Themed collection The Chemical Biology of Peptides

Chemical methods for protein site-specific ubiquitination
Chemical methods for protein site-specific ubiquitination are important for the understanding of Ub signaling.
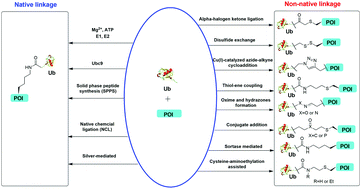
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 450-467
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00215A
Strategies to expand peptide functionality through hybridisation with a small molecule component
This review details discovery strategies and established applications of peptide-small molecule hybrids, classified by the added functionality imparted by the small molecule component.
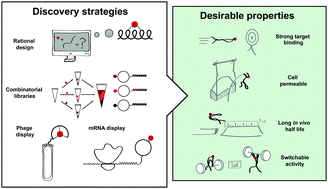
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 151-165
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00167H
Activatable cell-penetrating peptides: 15 years of research
Since the first report on activatable CPPs (ACPPs) in 2004, various methods of activation have been developed. Here, we provide an overview of the different ACPP strategies known to date and summarize the benefits, drawbacks, and future directions.
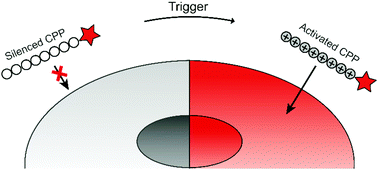
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 192-203
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00114G
Harnessing cyclotides to design and develop novel peptide GPCR ligands
Cyclotides are plant-derived cyclic peptides that have emerged as promising scaffold molecules for designing peptide-based therapeutics. Cyclotide engineering may lead to the development of novel ligands of G protein-coupled receptors with improved pharmacological properties.
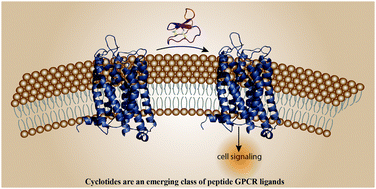
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 177-191
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00062K
Matters of class: coming of age of class III and IV lanthipeptides
In this review, we give a concise overview of the known biosynthetic princples of class III and IV lanthipeptide synthtases.

RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 110-127
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00073F
Targeted disruption of PKC from AKAP signaling complexes
We report the development of AKAP derived, conformationally constrained peptides designed to probe AKAP-localized PKC. The lead peptides, CSTAD5 and CSTAD6 permeate cells, bind PKC, disrupt its scaffolding by AKAPs to inhibit its scaffolded activity.
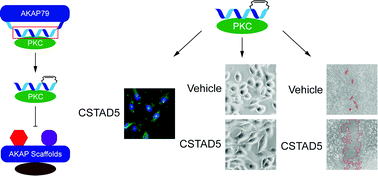
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 1227-1231
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CB00106J
Rational design of a stapled JAZ9 peptide inhibiting protein–protein interaction of a plant transcription factor
A rationally designed stapled JAZ peptide selectively inhibited MYCs, master-regulators of the jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. It is proposed as a novel chemical tool for the analysis of MYC related jasmonate signaling.
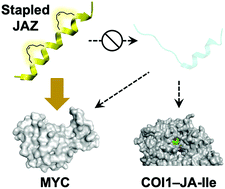
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 499-502
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00204F
Chemical synthesis of a haemathrin sulfoprotein library reveals enhanced thrombin inhibition following tyrosine sulfation
The synthesis and thrombin inhibitory activity of eight homogeneously sulfated variants of the haemathrin proteins from tick saliva is described.
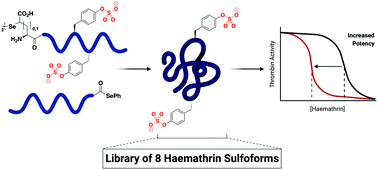
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 379-384
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00146E
A cell permeable bimane-constrained PCNA-interacting peptide
A small, inherently fluorescent macrocyclic peptide constrained with a bimane-linker is cell permeable, and binds the human sliding clamp protein, PCNA, in a 310-helical conformation with nanomolar affinity.
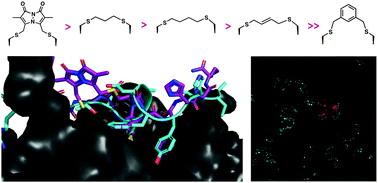
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 1499-1508
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CB00113B
Entropy of stapled peptide inhibitors in free state is the major contributor to the improvement of binding affinity with the GK domain
The significant improvement in the binding affinity of the stapled peptide to the PSD-95 GK domain is mostly contributed by the reduction in the entropy penalty of the stapled peptide due to the restriction in the α-helical structure by stapling in the free state.
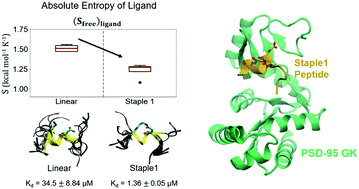
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 1274-1284
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CB00087J
Mitochondria-targeted inhibitors of the human SIRT3 lysine deacetylase
SIRT3 is a mitochondrial lysine deacetylase enzyme, regulating the activity of numerous mitochondrial proteins. Here, we have designed inhibitors of this enzyme, which exhibit selective inhibition of SIRT3 in cells by specific organelle localizing.
