Themed collection Host–guest chemistry

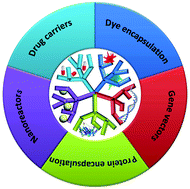
Recognition-driven chemical labeling of endogenous proteins in multi-molecular crowding in live cells
Endogenous protein labeling is one of the most invaluable methods for studying the bona fide functions of proteins in live cells.
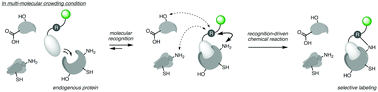
Chem. Commun., 2017,53, 11972-11983
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CC07177A
Properties and emerging applications of mechanically interlocked ligands
We discuss the properties and potential future applications in catalysis, sensing and materials of ligands based on mechanically interlocked molecules.

Chem. Commun., 2017,53, 298-312
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC07377H
Supramolecular aggregates as sensory ensembles
Recent research progress in sensing based on induced supramolecular aggregation or disaggregation.
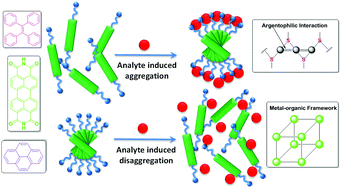
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 12929-12939
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC06075G
The death of the Job plot, transparency, open science and online tools, uncertainty estimation methods and other developments in supramolecular chemistry data analysis
The failure of the Job plot, best-practice in uncertainty estimation in host–guest binding studies and an open access webportal for data analysis are reviewed in this Feature Article.
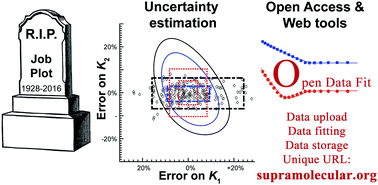
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 12792-12805
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03888C
Selective molecular recognition on calixarene-functionalized 3D surfaces
Calixarene based various 3D surface materials with unique signal amplification in molecular recognition are presented, including quantum dots (QDs), metal nanoparticles (NPs), nanotubes, and mesoporous silica.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 12685-12693
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC05876K
Multicavity macrocyclic hosts
Multicavity macrocyclic hosts are host molecules comprising more than one macrocyclic guest binding components connected through multipoint linkages.
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 12130-12142
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03651A
Kinetic trapping – a strategy for directing the self-assembly of unique functional nanostructures
Kinetic trapping via supramolecular approaches or physical processing pathways can be an efficient strategy for directing functional molecular self-assemblies.
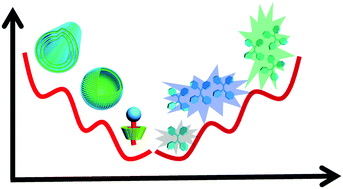
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 11870-11884
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03620A
Host–guest binding motifs based on hyperbranched polymers
Host–guest systems based on hyperbranched polymers together with their unique properties and various applications have been summarized.
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 11728-11743
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03643K
Host–guest chemistry in two-dimensional supramolecular networks
In this feature article, we survey recent developments in host–guest chemistry studied in surface-adsorbed physisorbed supramolecular networks.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 11465-11487
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC05256H
Molecular tweezers for lysine and arginine – powerful inhibitors of pathologic protein aggregation
Molecular tweezers prevent tau deposition in mouse brains.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 11318-11334
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04640A
Precise protein assembly of array structures
The assembly of proteins into various nano-objects with regular and periodic microstructures, i.e. protein arrays, is a fast-growing field in materials science.
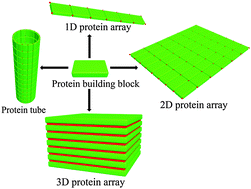
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10595-10605
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04190F
Molecular recognition and activation by polyaza macrocyclic compounds based on host–guest interactions
This paper highlights the recent progress in the recognition and activation of molecules and anions by polyaza macrocyclic compounds.
