Themed collection Recent advances in the chemical physics of nanoalloys

Recent advances in the chemical physics of nanoalloys
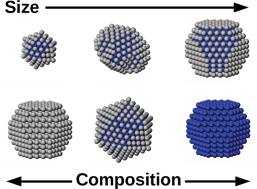
Nanoalloys present a rich variety of structures and properties, which depend on both size and composition, and make them suitable for applications in catalysis, plasmonics, magnetic data storage, and biomedicine.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27920-27921
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP90142A
Intrinsic magnetic properties of bimetallic nanoparticles elaborated by cluster beam deposition
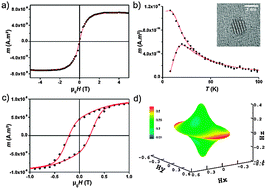
Chemical order effects and intrinsic magnetic properties of well-defined bimetallic L10 CoPt-type, B2 FeRh-type and core/shell CoAu-type nanoalloys.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27996-28004
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00943J
Nanosystems: the use of nanoalloys, metallic, bimetallic, and magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications
There is a growing interest in the use of nanosystems in biomedical applications. In this perspective, we survey current applications and advances in magnetic nanoparticles used in biomedical applications, so as to understand the material properties that can pave the way for the use of nanoalloys.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27981-27995
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00831J
Magnetic and noble metal nanocomposites for separation and optical detection of biological species
Nanoalloys and nanocomposites are widely studied classes of nanomaterials within the context of biological systems. This article presents an overview of methods currently used for nanoalloy and nanocomposite synthesis and characterization, focusing on Au-Ag and FexOy@Au structures as primary components in detection platforms for plasmonic and magnetically enabled plasmonic bio-sensing.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27968-27980
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01219H
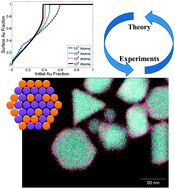
Segregation in bimetallic nanoparticles
Theoretical models and experimental results for segregation in bimetallic nanoparticles are discussed and compared in this perspective.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27940-27951
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01492A
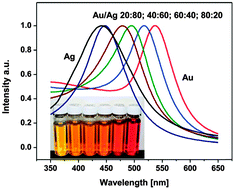
Optical properties of nanoalloys
Optical absorption spectra of bare (left) and monolayer-protected (right) metal nanoalloys.
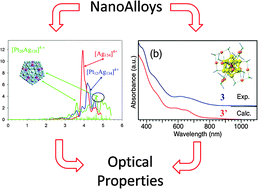
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27952-27967
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00498E
Thermodynamics of nanoalloys
Nanoalloys exhibit composition- and size-dependent shapes that are influenced by temperature at equilibrium.
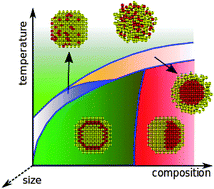
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 27922-27939
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00274E
Chemical ordering phenomena in nanostructured FePt: Monte Carlo simulations
Selective surface-induced destabilization of L10 superstructure variants is simulated in FePt nanostructures of diverse dimensionalities.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28394-28406
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01054C
Synthesis and thermodynamics of Ag–Cu nanoparticles
A melting temperature depression of around 14 °C for Ag–Cu nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical reduction method has been experimentally measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).
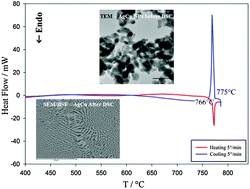
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28387-28393
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP02058A
Orbit and spin resolved magnetic properties of size selected [ConRh]+ and [ConAu]+ nanoalloy clusters
XMCD measurements on doped Co clusters in the gas phase reveal their fluctuating spin and orbital magnetic moments.
