A peptidic inhibitor for PD-1 palmitoylation targets its expression and functions†
Abstract
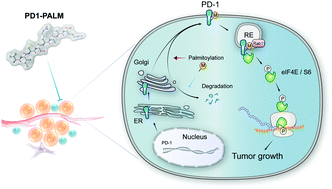
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a crucial anticancer target, but the relatively low response rate and acquired resistance to existing antibody drugs highlight an urgent need to develop alternative targeting strategies. Here, we report the palmitoylation of PD-1, discover the main DHHC enzyme for this modification, reveal the mechanism of its effect on PD-1 protein stability, and rationally develop a peptide for targeting PD-1 expression. Palmitoylation promoted the trafficking of PD-1 to the recycling endosome, thus preventing its lysosome-dependent degradation. Palmitoylation of PD-1, but not of PD-L1, promoted mTOR signaling and tumor cell proliferation, and targeting palmitoylation displayed significant anti-tumor effects in a three-dimensional culture system. A peptide was designed to competitively inhibit PD-1 palmitoylation and expression, opening a new route for developing PD-1 inhibitors and combinatorial cancer immunotherapy.
- This article is part of the themed collections: The Chemical Biology of Peptides and 2021 RSC Chemical Biology HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...