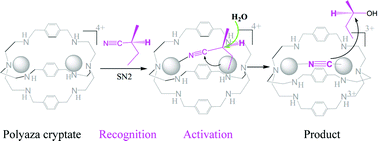
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10322-10337
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03660K
Recent advances in the template-directed synthesis of porphyrin nanorings
This Feature Article reviews recent advances in the template-directed synthesis of porphyrin nanorings, including new templating methods, novel structures, and their applications in host–guest chemistry and artificial light-harvesting.
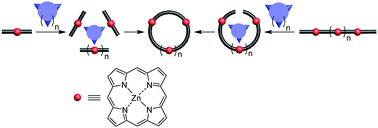
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10205-10216
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04556A
Host–guest chemistry that directly targets lysine methylation: synthetic host molecules as alternatives to bio-reagents
Post-translational methylation regulates the function of hundreds of proteins in profound ways, and is the target of many efforts to use host–guest chemistry to solve biochemical and biological problems.
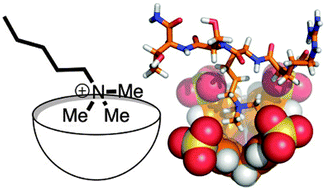
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10093-10108
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04771H
Efficient complexation between pillar[5]arenes and neutral guests: from host–guest chemistry to functional materials
This feature article covers the molecular recognition of pillar[5]arenes and neutral guests, and its application in making supramolecular structures, polymers and functional materials.
![Graphical abstract: Efficient complexation between pillar[5]arenes and neutral guests: from host–guest chemistry to functional materials](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03999E&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9858-9872
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03999E
Anion recognition by oligo-(thio)urea-based receptors
Recent progress in the construction of metal-coordination-assisted and covalently connected oligourea receptors and their anion coordination chemistry is presented.
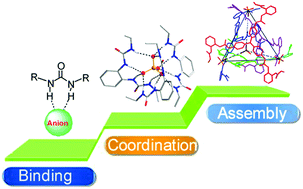
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9614-9627
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03761E
Recent advances in pillar[n]arenes: synthesis and applications based on host–guest interactions
Pillar[n]arenes (n = 5–15) are a novel class of macrocyclic molecules with hydroquinone as the repeating unit linked by methylene bridges at para-positions.
![Graphical abstract: Recent advances in pillar[n]arenes: synthesis and applications based on host–guest interactions](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03641D&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9316-9326
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03641D
Recent progress in stimuli-induced polydiacetylenes for sensing temperature, chemical and biological targets
In this feature article, we covered recent progress in stimuli-induced polydiacetylenes for sensing temperature, chemical and biological targets.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9178-9196
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03584A
Imaging and therapeutic applications of zinc(II)-dipicolylamine molecular probes for anionic biomembranes
Synthetic ZnDPA receptors are used for molecular imaging of disease and targeted therapeutics.
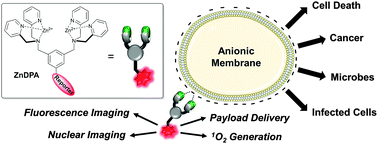
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8787-8801
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03669D
Halogen bonding anion recognition
The development of solution-based anion receptor molecules which exploit halogen bonding interactions is an emerging area of research. This Feature Article reviews recent advances which have been made in this rapidly developing field, surveying the use of iodoperfluoroarene, haloimidazolium and halotriazole/triazolium halogen-bond-donor motifs in anion receptor design and describing the application of mechanically interlocked rotaxane and catenane frameworks as halogen bonding anion host systems.
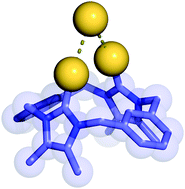
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8645-8658
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03638D
Using low-energy near infrared light and upconverting nanoparticles to trigger photoreactions within supramolecular assemblies
This overview highlights how the high-energy ultraviolet or visible light required to drive photochemical reactions can be overcome by integrating the chromophores into supramolecular structures containing upconverting nanoparticles with trivalent lanthanide dopants (such as Tm3+ and Er3+).

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8636-8644
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03864F
Photoresponsive gelators
We review the different approaches that have been used to form low molecular weight gels that respond to light.
