary organic aerosols formed from monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
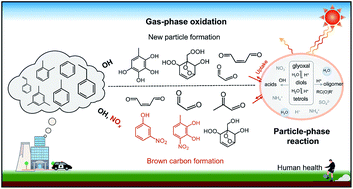
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 351-379
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00409C
Particulate nitrate photolysis in the atmosphere
Particulate nitrate photolysis can lead to the formation of secondary inorganic and organic aerosols that affect climate, air quality, and human health.

Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2022,2, 111-127
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00087J
Boosting CO2 electroreduction towards C2+ products via CO* intermediate manipulation on copper-based catalysts
An overview of the strategies for boosting C2+ selectivity by manipulating CO*(CO).

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 911-953
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00977J
Geochemical controls on CO2 interactions with deep subsurface shales: implications for geologic carbon sequestration
CO2 sequestration in shales is controlled by the intrinsic properties of shale and external factors shown in grey and green boxes, respectively. The adsorption capacity (orange box) is influenced by both intrinsic properties and external factors.
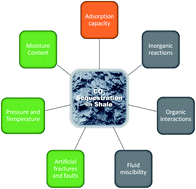
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1278-1300
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00109D
Aging of atmospheric aerosols and the role of iron in catalyzing brown carbon formation
Iron in mineral dust can catalyze reactions with atmospheric organics that lead to the formation of brown carbon (BrC) that impact the climate in a number of ways.

Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 297-345
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00038A
The progress of nanomaterials for carbon dioxide capture via the adsorption process
This review article describes the main technologies for CO2 capture, highlights the latest research status of nanomaterials for CO2 capture, and investigates the influence of surface microstructure and modification of materials on CO2 capture.
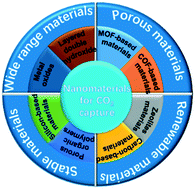
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 890-912
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN01140A
Formation pathways of aldehydes from heated cooking oils
We studied the mechanisms of cooking oil decomposition that lead to emission of aldehydes, an important group of air pollutants, from food cooking.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 165-175
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00532D
Identification of the active site during CF4 hydrolytic decomposition over γ-Al2O3
CF4 hydrolytic decomposition was studied at three-coordinated Al sites on the γ-Al2O3 (110) surface.
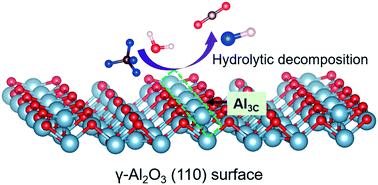
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 954-963
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01202A
Decomposition mechanism of α-alkoxyalkyl-hydroperoxides in the liquid phase: temperature dependent kinetics and theoretical calculations
The decomposition rates of organic hydroperoxides derived from ozonolysis of terpene-alcohol in the presence of short-chain alcohols in aqueous organic media is markedly increased as the temperature is increased.
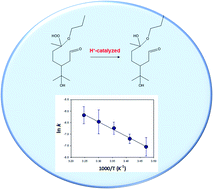
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2022,2, 241-251
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00076D
Towards a broad-operation window for stable CO2 electroreduction to HCOOH by a design involving upcycling electroplating sludge-derived Sn@N/P-doped carbon
Sn@NPC composite is synthesized by a design involving the upcycling of Sn electroplating sludge, and exhibits high selectivity and stability for CO2RR to HCOOH.
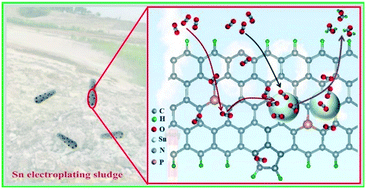
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2022,9, 511-522
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00930C
Hygroscopicity of polycatechol and polyguaiacol secondary organic aerosol in sub- and supersaturated water vapor environments
Polycatechol and polyguaiacol are light-absorbing and water-insoluble compounds that are produced from biomass burning emissions. The aerosol can act as seeds for cloud droplet formation.
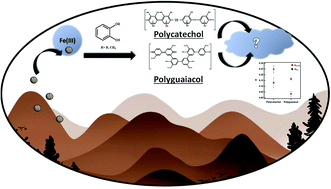
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2022,2, 24-33
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00063B
Abiotic reduction of nitrite by Fe(II): a comparison of rates and N2O production
Nitrite reduction by Fe(II) in an agricultural sediment and complete conversion to N2O suggests chemodenitrification is important to N2O emissions.
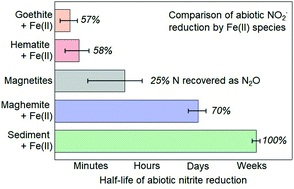
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 1531-1541
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00222H
A modelling study of OH, NO3 and H2SO4 in 2007–2018 at SMEAR II, Finland: analysis of long-term trends
We applied the 1D model SOSAA to simulate the atmospheric concentrations of OH, NO3, and H2SO4 from 2007 to 2018 at SMEAR II. The results showed that daily OH increased by 2.39% per year and NO3 and H2SO4 decreased by 3.41% per year and 2.78% per year, respectively.
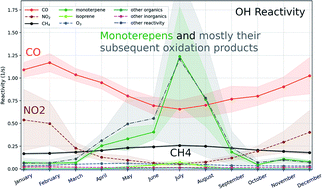
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 449-472
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00020A
Natural greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance sources and sinks from the peat bogs of Connemara, Ireland from 1994–2020
New emissions of methane and chloroform, with concurrent depositions of ozone and hydrogen were determined from the peat bogs of Ireland.
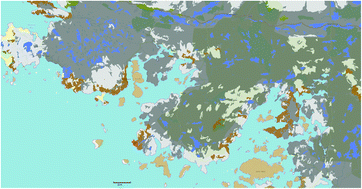
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 406-415
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EA00040C
Unraveling high-pressure gas storage mechanisms in shale nanopores through SANS
Three essential factors, including the final injection pressure, total organic carbon (TOC), and porosity of open pores, could determine methane storage and long-term CO2 sequestration potentials in depleted shale reservoirs.
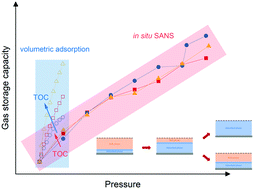
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2706-2717
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00419K
Plasma-induced construction of defect-enriched perovskite oxides for catalytic methane combustion
An innovative plasma-induced strategy was employed to one-step prepare defect-enriched porous LaMnO3 and cerium-substituted LaMnO3 perovskite oxides with excellent performance in methane combustion.
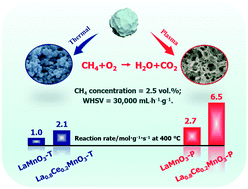
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2386-2395
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00339A
Resolving the organization of CO2 molecules confined in silica nanopores using in situ small-angle neutron scattering and molecular dynamics simulations
This work quantifies the core–shell structure of nano-confined CO2 molecules under pressure in silica pores using in operando small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) measurements and molecular dynamics simulations.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2006-2018
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN01282C
Activation and adsorption performance of sewage sludge carbon for CO2: unusual enhancement effect of HF treatment
The unusual enhancement effect of HF-treated sludge carbon for CO2 adsorption was found, which contributed to the HF activation role, resulting in the formation of abundant CO2-philic ultra-micropores and C–F functional groups.

