Themed collection Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs)

Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)
Guest editors Hong-Cai “Joe” Zhou and Susumu Kitagawa introduce the Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) themed issue of Chemical Society Reviews.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5415-5418
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS90059F
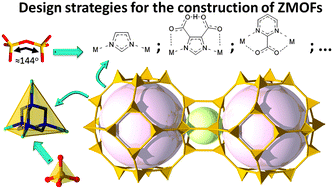
Zeolite-like metal–organic frameworks (ZMOFs): design, synthesis, and properties
Illustration of various strategies for the construction of zeolite-like metal–organic frameworks (ZMOFs) based on vertex decoration and/or edge-expansion.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015,44, 228-249
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00230J
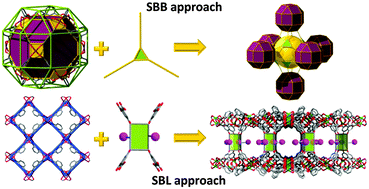
A supermolecular building approach for the design and construction of metal–organic frameworks
A toolbox for the design of made-to-order MOFs: Pinpointing the rationale and benefits of the Supermolecular Building Block (SBB) and Supermolecular Building Layer (SBL) approaches.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 6141-6172
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00135D
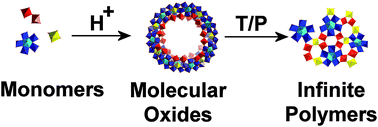
Polyoxometalate based open-frameworks (POM-OFs)
Polyoxometalate-based open frameworks (POM-OFs) are extended architectures incorporating metal-oxide cluster units and comprise an emergent family of materials with a large diversity of topologies, structural flexibility and functionality at the nanoscale.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5679-5699
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00097H
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies on structural transformations of porous coordination polymers
This review gives a brief overview of single-crystal X-ray diffraction studies and single-crystal to single-crystal transformations of porous coordination polymers.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5789-5814
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00129J
Metal–organic framework membranes: from synthesis to separation application
This review provides current techniques for the fabrication of MOF membranes and separation applications of diverse MOF membranes.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 6116-6140
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00159A
High valence 3p and transition metal based MOFs
This article focuses on high valence 3p and transition metal based metal organic frameworks.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 6097-6115
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00081A
Flexible metal–organic frameworks
Flexible metal–organic frameworks are state-of-the-art materials and their tailor made synthesis, in situ analysis and possible applications have gained wide attention in the scientific community.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 6062-6096
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00101J
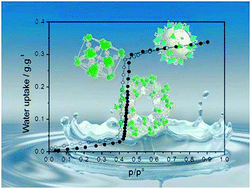
Water adsorption in MOFs: fundamentals and applications
MOF and water, friend or enemy?
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5594-5617
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00078A
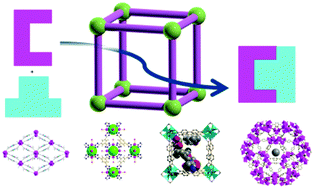
Applications of metal–organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis
The contributions of MOFs to the field of heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis are comprehensively reviewed with regard to active sites, selectivity, as well as host–guest chemistry.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 6011-6061
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00094C
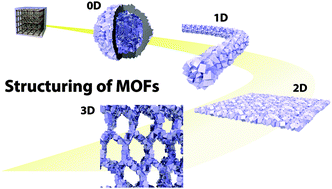
Structuring of metal–organic frameworks at the mesoscopic/macroscopic scale
This review conceptually categorizes the available synthetic methodologies for structuring of MOFs in the mesoscopic and macroscopic scales.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5700-5734
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00106K
MOF positioning technology and device fabrication
Methods for permanent localisation, dynamic localisation and spatial control of functional materials within MOF crystals are critical for the development of miniaturised MOF-based devices for a number of technological applications.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5513-5560
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00089G
MOF-based electronic and opto-electronic devices
Emergent properties resulting from the ordered structure and synthetic versatility of nanoporous metal–organic frameworks offer exciting possibilities for electronic devices.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5994-6010
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00096J
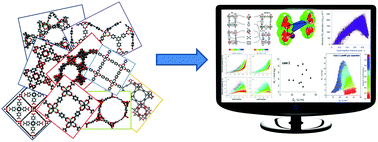
High-throughput computational screening of metal–organic frameworks
High-throughput computational screening of MOFs allows identification of promising candidates, new structure–property relationships, and performance limits.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5735-5749
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00070F
Metal–organic frameworks for artificial photosynthesis and photocatalysis
This article reviews the latest progress in light-harvesting, organic photocatalysis, proton and CO2 reduction, and water oxidation using MOFs.
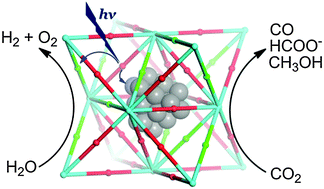
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5982-5993
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00103F
Substitution reactions in metal–organic frameworks and metal–organic polyhedra
This review summarizes the advances in the study of substitution reactions in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and metal–organic polyhedra (MOPs).
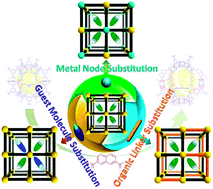
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5952-5981
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00033A
Post-synthetic metalation of metal–organic frameworks
Post-synthetic metalation (PSMet) offers expansive scope for a targeted approach to tailoring the properties of MOFs.
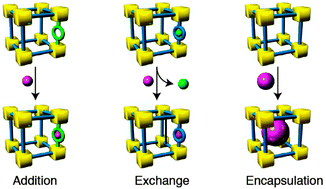
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5933-5951
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00076E
MOFs as proton conductors – challenges and opportunities
Recent developments in the field of proton-conducting MOFs are reviewed, with a special focus on the design strategies and structural characteristics of the best performers in the low temperature (<100 °C) and the high-temperature (>100 °C) regimes.