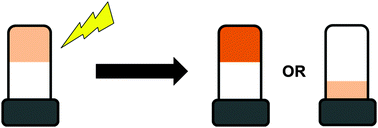
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8196-8206
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03485C
Supramolecular organic frameworks: engineering periodicity in water through host–guest chemistry
Recent advances in emerging homogeneous supramolecular organic frameworks (SOFs) assembled through three-component host–guest chemistry in water are described.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 6351-6362
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC02331B
Macroscopic switches constructed through host–guest chemistry
In this feature article, we discuss recent developments in macroscopic contact angle switches formed by different macrocyclic hosts and highlight the properties of these new functional surfaces and their potential applications.
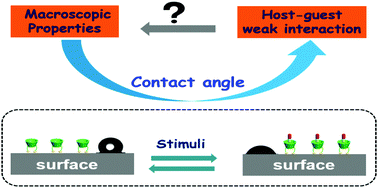
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 4602-4612
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC00338A
Boronic acids for fluorescence imaging of carbohydrates
Carbohydrate biomarkers are particularly important targets for fluorescence imaging given their pivotal role in numerous important biological events. This review highlights the development of fluorescence imaging agents based on boronic acids.
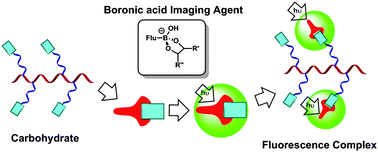
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 3456-3469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC08633G
Construction of cyclic arrays of Zn-porphyrin units and their guest binding at the solid–liquid interface
Cyclic arrays of six zinc-porphyrin units are formed on which fullerene molecules are immobilized at the solid/liquid interface.
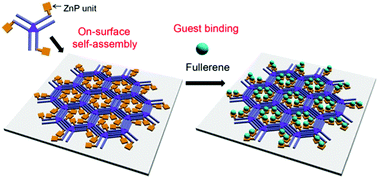
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 14419-14422
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC07121J
Glycosidase activated release of fluorescent 1,8-naphthalimide probes for tumor cell imaging from glycosylated ‘pro-probes’
Glycosylated 4-amino-1,8-naphthalimide derivatives can be selectively hydrolysed in situ by glycosidase enzymes to release the naphthalimide as a fluorescent imaging agent.
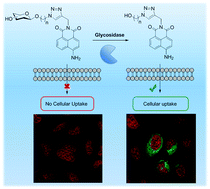
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 13086-13089
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC06451E
Probing and evaluating anion–π interaction in meso-dinitrophenyl functionalized calix[4]pyrrole isomers
We report the comprehensive structural and binding isotherm analyses of meso-3,5-dinitrophenyl-substituted calix[4]pyrroles with a variety of anions, displaying anion–π interactions.
![Graphical abstract: Probing and evaluating anion–π interaction in meso-dinitrophenyl functionalized calix[4]pyrrole isomers](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC04562F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 11139-11142
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04562F
Endohedral dynamics of push–pull rotor-functionalized cages
Push–pull-functionalized ligands carrying molecular rotors assemble to [Pd2L4] coordination cages whose endohedral dynamics are controlled by the substitution pattern, solvent effects and guest encapsulation.
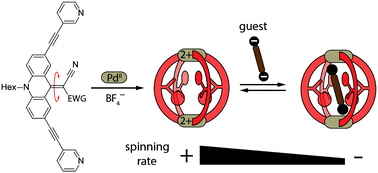
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10411-10414
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04155H
Tuning cation-binding selectivity and capacity via side chain-dependent molecular packing in the solid state
Cavity-containing macrocycles assemble, via side chain-dependent molecular packing, into various nanostructures able to bind cations in varying selectivities and capacities.