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2021,8, 2019-2029
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00037C
Degradation mechanisms of simple aliphatic amines under ozonation: a DFT study
Degradation mechanisms of simple aliphatic amines during ozonation have been investigated by using the DFT method.
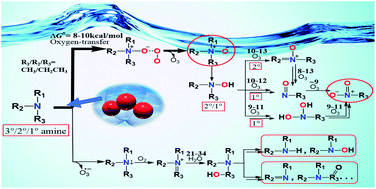
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2021,23, 480-490
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00476F
Peroxy radical kinetics and new particle formation
Chamber experiments may over emphasize peroxy radical cross reactions due to lower concentrations of reactants that directly convert OH into HO2.
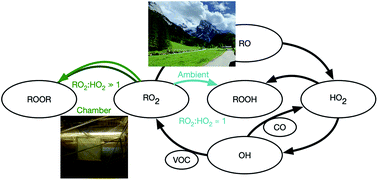
Environ. Sci.: Atmos., 2021,1, 79-92
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EA00017E
Anaerobic respiration pathways and response to increased substrate availability of Arctic wetland soils
Divergent soil biogeochemical conditions will determine the fate and pathways of labile carbon released during permafrost thaw, thereby influencing the production of greenhouse gas mixtures and radiative forcing of tundra soils.
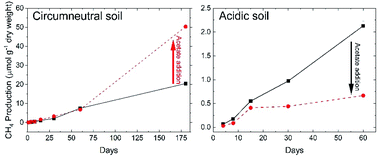
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 2070-2083
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00124D
Influence of dissolved organic matter on carbonyl sulfide and carbon disulfide formation from cysteine during sunlight photolysis
Sunlight photolysis of cysteine and dissolved organic matter (DOM) from freshwater to open ocean water sources generates carbonyl sulfide (COS) but not carbon disulfide (CS2).
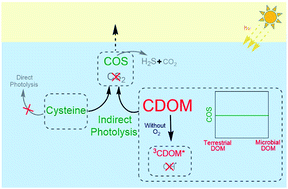
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1852-1864
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00219D
Secondary organic aerosol formation from evaporated biofuels: comparison to gasoline and correction for vapor wall losses
With an ongoing interest in displacing petroleum-based sources of energy with biofuels, we measure and model the formation and composition of secondary organic aerosol (SOA) from organic compounds present in biofuels.
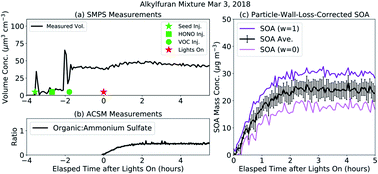
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1461-1474
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EM00103A
Assessing the prevalence, products, and pathways of dissolved organic matter partial photo-oxidation in arctic surface waters
Isotope tracer experiments reveal that rates of dissolved organic matter partial photochemical oxidation are considerably underestimated in arctic surface waters.
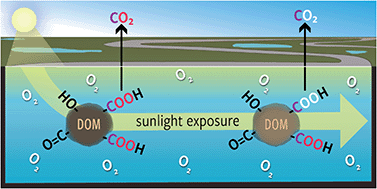
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2020,22, 1214-1223
https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EM00504H