Themed collection Nanotoxicology

Nanoparticle–blood interactions: the implications on solid tumour targeting
This review examines nanoparticle–blood interactions, their implications on solid tumour targeting, and provides an outlook to guide future nanoparticle design.
Chem. Commun., 2015,51, 2756-2767
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC07644C
The nanoparticle biomolecule corona: lessons learned – challenge accepted?
Besides the wide use of engineered nanomaterials (NMs) in technical products, their applications are not only increasing in biotechnology and biomedicine, but also in the environmental field.

Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015,44, 6094-6121
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00217F
Silver nanoparticles – wolves in sheep's clothing?
We review the cellular and molecular mechanisms behind silver nanoparticle toxicity and their intracellular fate. In addition, the role of silver ions in the toxicity of silver nanoparticles is discussed.
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 563-575
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00110A
Upconverting nanoparticles: assessing the toxicity
Based on a survey of existing studies, low nanotoxicity of lanthanide doped upconverting nanoparticles holds promise for their safety and suitability for biomedical detection and imaging.
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015,44, 1561-1584
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00177J
Genotoxicity of metal oxide nanomaterials: review of recent data and discussion of possible mechanisms
An increasing number of publications report genotoxicity studies for metal oxide and silica nanomaterials which may induce different kinds of genotoxicity via a variety of mechanisms.
Nanoscale, 2015,7, 2154-2198
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR06670G
Perturbation of physiological systems by nanoparticles
Nanoparticle translocation and potential toxicity at the physiological system level.
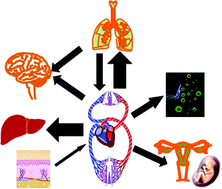
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43, 3762-3809
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60338E
Physical, chemical, and in vitro toxicological characterization of nanoparticles in chemical mechanical planarization suspensions used in the semiconductor industry: towards environmental health and safety assessments
This tutorial review focuses on aqueous slurries of dispersed engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) used in chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) for polishing wafers during manufacturing of semiconductors.
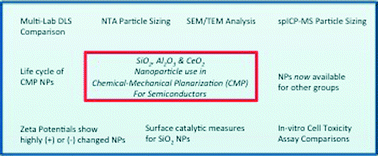
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2015,2, 227-244
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00046G
Toxicity of halloysite clay nanotubes in vivo: a Caenorhabditis elegans study
Halloysite nanotubes in the C. elegans foregut (merged enhanced dark-field and fluorescence images).

Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2015,2, 54-59
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EN00135D
In vitro fluorescence and phototoxicity of β-SnWO4 nanoparticles
The nanoparticulate photocatalyst β-SnWO4 is transfected into human liver carcinoma cells (HepG2).
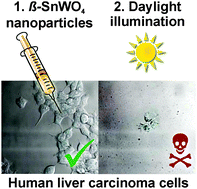
Chem. Commun., 2014,50, 6600-6603
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC00308J
Impacts of gold nanoparticle charge and ligand type on surface binding and toxicity to Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria
Higher cationic charge density on nanoparticles is correlated with higher toxicity to bacteria.
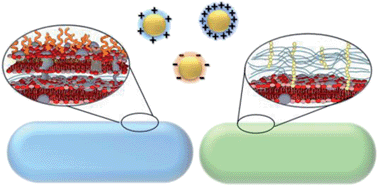
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 5186-5196
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00792E
Silica nanoparticles induced the pre-thrombotic state in rats via activation of coagulation factor XII and the JNK-NF-κB/AP-1 pathway
The pre-thrombotic state induced by SiNPs via the interaction between platelet activation, coagulation hyperfunction, anti-coagulation and fibrinolytic resistance.
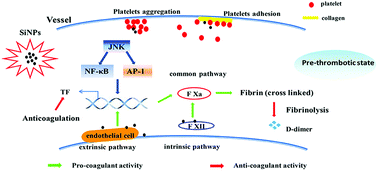
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 1453-1464
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TX00118H
Partial protection of N-acetylcysteine against MPA-capped CdTe quantum dot-induced neurotoxicity in rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons
CdTe QD exposure caused death and apoptosis of rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons via generating reactive oxygen species and increasing intracellular calcium levels, which could be reversed by a common antioxidant NAC.
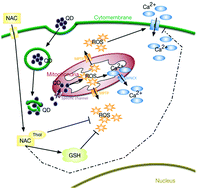
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 1613-1622
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TX00127G
Synthesis and in vivo toxicity assessment of CdSe:ZnS quantum dots functionalized with EDTA-Bis-Cysteamine
Synthesis and in vivo toxicity assessment of radiolabeled Bis-ligand functionalized core shell quantum dot.
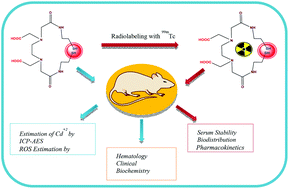
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 1416-1425
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TX00090D
Toxicity of exfoliated-MoS2 and annealed exfoliated-MoS2 towards planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells in the presence of electron donor
EDTA, as an electron donor, used for the first time in the antibacterial study of MoS2.
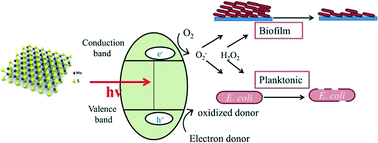
Environ. Sci.: Nano, 2015,2, 370-379
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00031A
Biocompatibility studies on lanthanum oxide nanoparticles
Biocompatibility on lanthanum oxide nanoparticles (LONP) were investigated. LONP was cytotoxic to balb/3T3 cells via release of ROS. LONP and/or extracts were non-irritant, non-sensitizer and non-mutagenic. LONP extracts did not show acute systemic toxicity. Whereas, LONP exerted hepatotoxicity following oral administration.
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 1037-1044
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00198B
Do poly(epsilon-caprolactone) lipid-core nanocapsules induce oxidative or inflammatory damage after in vivo subchronic treatment?
Among the toxicity mechanisms linked to nanoparticles (NPs), oxidative stress (OS) and inflammation are, in general, presumed to mediate their toxicological responses.
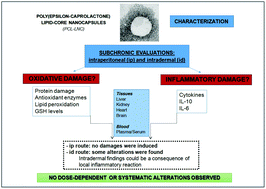
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 994-1005
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TX00030K
Toxicity mechanism of graphene oxide and nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots in RBCs revealed by surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy
GO can extract the lipid bilayer of RBCs membranes, resulting in hemolysis and aberrant forms. In contrast, GQDs just disturb the structure and conformation of the lipid, resulting in only aberrant cells.

Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 885-894
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00138A
Quantum dot induced cellular perturbations involving varying toxicity pathways
Quantum dots (QD) with varying surface chemistry can have an impact on cellular uptake and a range of indicators for cell perturbation.
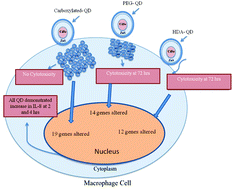
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 623-633
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00175C
Uptake of gold nanoparticles in primary human endothelial cells
Single-particle resolution techniques show that endothelial cells internalise 80 nm unmodified gold nanoparticles by endocytosis with subsequent transport to vesicles.
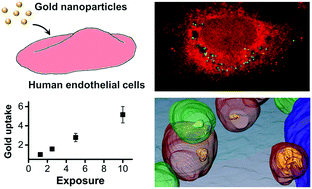
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 655-666
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00061G
Toxic effect comparison of three typical sterilization nanoparticles on oxidative stress and immune inflammation response in rats
Three typical sterilization nanoparticles can cause oxidative stress and immune inflammation response to rats, and their toxicities showed significant differences.
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 486-493
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00154K
Cerium dioxide nanoparticles protect against oxidative stress induced injury through modulation of TGF-β signalling
Cerium oxide nanoparticles attenuate oxidative stress induced alterations in TGF-β signalling pathway members.
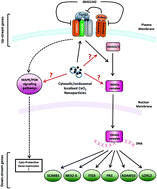
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 464-475
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00210E
A gene signature for gold nanoparticle-exposed human cell lines
A unique four-gene signature for AuNP exposure was identified using the cDNA microarray and evaluated by qPCR and biological assays in mammalian cell lines.
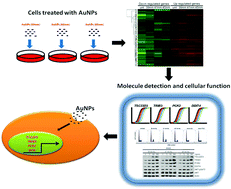
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 365-375
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00181H
Cytotoxic effects and cellular oxidative mechanisms of metallic nanoparticles on renal tubular cells: impact of particle solubility
Many uncertainties remain regarding the potential toxic effect of nanoparticles.
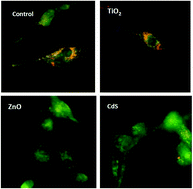
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 409-422
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00184B
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhance macrophage activation by LPS through a TLR4-dependent intracellular pathway
TiO2 nanoparticles enhance LPS-dependent NO production and cytokine secretion through a mechanism that involves TLR4-mediated p38-signalling and requires phagocytosis.
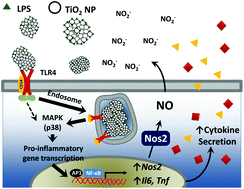
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 385-398
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00193A
Transgenerational safety of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and the underlying cellular mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans
Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) are safe for environmental release.
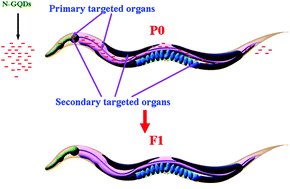
Toxicol. Res., 2015,4, 270-280
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00123K
Taurine attenuates nano-copper-induced oxidative hepatic damage via mitochondria-dependent and NF-κB/TNF-α-mediated pathway
Effect of taurine of propidium iodine staining on nano copper induced liver tissue.

