Post-synthetic metalation of metal–organic frameworks
Abstract
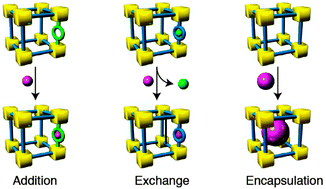
Post-synthetic metalation (PSMet) offers expansive scope for a targeted approach to tailoring the properties of MOFs. Numerous methods for carrying-out PSMet chemistry have been reported, however, these can be categorized into three general strategies: (a) addition to coordinating groups; (b) counter-ion exchange in charged frameworks; or, (c) host–guest encapsulation of metal-containing entities within the pores of the framework. PSMet has been applied to enhance the performance characteristics of parent MOFs for gas storage and separation, and catalysis. Notably, PSMet is a prominent strategy in the field of MOF catalysis as it offers a route to design size-selective catalysts, based on the premise of reticular chemistry in MOFs and the ability to incorporate a range of catalytically-active metal centres. Other applications for materials produced via or utilising PSMet strategies include enhancing gas storage or molecular separations, the triggered release of drugs, sensing and tunable light emission for luminescent materials. This review surveys seminal examples of PSMet to highlight the broad scope of this technique for enhancing the performance characteristics of MOFs and to demonstrate how the PSMet concept can be developed for future applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...