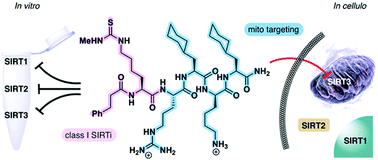
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 627-635
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00216J
Mechanism-based inhibitors of SIRT2: structure–activity relationship, X-ray structures, target engagement, regulation of α-tubulin acetylation and inhibition of breast cancer cell migration
Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) is a protein deacylase enzyme that removes acetyl groups and longer chain acyl groups from post-translationally modified lysine residues. Here, we developed small peptide-based inhibitors of its activity in living cells in culture.
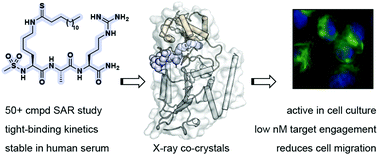
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 612-626
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00036A
Short oligoalanine helical peptides for supramolecular nanopore assembly and protein cytosolic delivery
The helical enhancement of a short oligoalanine peptide scaffold in anionic membranes triggered the supramolecular assembly of a nanopore, which allowed the transport and release of proteins in the cytosol of cells and tissues.
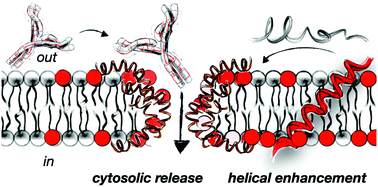
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 503-512
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00103A
Site-specific single point mutation by anthranilic acid in hIAPP8–37 enhances anti-amyloidogenic activity
β-Amino acid based peptidomimetics are attractive scaffolds for therapeutics design towards T2D. They prevent amyloid formation of hIAPP by forming non-fibrillar non-toxic aggregates.
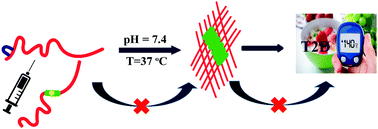
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 266-273
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00178C
A peptidic inhibitor for PD-1 palmitoylation targets its expression and functions
We show for the first time that PD-1 is palmitoylated, identify DHHC9 as the predominant enzyme for its palmitoylation, and reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects on PD-1 stability and functions. Importantly, we also designed PD1-PALM, a competitive inhibitor of PD-1 palmitoylation, and this first-in-class molecule may inspire the development of new checkpoint inhibitors.
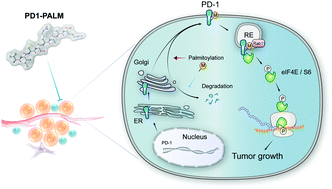
RSC Chem. Biol., 2021,2, 192-205
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00157K
Cyclic peptide scaffold with ability to stabilize and deliver a helical cell-impermeable cargo across membranes of cultured cancer cells
A new helix-loop-helix peptide scaffold with dual ability to transport cargo across cancer cell membranes and disrupt mitochondrial membrane function.
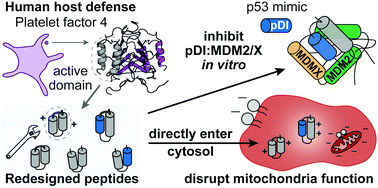
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 405-420
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00099J
Harnessing the PD-L1 interface peptide for positron emission tomography imaging of the PD-1 immune checkpoint
Leveraging interface peptides in PD-L1 for PET imaging of PD-1, providing a new paradigm for radiotracer development.
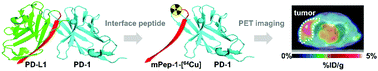
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 214-224
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00070A
Long-range PEG stapling: macrocyclization for increased protein conformational stability and resistance to proteolysis
Long-range stapling of two Asn-linked PEG oligomers via olefin metathesis substantially increases the conformational stability of the WW and SH3 domain tertiary structures and the GCN4 coiled-coil quaternary structure.
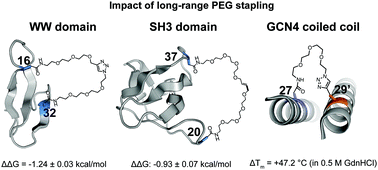
RSC Chem. Biol., 2020,1, 273-280
https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CB00075B
About this collection
Peptides are hugely important biological polymers in living systems, and take on a variety of roles in signalling, the development of disease, natural defence and much more besides. Peptides can be non-ribosomal, oligomeric, cyclic, long, helical, or simple. Chemical biologists are exploring exciting and unique aspects of peptides in their research, including in drug discovery, the inhibition of peptide-peptide interactions, signal disruption, labelling, post-translational modifications, and countless other new applications.
Much of this exciting and ground-breaking research into and of peptides has been published in RSC Chemical Biology and is collected here for you to explore.
New articles on the topic will be added periodically.