Themed collection Measurement and prediction of quantum coherence effects in biological processes

Measurement and prediction of quantum coherence effects in biological processes
This themed issue presents a collection of articles on the measurement and prediction of quantum coherence effects in biological processes.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30772-30774
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP90134K
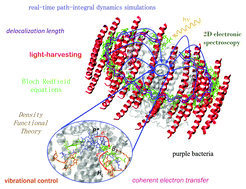
Limits and potentials of quantum chemical methods in modelling photosynthetic antennae
A critical overview of quantum chemical approaches to simulate the light-harvesting process in photosynthetic antennae is presented together with a perspective on the developments that need to be introduced to reach a quantitative predictive power.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30783-30792
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00986C
Nuclear quantum tunnelling in enzymatic reactions – an enzymologist's perspective
The roles of nuclear quantum tunnelling and dynamics in enzyme reactions are discussed in this perspective on H-transfer reactions.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30775-30782
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00614G
Vibronic couplings and coherent electron transfer in bridged systems
A computational strategy to analyze the dynamics of coherent electron transfer processes in bridged systems, involving three or more electronic states, is presented.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30937-30945
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01190F
Spectral lineshapes in nonlinear electronic spectroscopy
An approach for realistic lineshape modeling in nonlinear spectra which couples accurate computations of the high-lying excited states to mixed quantum-classical dynamics simulations is presented and applied to bi-dimensional electronic spectroscopy of pyrene.
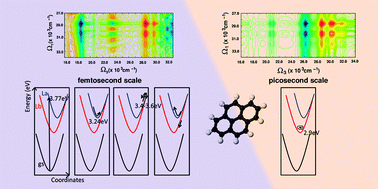
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30925-30936
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01167A
Electronic coherence and the kinetics of inter-complex energy transfer in light-harvesting systems
Comparison of inter-complex excitation energy transfer rates obtained in a general system (original, red) and in an alternative parameterization of the system that preserves static coherence while eliminating dynamic coherence (SCP, black) reveals that static coherence largely governs the kinetics of incoherent inter-complex EET in model light-harvesting networks, whereas dynamic coherence plays only a minor role.
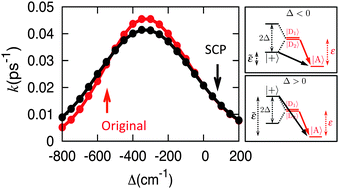
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30914-30924
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP02517F
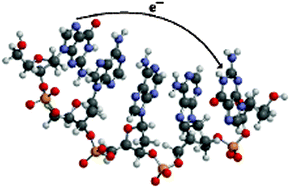
Electron transfer within a reaction path model calibrated by constrained DFT calculations: application to mixed-valence organic compounds
Dissipative quantum dynamics of CT in mixed-valence compounds is studied using a reaction path model calibrated by cDFT calculations.
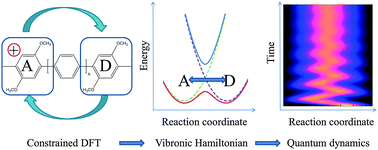
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30889-30903
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01194A
Quantum coherence effects in natural light-induced processes: cis–trans photoisomerization of model retinal under incoherent excitation
Cis–Trans isomerization of retinal induced by incoherent solar light. Shown are ground and excited-state diabatic potentials; the horizontal lines represent bright eigenstates (red), intermediate eigenstates (blue), and product eigenstates (green). The inset: the photoreaction efficiency vs. time with (red) and without (blue) Fano coherences.