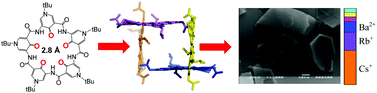
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10361-10364
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04526J
A macrocyclic 1,4-bis(4-pyridylethynyl)benzene showing unique aggregation-induced emission properties
A box-like macrocycle was constructed efficiently (60% yield). Because the intramolecular rotations are restricted by water clusters around the ionic moieties, the box shows unique aggregation-induced emission enhancement property.
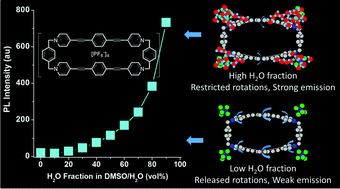
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10365-10368
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC02851A
Cavity-containing supramolecular gels as a crystallization tool for hydrophobic pharmaceuticals
We present two approaches to low-molecular-weight supramolecular gels bearing hydrophobic cavities based on calixarene-containing building blocks.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 10113-10116
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04037C
Aromatic oligureas as hosts for anions and cations
Intramolecularly H-bonded urea moieties of aromatic oligoureas bind anions in modest affinities. Extending backbone length results in a cation-binding cavity, allowing the resultant oligomer to bind both anions and cations.
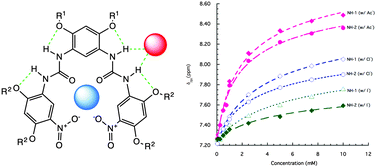
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9905-9908
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03681C
Indomethacin-guided cancer selective prodrug conjugate activated by histone deacetylase and tumour-associated protease
Indomethacin-guided cancer selective prodrug system activated by histone deacetylase and tumour-associated protease.
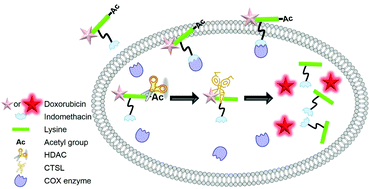
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9965-9968
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04255D
Halogen bonded supramolecular capsules: a challenging test case for quantum chemical methods
By state-of-the-art dispersion corrected density functional theory, the complexation properties of a recently synthesized halogen-bonded capsule with about 400 atoms are investigated and predictions for improved binding affinities are made.
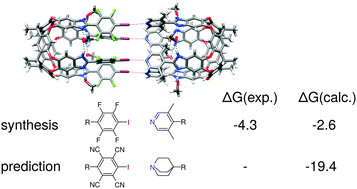
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9893-9896
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03664C
Permselective 2D-polymer-based membrane tuneable by host–guest chemistry
A nanoporous membrane with tuneable permselectivity through non-covalent surface modification has been fabricated by deposition of a cucurbit[6]uril-based 2D polymer film onto a simple support membrane.
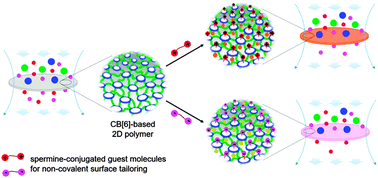
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9676-9678
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03616C
Three-dimensional protein assemblies directed by orthogonal non-covalent interactions
In this report, an orthogonal non-covalent interaction strategy based on specific recognition between sugar and protein, and host–guest interaction, was employed to construct artificial three dimensional (3D) protein assemblies in the laboratory.
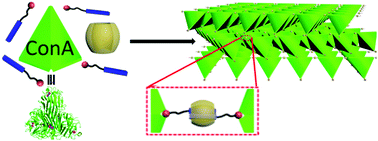
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9687-9690
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04250C
Harnessing solid-state packing for selective detection of chloride in a macrocyclic anionophore
We report the synthesis of a macrocyclic receptor that displays a selective fluorescent response to chloride in the solid state.
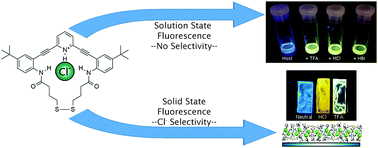
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9506-9509
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03795J
Multifunctional supramolecular vesicles based on the complex of ferrocenecarboxylic acid capped pillar[5]arene and a galactose derivative for targeted drug delivery
Supramolecular vesicles have been constructed based on the host–guest complexation, which show dual-responsiveness and cancer cells targetability.