Toxicol. Res., 2014,3, 474-486
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TX00030G
Computer-aided nanotoxicology: assessing cytotoxicity of nanoparticles under diverse experimental conditions by using a novel QSTR-perturbation approach
This work focuses on creating a QSTR-perturbation model to enable computer-aided predictions of cytotoxicity of nanoparticles under dissimilar experimental conditions.
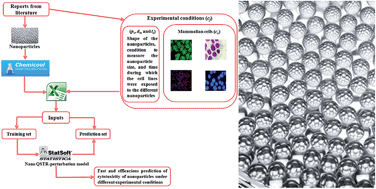
Nanoscale, 2014,6, 10623-10630
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR01285B
The toxic effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes are linked to the phagocytic ability of cells
We show here that the phagocytic ability of cells exposed to single-walled carbon nanotubes is directly correlated to the toxic effects to the cells.
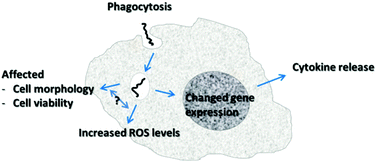
Toxicol. Res., 2014,3, 228-241
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TX50099C
A general mechanism for intracellular toxicity of metal-containing nanoparticles
We demonstrate a general mechanism for the toxicity induced by metal-containing NPs, named “lysosome-enhanced Trojan horse effect”, which provides design rules to engineer safer NPs.
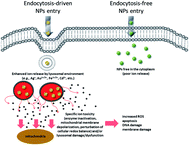
Nanoscale, 2014,6, 7052-7061
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR01234H
Reducing ZnO nanoparticle cytotoxicity by surface modification
ZnO surface properties control cytotoxicity by regulating nanoparticle uptake rather than by altering either intracellular or extracellular Zn dissolution rates.
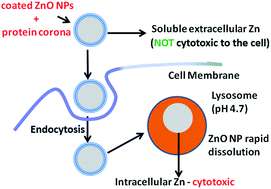
Nanoscale, 2014,6, 5791-5798
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR00458B
Reaction of monocytes to polystyrene and silica nanoparticles in short-term and long-term exposures
The increased use of nanoparticles (NPs) in industrial, health and consumer products may cause short-term and long-term cellular effects.
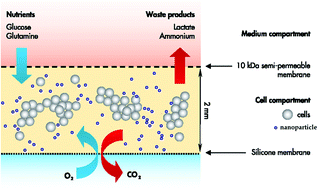
Toxicol. Res., 2014,3, 86-97
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TX50112D
Bicontinuous cubic phase nanoparticle lipid chemistry affects toxicity in cultured cells
This study has shown that the haemolytic activity and toxicity of phytantriol cubosomes is considerably greater than that of glycerol monooleate cubosomes.
Toxicol. Res., 2014,3, 11-22
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TX50075F
Comparative cytotoxicity of cadmium forms (CdCl2, CdO, CdS micro- and nanoparticles) in renal cells
Cadmium (Cd) is a potent selective toxicant that preferentially accumulates in the kidneys where it is known to induce cellular injury.
Toxicol. Res., 2014,3, 32-41
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TX50063B
About this collection
This web collection contains a selection of articles and reviews on the theme of nanotoxicology. Nanomaterials are used in many industry sectors including the biomedical sciences, catalysis, and much more. As such, it has become increasingly important to investigate the potential risks and health impacts associated with nanomaterial exposure. This collection of papers provides insights into the toxicological effects of rare earth, noble metal, carbon, silica, and lipid nanomaterials in various systems, and the impacts for health and disease.
Additional papers on the theme of nanotoxicology in the environment can be found in the Environmental Science: Nano collection, Guest Edited by Kristin Schirmer and Melanie Auffan: http://rsc.li/nanotox