![Graphical abstract: Orbit and spin resolved magnetic properties of size selected [ConRh]+ and [ConAu]+ nanoalloy clusters](/EN/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C5CP01923K&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2015)
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28372-28378
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01923K
Surface plasmons in quantum-sized noble-metal clusters: TDDFT quantum calculations and the classical picture of charge oscillations
The dynamics of the electronic density corresponds to a collective charge oscillation, albeit influenced by the inhomogeneity of noble metals.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28379-28386
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01177A
Phase diagrams of nanoalloys: influence of size and morphology
A non-monotonous variation of the critical temperature as a function of the length of the nanotubes.
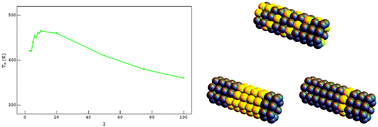
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28347-28353
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01593F
Platinum–ruthenium bimetallic clusters on graphite: a comparison of vapor deposition and electroless deposition methods
A comparison of bimetallic Pt–Ru clusters grown by vapor deposition (VD) and electroless deposition (ED) of Pt on Ru seed clusters.
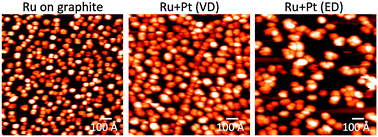
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28354-28363
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00075K
Multiscale approach for studying melting transitions in CuPt nanoparticles
Melting temperature dependence on the radius of CuPt clusters by CALPHAD and atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. The formation of a supercooled region for 3 nm particle is highlighted by the huge hysteresis during the freezing process.
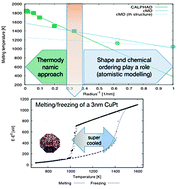
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28364-28371
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01096A
Quasi-combinatorial energy landscapes for nanoalloy structure optimisation
Nanoalloy energy landscapes explored in continuous and discrete metric spaces simultaneously.
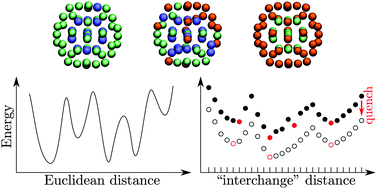
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28331-28338
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01198A
New insights into the mixing of gold and copper in a nanoparticle from a structural study of Au–Cu nanoalloys synthesized via a wet chemistry method and pulsed laser deposition
Insights into the mixing of gold and copper atoms at the nanoscale for the controlled synthesis of Au–Cu nanoalloys.
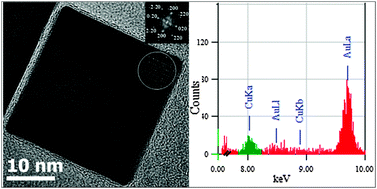
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28339-28346
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01491C
Theoretical study of the structures and chemical ordering of cobalt–palladium nanoclusters
Global optimization of 1 : 1 compositions of (Co–Pd)N/2 up to N = 150 and all compositions of 34- and 38-atom binary clusters has been performed using a genetic algorithm, coupled with the Gupta empirical potential to model interatomic interactions.
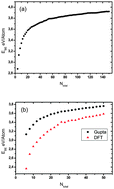
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28311-28321
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01029B
Heat-induced spinodal decomposition of Ag–Cu nanoparticles
The predicted spinodal decomposition of metastable Ag–Cu nanoparticles was experimentally induced (and detected) by heating on an high temperature X-ray diffractometer (HT XRD).
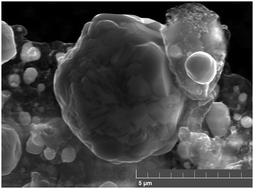
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28277-28285
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00198F
Challenges of modelling real nanoparticles: Ni@Pt electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Core–shell nanoparticle properties strongly dependent on cluster size and composition.
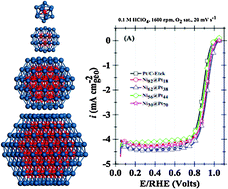
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28286-28297
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00503E
A correlation between thermodynamic properties, thermal expansion and electrical resistivity of Ag–28% Cu nanopowders processed by the mechanical alloying route
The relative electrical resistivity, Gibbs free energy function and crystallite size of the Ag–28% Cu nanopowders as a function of temperature.