![Graphical abstract: Multifunctional supramolecular vesicles based on the complex of ferrocenecarboxylic acid capped pillar[5]arene and a galactose derivative for targeted drug delivery](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03637F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9578-9581
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03637F
Crystal structure of a complex between β-glucopyranose and a macrocyclic receptor with dendritic multicharged water solubilizing chains
The first solid state structure of a synthetic receptor-monosaccharide host–guest complex crystallized from water is reported.
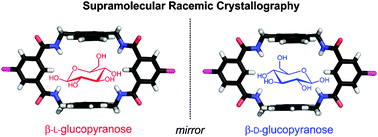
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9355-9358
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04466B
A srikaya-like light-harvesting antenna based on graphene quantum dots and porphyrin unimolecular micelles
A novel hybrid light-harvesting antenna with a srikaya-like structure of multi-graphene quantum dots (GQDs) as donors and one porphyrin unimolecular micelle as the acceptor was constructed through electrostatic self-assembly.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 9394-9397
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03595G
M12L8 metallo-supramolecular cube with cyclotriguaiacylene-type ligand: spontaneous resolution of cube and its constituent host ligand
(±)-Tris-(4-methylthiazolyl)cyclotriguaiacylene forms chirally resolved clathrate complexes and self-assembles with Ag(I) to form a homochiral cubic coordination cage with spontaneous resolution.
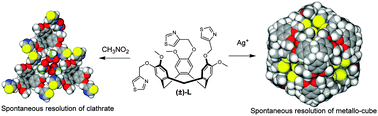
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8699-8702
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04130B
Using steric bulk for selective recognition; blocking the binding site to differentiate guests
Amenable to bendable: blocking the binding cleft enhances selectivity for flexible guests.
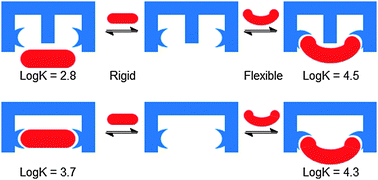
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8719-8721
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04549A
Coumarin-decorated Schiff base hydrolysis as an efficient driving force for the fluorescence detection of water in organic solvents
A Schiff base bearing coumarin is found to be an excellent indicator of trace amounts of moisture in organic solvents.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8675-8678
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC04285F
4-Methylcoumarin-bridged fluorescent responsive cryptand: from [2+2] photodimerization to supramolecular polymer
A fluorescent responsive BMP32C10-based cryptand host was successfully synthesized by introducing a 4-methylcoumarin group to the third arm of the cryptand.
![Graphical abstract: 4-Methylcoumarin-bridged fluorescent responsive cryptand: from [2+2] photodimerization to supramolecular polymer](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03624D&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8715-8718
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03624D
Design and synthesis of squaramide-based MOFs as efficient MOF-supported hydrogen-bonding organocatalysts
Herein, we utilize a new, squaramide-based ligand, combined with a postsynthetic exchange (PSE) synthetic approach to prepare a series of Cu(II)–squaramide MOFs that are active catalysts for the Friedel–Crafts reaction.
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8585-8588
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03190K
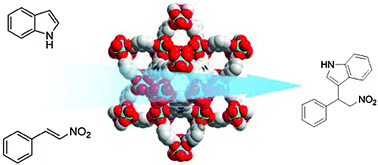
Predictive recognition of native proteins by cucurbit[7]uril in a complex mixture
The recognition of human growth hormone (hGH) by the synthetic host molecule cucurbit[7]uril (Q7) was predicted on the basis of its N-terminal phenylalanine. A resin presenting Q7 groups was prepared and shown to recognize hGH and insulin in the context of human serum.
![Graphical abstract: Predictive recognition of native proteins by cucurbit[7]uril in a complex mixture](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03193E&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8537-8540
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03193E
Ship in a breakable bottle: fluoride-induced release of an organic molecule from a Pr(III)-linked molecular cage
A 3-dimensional networked molecular cage, NMC-1, has been synthesized that acts like a ‘molecular ship’ in a ‘breakable bottle’.