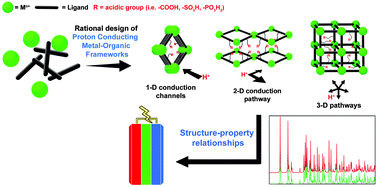
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5913-5932
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00093E
Beyond post-synthesis modification: evolution of metal–organic frameworks via building block replacement
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are hybrid porous materials with many potential applications, which intimately depend on the presence of chemical functionality either at the organic linkers and/or at the metal nodes.
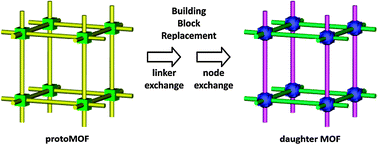
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5896-5912
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00067F
Multifunctional metal–organic frameworks constructed from meta-benzenedicarboxylate units
meta-Benzenedicarboxylate units have led to a large number of multifunctional metal–organic frameworks.
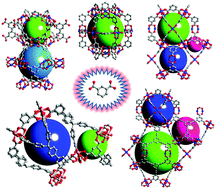
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5618-5656
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00041B
Metal–organic frameworks based on flexible ligands (FL-MOFs): structures and applications
This review presents the recent developments on FL-MOFs, including their structures and applications in gas adsorption, catalysis and proton conduction.
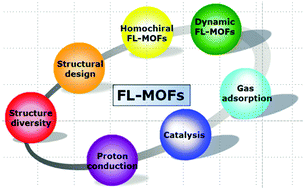
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5867-5895
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60483G
Metal–metalloporphyrin frameworks: a resurging class of functional materials
This review presents comprehensively recent progress in metal–metalloporphyrin frameworks with an emphasis on versatile functionalities.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5841-5866
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00001C
Methane storage in metal–organic frameworks
Porous metal–organic frameworks have been emerging as very promising materials for methane (natural gas) storage.
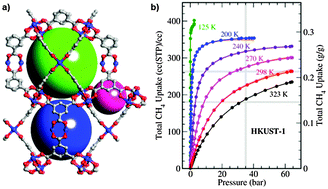
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5657-5678
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00032C
Adsorptive separation on metal–organic frameworks in the liquid phase
While much attention of the MOF community has been devoted to adsorption and purification of gases, there is now also a vast body of data on the capability of MOFs to separate and purify liquid mixtures.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5766-5788
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00006D
Metal–organic framework composites
This review focuses on the recent progress in designing and fabricating metal–organic framework (MOF) composites for diverse functional applications.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5468-5512
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60472A
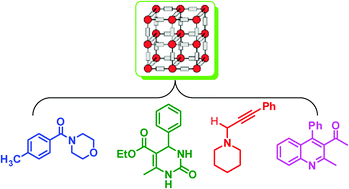
Metal–organic frameworks as solid catalysts for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing heterocycles
This Critical Review summarizes the recent developments in the use of metal–organic frameworks as catalysts for the synthesis of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5750-5765
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60442J
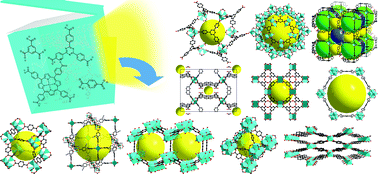
Tuning the structure and function of metal–organic frameworks via linker design
Advances in metal–organic frameworks are highlighted with an emphasis on tuning the structure and function via linker design.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5561-5593
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00003J
Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection
This review provides an update on the photoluminescence properties of LMOFs and their utility in chemical sensing and explosive detection.
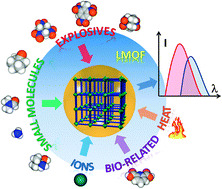
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5815-5840
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00010B
Template-directed synthesis of metal–organic materials
This tutorial review details the emergence of template-directed synthesis of metal–organic materials (MOMs) with emphasis upon reports of MOMs in which the template is retained, template@MOMs, and structurally characterized.
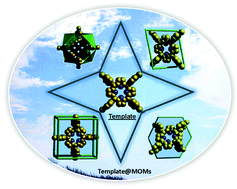
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5444-5455
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00075G
Cation exchange at the secondary building units of metal–organic frameworks
This review examines the governing factors of cation exchange at the secondary building units of MOFs and reviews its applications.
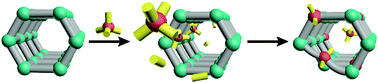
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5456-5467
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00002A
Supramolecular templating of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks
This tutorial review summarises recent advances in the soft templating of metal–organic frameworks with hierarchical porosity across the micro- and mesoporous regimes.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5431-5443
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00127C
Toxic gas removal – metal–organic frameworks for the capture and degradation of toxic gases and vapours
The adsorptive and catalytic properties of metal–organic frameworks are advantageous for the capture, sensing and degradation of harmful gases and vapors.
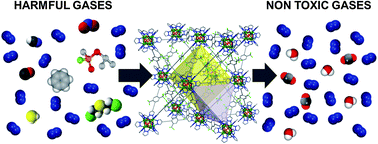
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 5419-5430
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60475F
About this collection
Chemical Society Reviews is delighted to present its themed issue on Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs), guest edited by Susumu Kitagawa and Hong-Cai “Joe” Zhou. This issue is published in follow-up to the prominent 2009 Chemical Society Reviews themed issue on MOFs (Editors: Jeffrey R. Long and Omar M. Yaghi). New articles will be added to this collection as they are published.