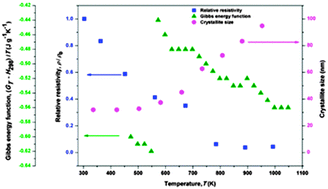
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28322-28330
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01390A
Revealing chemical ordering in Pt–Co nanoparticles using electronic structure calculations and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
PtYCo1−Y-core@Co-rich-subsurface@Pt-shell structure is identified in several nm large Pt–Co particles using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and an optimization method based on density-functional calculations.
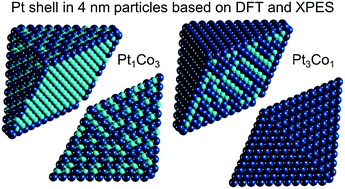
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28298-28310
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01070E
A DFT-based genetic algorithm search for AuCu nanoalloy electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction
The global minimum for a 309-atom icosahedral Au–Cu nanoalloy is identified, with potential application for electrochemical production of CO.
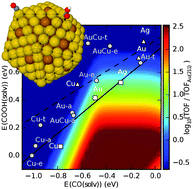
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28270-28276
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00298B
Au–Ag nanoalloy molecule-like clusters for enhanced quantum efficiency emission of Er3+ ions in silica
(Au–Ag)N nanoalloy clusters made up of N = 10–15 atoms increase by an order of magnitude the room temperature photoemission intensity of Er3+ in silica, better than monometallic AuN clusters of the same size.
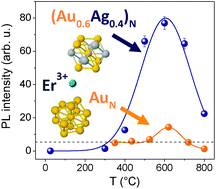
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28262-28269
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01084E
Doped golden fullerene cages
A first-principles investigation of the effect of the doping of golden cages of 32 atoms is proposed.
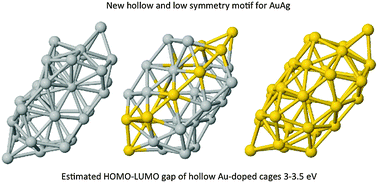
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28256-28261
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01061F
Self-diffusion in nanocrystalline alloys
Operando PXRD shows slow diffusion kinetics of controllable, reversible segregation in a PdAg nanoalloy that is explained by atomistic modeling.
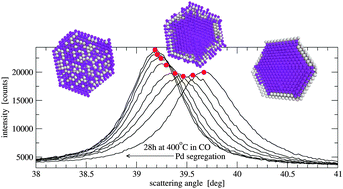
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28250-28255
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00312A
Evolution of structure and local magnetic fields during crystallization of HITPERM glassy alloys studied by in situ diffraction and nuclear forward scattering of synchrotron radiation
In situ transformation of local structure and hyperfine interactions are simultaneously followed in real time during temperature annealing of metallic glasses.
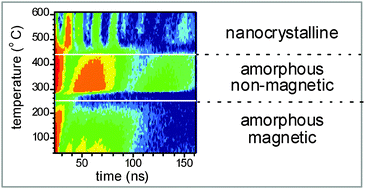
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28239-28249
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00245A
Structural evolution of Ag–Cu nano-alloys confined between AlN nano-layers upon fast heating
The paper presents a first comprehensive experimental investigation of the structural evolution of eutectic Ag–Cu nano-alloys, as confined between inert AlN barriers in a nano-multilayered configuration, upon fast heating.
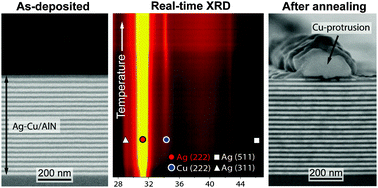
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28228-28238
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00782H
Ageing of out-of-equilibrium nanoalloys by a kinetic mean-field approach
Ageing of nanoalloys: the nanoparticle passes through a metastable onion-like configuration on its way to its equilibrium core–shell structure.
