Themed collection Theoretical chemical physics of biological systems

Computational enzymatic catalysis – clarifying enzymatic mechanisms with the help of computers
Computational methods offer an unparalleled opportunity to dissect in minute detail enzymatic reaction mechanisms.
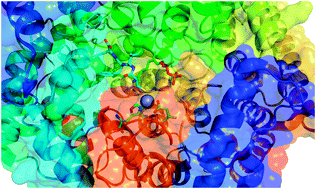
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12431-12441
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41180F
Implementation and validation of a multi-purpose virtual spectrometer for large systems in complex environments
Toward a multifrequency virtual spectrometer: status and perspectives.
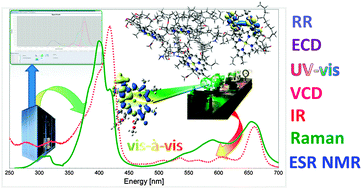
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12404-12422
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41006K
On developing coarse-grained models for biomolecular simulation: a review
A review of the basic ingredients of developing coarse-grained models and conditions to be satisfied for preserving the correct physical mechanisms.
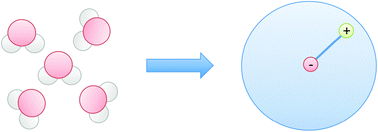
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12423-12430
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40934H
Identifying the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) as a potential target for hypericin – a theoretical study
The chemical structure of hypericin and the crystal structure of SERCA1A with the identified binding pockets that were subject to docking in the present study.
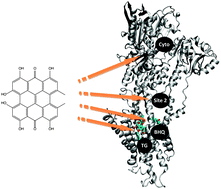
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12637-12646
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP42237A
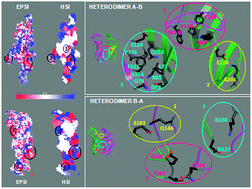
A first step towards the understanding of the 5-HT3 receptor subunit heterogeneity from a computational point of view
The physicochemical characterization of the several 5-HT3-R interfaces allows the prediction, on atomistic bases, of the role played by the extracellular moieties of the A–E subunits in the formation of functional or non-functional receptors.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12625-12636
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41028A
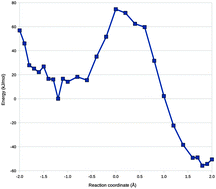
Convergence of QM/MM free-energy perturbations based on molecular-mechanics or semiempirical simulations
We show severe convergence problems for QM/MM free-energy perturbations even if based on tailored force fields or semiempirical calculations.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12592-12604
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41005B
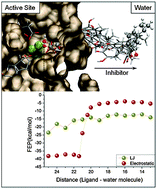
Theoretical studies of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibition
Computational methods for accurately calculating the binding affinity of a ligand for a protein play a pivotal role in rational drug design.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12614-12624
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40953D
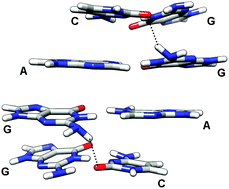
Understanding the role of base stacking in nucleic acids. MD and QM analysis of tandem GA base pairs in RNA duplexes
Towards elucidating the role of base stacking in the conformational preference of tandem GA base pairs in RNA.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12580-12591
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40556C
The catalytic mechanism of mouse renin studied with QM/MM calculations
The picture shows the enzyme renin, whose catalytic mechanism was studied in atomistic detail. The enzyme is coloured grey, the substrate is coloured orange, and the cleavage point (Leu10-Val11), the catalytic aspartic dyad and the water molecule are coloured by element, and depicted in ball and stick representation.
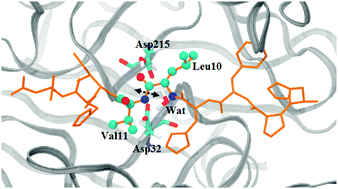
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12605-12613
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41422H
Quantum chemical modeling of rhodopsin mutants displaying switchable colors
The color variation of computationally designed rhodopsin mutants is investigated using a multiconfigurational quantum chemistry based QM/MM method.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12485-12495
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40940B
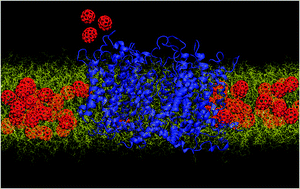
Interaction of C70 fullerene with the Kv1.2 potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels exposed to fullerene.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12526-12533
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41117B
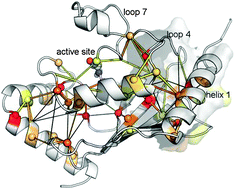
Paths of long-range communication in the E2 enzymes of family 3: a molecular dynamics investigation
MD simulations of E2 enzymes were carried out and analyzed to provide a quantitative description of their functional dynamics. The functionally relevant differences between the closed and open conformations were unravelled, and critical residues involved in long-range communication paths were detected.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12515-12525
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41224A
A hybrid elastic band string algorithm for studies of enzymatic reactions
In this work we describe a computationally efficient algorithm to determine minimum energy paths in complex systems.
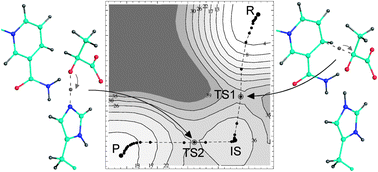
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12544-12553
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40918F
Stability and iron coordination in DNA adducts of Anthracycline based anti-cancer drugs
There is evidence that the interaction of the α-ketol group of the Doxorubicin and Epirubicin anti-cancer drugs with Fe(III) generates hydroxyl radicals under aerobic conditions, which may cause cardiotoxicity in patients.