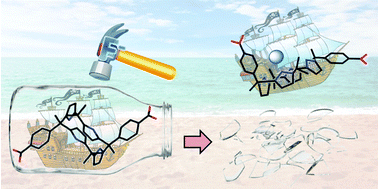
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8514-8517
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03471C
Are two better than one? Comparing intermolecular and intramolecular indicator displacement assays in pyrophosphate sensors
Pyrophosphate recognition using indicator displacement assays is compared to that of analogous receptors with covalently attached indicators.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8463-8466
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03680E
Fluorescent zinc and copper complexes for detection of adrafinil in paper-based microfluidic devices
Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes are used in the recognition and sensing of adrafinil through an easy-to-detect fluorescence response.
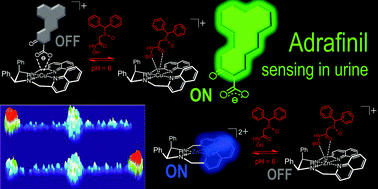
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8279-8282
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03640F
Light-triggered reversible “one-to-two” morphological transition in a “latent double-amphiphilic” linear-hyperbranched supramolecular block copolymer
This work reports a light-responsive reversible “one-to-two” morphological transition from vesicles to nanosheets and nanofibers in linear-hyperbranched supramolecular block copolymers.
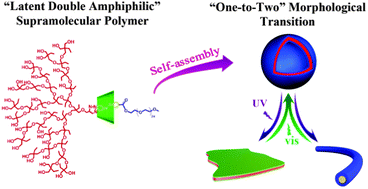
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8223-8226
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03445D
Tetrameric psuedo-peptide receptors with allosteric properties
This paper reports the binding properties of tetrameric pseudo-peptide receptors for protonated cytidines.
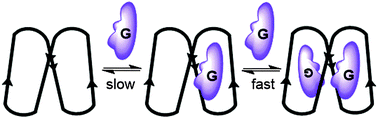
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8103-8106
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03296F
Supramolecular protection from the enzymatic tyrosine phosphorylation in a polypeptide
Two pseudopeptidic cages bind the EYE peptide motif of poly(EY) in buffered water, as shown by NMR and fluorescence spectroscopy. This supramolecular interaction protects the Tyr residues from the enzymatic phosphorylation by PTK.

Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8142-8145
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03875A
2-Methylresorcinarene: a very high packing coefficient in a mono-anion based dimeric capsule and the X-ray crystal structure of the tetra-anion
Mono- and tetra-deprotonated 2-methylresorcinarene anions (1 and 2) as their trans-1,4-diammoniumcyclohexane (TDAC)2+ inclusion complexes are reported.
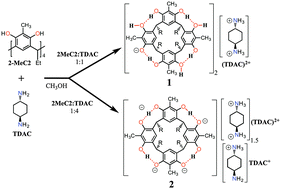
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8115-8118
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03289C
Selective precipitation of alkyl dihalides using a newly synthesized water-soluble bisphosphorylpillar[5]arene
Bisphosphorylpillar[5]arene H2 binds strongly to alkyldiammonium ions and alkyl dihalides. The halogen bonds between H2 and alkyl dihalides lead to the rapid precipitation of the complex in water.
![Graphical abstract: Selective precipitation of alkyl dihalides using a newly synthesized water-soluble bisphosphorylpillar[5]arene](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC03494B&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 8075-8078
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03494B
Lower critical solution temperature (LCST) phase behaviour of an ionic liquid and its control by supramolecular host–guest interactions
Unique LCST phase behaviour of imidazolium-based ionic liquids is reported, which can be controlled by concentration, the choice of cation, anion and solvent, and by supramolecular complex formation. MD simulations provide insight into the molecular basis of this LCST phenomenon.