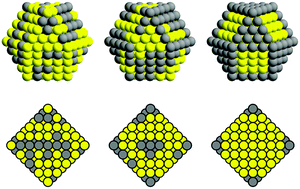
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28193-28199
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00600G
Thermally-induced chemical-order transitions in medium–large alloy nanoparticles predicted using a coarse-grained layer model
A new coarse-grained layer model (CGLM) predicts symmetry-breaking transitions in Pt–Ir nanoparticles furnishing a unique nanophase diagram.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28211-28218
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00497G
AuRu/AC as an effective catalyst for hydrogenation reactions
AuRu bimetallic catalysts have been prepared by sequential deposition of Au on Ru or vice versa obtaining different nanostructures: when Ru has been deposited on Au, a Aucore–Rushell has been observed, whereas the deposition of Au on Ru leads to a bimetallic phase with Ru enrichment on the surface.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28171-28176
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00632E
Structural evolution of an intermetallic Pd–Zn catalyst selective for propane dehydrogenation
Formation of PdZn intermetallic nanoalloys selective for propane dehydrogenation tracked using in situ synchrotron XRD.
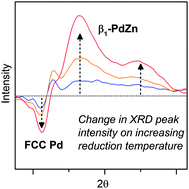
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28144-28153
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00222B
CO oxidation catalysed by Pd-based bimetallic nanoalloys
Density functional theory based global geometry optimization has been used to demonstrate the crucial influence of the geometry of the catalytic cluster on the energy barriers for the CO oxidation reaction over Pd-based bimetallic nanoalloys.
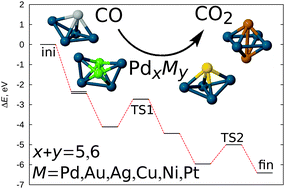
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28010-28021
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00889A
Role of the nanocrystallinity on the chemical ordering of CoxPt100−x nanocrystals synthesized by wet chemistry
In situ heating TEM reveals the influence of the nanocrystallinity on the ordering transition of CoPt nanoalloys.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28162-28170
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01062D
Influence of Sn content on the hydrogenation of crotonaldehyde catalysed by colloidally prepared PtSn nanoparticles
For increasing tin concentrations PtSn nanoparticles of similar size show a monotonically increasing selectivity towards crotylalcohol and a volcano like activity.
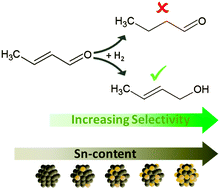
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28186-28192
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00280J
Ab initio and anion photoelectron study of AunRhm (n = 1–7, m = 1–2) clusters
Anion photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT calculations study on AunRhm (n = 1–7 and m = 1–2). PES spectra, vertical and adiabatic detachment energies, are compared. The characteristic planarity for gold clusters is preserved for many of the bimetallic clusters.
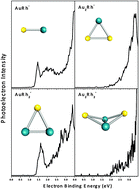
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28219-28227
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00115C
Direct observation of the dealloying process of a platinum–yttrium nanoparticle fuel cell cathode and its oxygenated species during the oxygen reduction reaction
Size-selected 9 nm PtxY nanoparticles have recently shown an outstanding catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction, representing a promising cathode catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs).
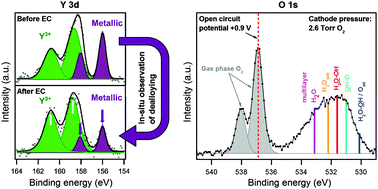
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28121-28128
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00283D
Modelling of phase diagrams of nanoalloys with complex metallic phases: application to Ni–Sn
A novel method for modelling of size-dependent phase diagrams combines the CALPHAD method and ab initio calculations of surface stresses.