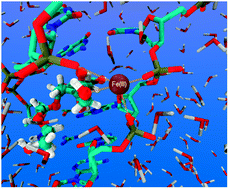
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12505-12514
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40931C
Reactions of cisplatin and glycine in solution with constant pH: a computational study
In this study interaction between glycine and cisplatin is explored.
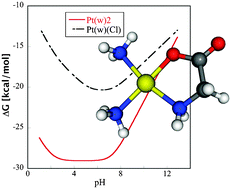
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12571-12579
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP41016H
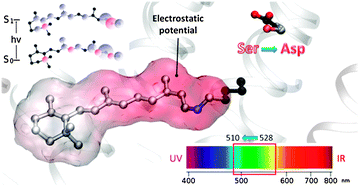
Spectral properties of polypyridyl ruthenium complexes intercalated in DNA: theoretical insights into the surrounding effects of [Ru(dppz)(bpy)2]2+
The UV/Visible absorption properties of a polypyridyl ruthenium complex upon intercalation on DNA are studied at the mixed quantum mechanics molecular mechanics level of theory.
![Graphical abstract: Spectral properties of polypyridyl ruthenium complexes intercalated in DNA: theoretical insights into the surrounding effects of [Ru(dppz)(bpy)2]2+](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C2CP40935F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2012)
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12496-12504
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40935F
On the evolution of one-electron-oxidized deoxyguanosine in damaged DNA under physiological conditions: a DFT and ONIOM study on proton transfer and equilibrium
Deprotonation of ground-state deoxyguanosine sites in one-electron-oxidized DNA has been investigated, including both the purine and the sugar moieties. A new mechanistic proposal is provided supporting the formation of C centered radicals under physiological conditions.
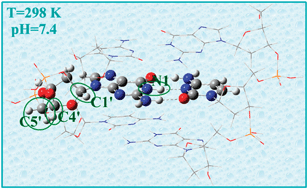
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12476-12484
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40799J
XYG3 and XYGJ-OS performances for noncovalent binding energies relevant to biomolecular structures
XYG3 and XYGJ-OS functionals provide an overall good agreement with reference values for the S22, S22x5 and JSCH-2005 benchmark sets.
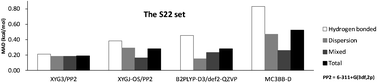
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12554-12570
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40904F
Aluminum speciation in biological environments. The deprotonation of free and aluminum bound citrate in aqueous solution
Investigation on the structure and acidity of citric acid upon its complexation to Al(III).
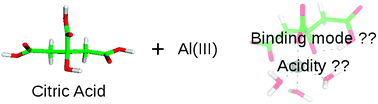
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12465-12475
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40671C
On the peroxyl scavenging activity of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives: mechanisms, kinetics, and importance of the acid–base equilibrium
Excellent antioxidants in aqueous solution, at physiological pH, via a single electron transfer mechanism from the phenoxide anions.
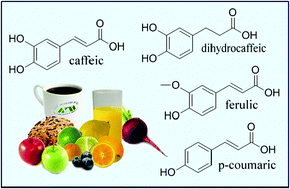
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12534-12543
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40651A
Cisplatin cytotoxicity: a theoretical study of induced mutations
This multi-scale theoretical study provides new insights into the cisplatin biological activity. The induced rare tautomeric form of the guanine–cytosine base pair in the A![[G with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0047_0332.gif)
![[G with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0047_0332.gif) context emerges as a well-suited candidate to promote its in vivo cytotoxicity.
context emerges as a well-suited candidate to promote its in vivo cytotoxicity.
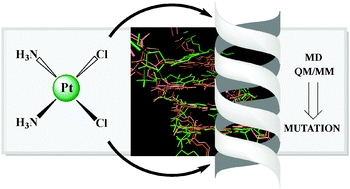
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12457-12464
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40515F
Turn-directed folding dynamics of β-hairpin-forming de novo decapeptide Chignolin
Extensive, unbiased simulations of a 10-residue β-hairpin disclose a turn-directed folding process and show that hydrophobic cross-strand side-chain interactions may cause packing frustration that could nucleate aggregative events.
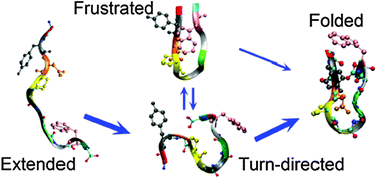
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12442-12450
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP40285H
Why voltage-gated Ca2+ and bacterial Na+ channels with the same EEEE motif in their selectivity filters confer opposite metal selectivity
We provide a physical basis for the opposite ion selectivity in Nav and Cav channels with the EEEE motif.
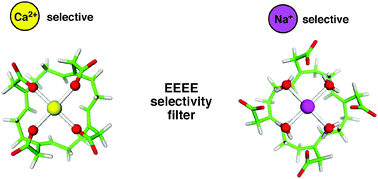
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012,14, 12451-12456
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP00036A
About this collection
PCCP is delighted to present a themed issue on theoretical chemical physics of biological systems, Guest Edited by Carlo Adamo, Leif Eriksson, Maria João Ramos, Nino Russo and Jesus Ugalde.
Theoretical chemical physics of biological systems has as its main aim the qualitative (and often quantitative) understanding of biological and biomolecular systems on different time and size scale, from angstrom to centimetres, from femtoseconds to hours. By its very nature theoretical chemical physics of biological systems is wonderfully diverse, and applications range over a vast number of topics.
This themed issue covers the most recent developments in the field of modeling and simulation of biological systems, new methodology and applications on "hot" topics such as drug modeling and development, enzymatic mechanisms, protein interactions, and much more.