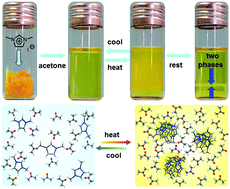
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7970-7973
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC02838A
Quantitative analysis of modeled ATP hydrolysis in water by a colorimetric sensor array
A self-assembled and colorimetric sensor assay is utilized to monitor a model of a metabolic reaction where ATP is hydrolyzed to pyrophosphate and AMP.
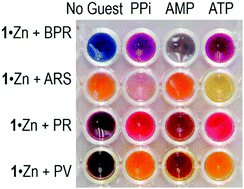
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7838-7841
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC02923J
Chloride anion transporters inhibit growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro
Anion transporters were tested for antimicrobial activity and shown to inhibit the growth of MRSA in vitro.
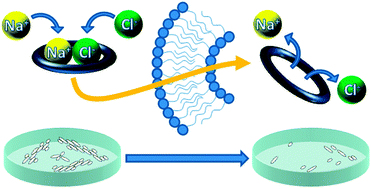
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7560-7563
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03645G
Fluorescence enhancement through the formation of a single-layer two-dimensional supramolecular organic framework and its application in highly selective recognition of picric acid
A novel two-dimensional (2D) supramolecular organic framework (SOF) has been assembled, which was further used as a fluorescent chemosensor to detect picric acid with high selectivity and sensitivity.
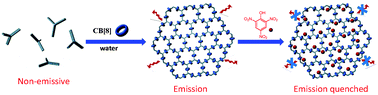
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7588-7591
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03631G
Influence of nucleobase stoichiometry on the self-assembly of ABC triblock copolymers
ABC triblock copolymers bearing adenine- and thymine-functionalized external blocks self-assembled into long-range, ordered lamellar microphase-separated morphologies on non-patterned substrates.
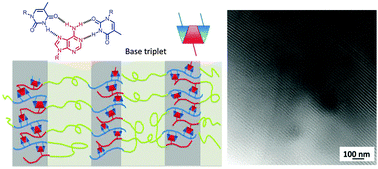
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7564-7567
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03502G
Small molecule recognition of mephedrone using an anthracene molecular clip
An anthracene molecular probe has been synthesised and shown to target mephedrone, a stimulant drug from the cathinone class of new psychoactive substances (NPS).
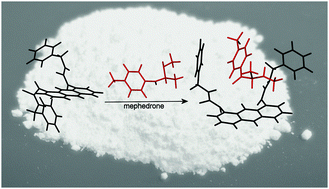
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7474-7477
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03404G
β-Perfluoroalkyl-substituted pyrrole as an anion-responsive π-electronic system through a single NH moiety
A pyrrole derivative possessing two perfluorohexyl (C6F13) chains at the β-positions was synthesized. The significant electron-withdrawing properties of the β-perfluoroalkyl chains induced fascinating anion-binding behaviour.
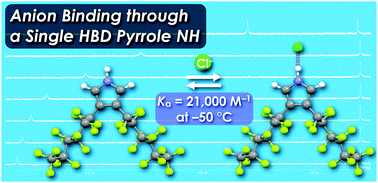
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 7364-7367
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03619H
Redox-responsive host–guest system using redox-active pillar[5]arene containing one benzoquinone unit
Pillar[5]arene with one benzoquinone formed weak complex with a guest, while pillar[5]arene containing one hydroquinone strongly captured the guest.
![Graphical abstract: Redox-responsive host–guest system using redox-active pillar[5]arene containing one benzoquinone unit](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC02777F&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 6479-6481
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC02777F
A high-yield synthesis of [m]biphenyl-extended pillar[n]arenes for an efficient selective inclusion of toluene and m-xylene in the solid state
[m]Bp-ExPn with a rigid and nanometer-sized cavity, as an extended version of pillar[n]arene by replacing 1,4-dimethoxybenzene monomers with biphenyl entities, was successfully designed and synthesized. Intriguingly, [m]Bp-ExPn possesses a wide array of potential applications in the purification of petrochemicals.