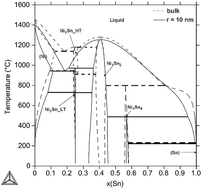
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28200-28210
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00281H
Towards optimal seeding for the synthesis of ordered nanoparticle arrays on alumina/Ni3Al(111)
Adsorption and nucleation of different transition metals on alumina/Ni3Al(111) have been studied to shed light on the first stages of the synthesis of supported nanoparticles, rationalizing the experimental evidence that Pd seeding is the optimal choice to give rise to highly ordered patterns.
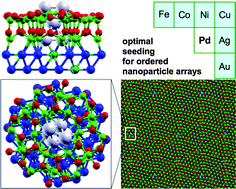
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28154-28161
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00304K
Geometric and electronic structure and magnetic properties of Fe–Au nanoalloys: insights from ab initio calculations
Fe–Au nanoparticles maintain almost a constant magnetic moment of ∼2.8 μB, which is 27% enhancement from the bulk value.
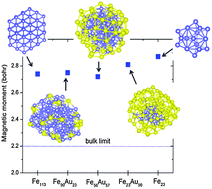
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28177-28185
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00299K
Kinetic analysis of the reduction of 4-nitrophenol catalyzed by Au/Pd nanoalloys immobilized in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes
We present a detailed study of the catalytic activity of Au/Pd nanoalloys with Au : Pd molar ratio 75 : 25 synthesized using spherical polyelectrolyte brushes (SPB) as carrier system.
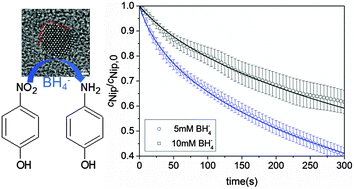
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28137-28143
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00519A
Synergistic effects of Ir–Au/TiO2 catalysts in the total oxidation of propene: influence of the activation conditions
Enhanced catalytic activity of the bimetallic Ir–Au/TiO2 catalyst, prepared by sequential deposition–precipitation with urea, in the total oxidation of propene due to a surface Ir0–Au0 synergism.
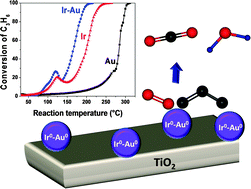
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28022-28032
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00590F
Au–Rh and Au–Pd nanocatalysts supported on rutile titania nanorods: structure and chemical stability
Au–Rh and Au–Pd nanoalloys synthesized by colloidal methods and immobilized on rutile titania nanorods are more stable than their monometallic counterparts for tetralin hydrogenation in the presence of sulfur.
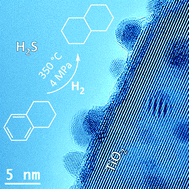
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28112-28120
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00249D
Modular construction of size-selected multiple-core Pt–TiO2 nanoclusters for electro-catalysis
Modular construction of platinum–titanium dioxide clusters, which exhibit multiple Pt cores with a preferred size of 30 ± 6 atoms.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28005-28009
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00285K
Dynamics and stability of icosahedral Fe–Pt nanoparticles
An ab initio theoretical study on icosahedral Fe–Pt clusters – one of the most interesting nanoalloys with high application potential.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28096-28102
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00277J
Gas phase selective hydrogenation over oxide supported Ni–Au
Ni–Au synergism on Al2O3 and TiO2 generates increased surface reactive hydrogen with elevated reaction rates in the hydrogenation of nitroarenes.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28088-28095
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00282F
Crossover among structural motifs in Pd–Au nanoalloys
The crossovers among the most abundant structural motifs (icosahedra, decahedra and truncated octahedra) of Pd–Au nanoalloys are determined theoretically in a size range between 2 and 7 nm and for three compositions equivalent to Pd3Au, PdAu and PdAu3.
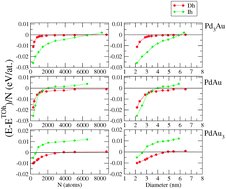
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28129-28136
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00491H
Nanoalloy electrocatalysis: simulating cyclic voltammetry from configurational thermodynamics with adsorbates
Simulated 2-dimensional cyclic voltammetry for nanoalloys with a hybrid ensemble scheme in Monte Carlo simulation based on the cluster expansion method.
