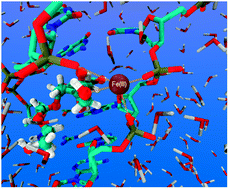
There is evidence that the interaction of the α-ketol group of the Doxorubicin and Epirubicin anti-cancer drugs with Fe(III) generates hydroxyl radicals under aerobic conditions, causing cardiotoxicity in patients. Considering that the formation of DNA adducts is one of the main targets of Anthracycline drugs, we have in the present study characterized several [Anthracycline–DNA]Fe(III) complexes with respect to their stability and Fe(III) coordination, by means of MD simulations. Iron is found to coordinate well to the drugs containing an α-ketol group, this being the only group of the drug that binds to the metal. The complexes containing an α-ketol group, [Doxorubicin–DNA]Fe(III) and [Epirubicin–DNA]Fe(III), thus show greater stability than those not containing it, i.e., [Daunorubicin–DNA]Fe(III), [Idarubicin–DNA]Fe(III) and [5-Imino-Daunorubicin]Fe(III). Metal attachment to the α-ketol group is furthermore facilitated by the phosphate groups of DNA. The coordination to iron in the [Doxorubicin–DNA]Fe(III) system is smaller than that found for the [Epirubicin–DNA]Fe(III) system, and the corresponding number of coordinating waters in the former is larger than in the latter. This may in turn result in higher hydroxyl radical production, thus explaining the increased cardiotoxicity noted for Doxorubicin.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...