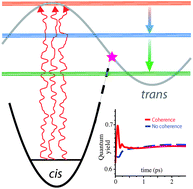
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30904-30913
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01388G
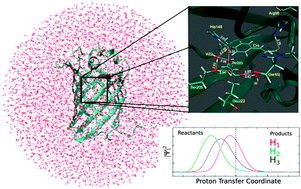
Transient low-barrier hydrogen bond in the photoactive state of green fluorescent protein
A transient low-barrier hydrogen bond has been found directly after photoexcitation using quantum dynamics to study the excited-state process in GFP.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30876-30888
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01067E
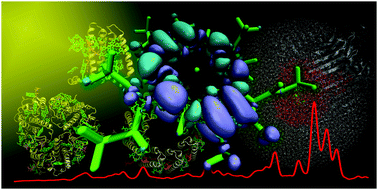
DFT-based Green's function pathways model for prediction of bridge-mediated electronic coupling
New LMO-GFM methodology enables intuitive understanding of electron tunneling in terms of through-bond and through-space interactions.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30842-30853
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01861G
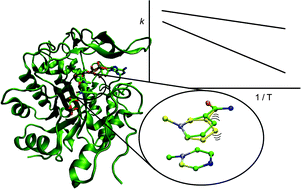
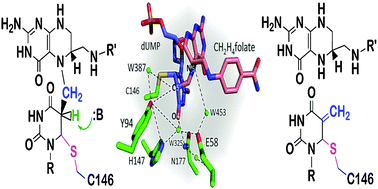
The general base in the thymidylate synthase catalyzed proton abstraction
The temperature dependence of intrinsic KIE studies reveal Y94 as a component of the general base facilitating proton abstraction step.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30867-30875
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01246E
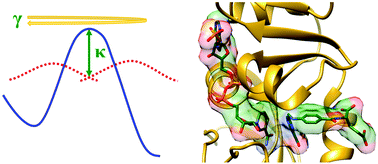
Protein motions and dynamic effects in enzyme catalysis
While the full catalytic power of dihydrofolate reductase depends on finely tuning protein motions in each step of the catalytic cycle, dynamic coupling to the actual chemical step is detrimental to catalysis.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30817-30827
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00794A
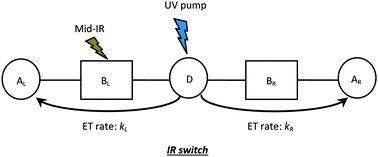
Vibrational control of electron-transfer reactions: a feasibility study for the fast coherent transfer regime
Electron donors are connected via left and right bridges to electron acceptors. Following electron-transfer initiation, the IR excitation of selected bridge vibrational modes can tune the directionality of electron transfer.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30854-30866
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00610D
The influence of active site conformations on the hydride transfer step of the thymidylate synthase reaction mechanism
QM/MM MD simulations from different X-ray structures support the concerted mechanism character in the rate limiting step of thymidylate synthase catalysis.
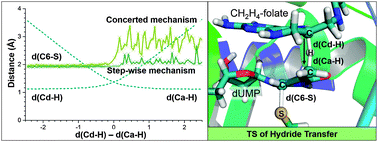
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30793-30804
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01239B
How exciton-vibrational coherences control charge separation in the photosystem II reaction center
Two-dimensional photon echo in the photosystem II reaction center reveals the exciton-vibrational coherences that promote directed energy/electron transfers.
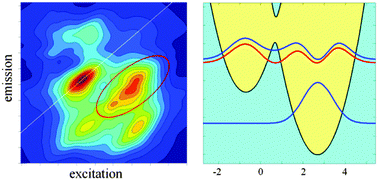
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30828-30841
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00582E
B800–B850 coherence correlates with energy transfer rates in the LH2 complex of photosynthetic purple bacteria
Delocalization of a model light-harvesting complex is investigated using multipartite measures inspired by quantum information science.
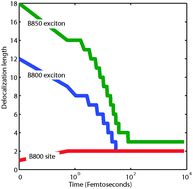
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 30805-30816
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00295H
About this collection
In recent years, experimental measurements have uncovered fine quantum effects (FQE) in biological systems. The appearance of these FQE may be surprising, given the warm soft nature of biological media, as opposed to the cold hard world where quantum effects dominate. The observation of long-lived coherences within photosynthetic antennas at room temperature for hundreds of femtoseconds is one striking example of such FQE.
This themed issue includes contributions from both experimental and computational scientists working at the forefront of biological systems that require “non-trivial” quantum mechanics. The guest editors are Aurélien de la Lande (CNRS), Vicent Moliner (Jaume I University) and Dennis Salahub (University of Calgary).