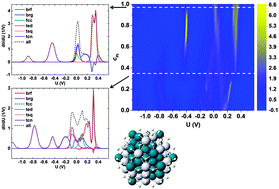
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28103-28111
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00394F
Study of structures and thermodynamics of CuNi nanoalloys using a new DFT-fitted atomistic potential
Structure and thermodynamics of CuNi nanoalloys determined by a new DFT-fitted atomistic potential.
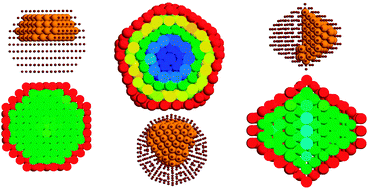
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28068-28075
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00215J
Gold–palladium core@shell nanoalloys: experiments and simulations
In this work, we report a facile synthesis route, structural characterization, and full atomistic simulations of gold–palladium nanoalloys.
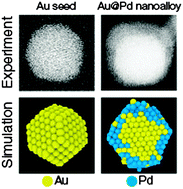
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28060-28067
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP06012A
Metastable alloy nanoparticles, metal-oxide nanocrescents and nanoshells generated by laser ablation in liquid solution: influence of the chemical environment on structure and composition
Metastable nanoalloys, metal-oxide nanocrescents and metal@oxide nanoshells are generated by laser ablation in liquid solution (LASiS).
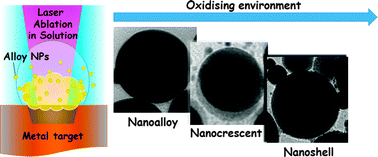
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28076-28087
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00279F
Vibrational properties and specific heat of core–shell Ag–Au icosahedral nanoparticles
The vibrational density of states (VDOS) of metal nanoparticles can be a fingerprint of their geometrical structure and determine their low-temperature thermal properties.
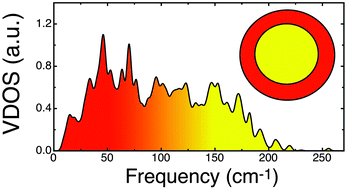
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28054-28059
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00232J
Structural disordering of de-alloyed Pt bimetallic nanocatalysts: the effect on oxygen reduction reaction activity and stability
We show how alloying and excessive de-alloying affect ORR activity and the structural integrity of PEMFC nanocatalysts.
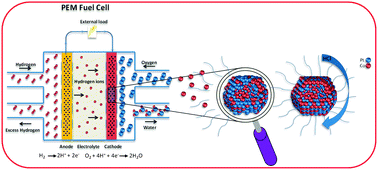
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28044-28053
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP04264F
A new magnetic superatom: Cr@Zn17
We report on the theoretical discovery of a novel magnetic alkali-like superatom, and discuss its possible spintronics or biomedical applications.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28033-28043
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP03753G
Correction: Study of structures and thermodynamics of CuNi nanoalloys using a new DFT-fitted atomistic potential
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015,17, 28407-28407
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP90107C
About this collection
In recent years, the interest in nanoalloys has increased dramatically, both from the points of view of experiment and of computation. Lively research activity has produced impressive advances in controlling the synthesis of nanoalloys. Also imaging and characterization techniques have been notably improved, especially in situ tools. New computational techniques for exploring the nanoalloy energy landscape have been developed, both at the ab-initio and at the atomistic level, together with impressive progress in calculating magnetic and optical properties.
This themed collection presents a thorough account of the most exciting current research in nanoalloys, with articles from the most active groups, who are defining the state of the art in the field. The Guest Editors for this themed collection are Riccardo Ferrando (Università Genova, Italy), Roy L. Johnston (University of Birmingham, UK) and Catherine Louis (UPMC-Paris 6, France).