![Graphical abstract: A high-yield synthesis of [m]biphenyl-extended pillar[n]arenes for an efficient selective inclusion of toluene and m-xylene in the solid state](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC01892K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 5804-5807
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC01892K
Oxatub[4]arene: a molecular “transformer” capable of hosting a wide range of organic cations
Oxatub[4]arene was found to be able to host a wide range of organic cations. This strong binding ability is believed to originate from its four interconvertible and deep-cavity conformers.
![Graphical abstract: Oxatub[4]arene: a molecular “transformer” capable of hosting a wide range of organic cations](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C6CC01052K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2016)
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 5666-5669
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC01052K
A G4·K+ hydrogel that self-destructs
A G4-quartet based hydrogel formed by self-assembly of borate esters of 5′-deoxy-5′-iodoguanosine (5′-IG 2) undergoes in situ cyclization to give 5′-deoxy-N3,5′-cycloguanosine (5′-cG 3). Formation of 5′-cG 3 causes self-destruction of the gel. This intramolecular cyclization can be used to release nucleoside analogs that have been pre-incorporated into the gel network.
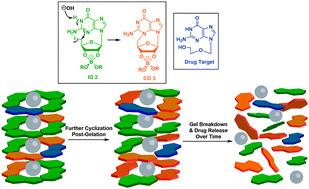
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 5037-5040
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC01494A
Thermo-responsive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) and tetraphenylethene hybrids for stimuli-responsive photoluminescence control
Poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) (POx), a typical thermo-responsive polymer, was conjugated with a tetraphenylethene derivative, having aggregation induced emission behavior, towards the thermal control of their fluorescence emission.
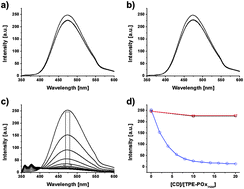
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 4152-4155
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC00722H
Pyrene-based heparin sensors in competitive aqueous media – the role of self-assembled multivalency (SAMul)
Simple functionalised pyrene derivatives can achieve ratiometric sensing of heparin with the precise sensing mechanism depending on whether the sensor self-assembles into a multivalent ligand display.
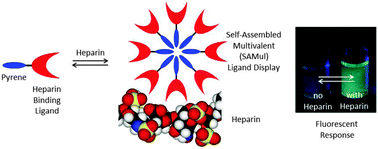
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 3785-3788
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC00163G
Crosslinked dendronized polyols as a general approach to brighter and more stable fluorophores
Fluorescent, aqueous-soluble, crosslinked dendronized polyols (CDPs) are obtained through a sequential process involving ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP), intra-chain ring-closing metathesis (RCM), and hydrolysis.
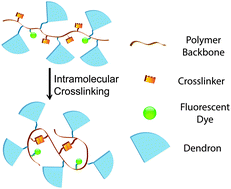
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 3781-3784
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC09430E
Moving systems of polar dimeric capsules out of thermal equilibrium by light irradiation
By inserting stimuli-responsive groups (azobenzene) in hetero-dimeric capsules, we are able to modify the equilibrium state of the system and the exchange between different host–guest assemblies in a reversible manner.
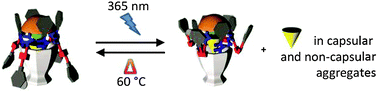
Chem. Commun., 2016,52, 3046-3049
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC10403C
About this collection
This web themed collection, guest edited by Feihe Huang, Jonathan Sessler, Christoph Schalley and Jonathan Steed aims to highlight the current achievements and future perspectives in the exciting field of “Host–guest chemistry”. It covers hostguest complexes based on crown ethers, cyclodextrins, calixarenes, cucurbiturils, pillararenes, as well as more complex supramolecular systems such as molecular switches, molecular machines, supramolecular polymers, supramolecular gels, macrocyclic amphiphiles and supramolecular amphiphiles.The issue also focuses on the recent achievements in the search of novel host–guest recognition motifs, exploration of novel macrocyclic hosts, novel stimuli-responsiveness, development of advanced characterization methods, and the potential applications of host–guest chemistry