Themed collection Editors’ Choice Collection

Chromium complexes for luminescence, solar cells, photoredox catalysis, upconversion, and phototriggered NO release
Cr(III) and Cr(0) complexes are earth-abundant alternatives to photosensitizers that are commonly made from precious metals.
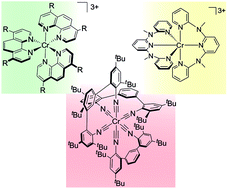
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 7359-7367
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03372A
Fully conjugated ladder polymers
Syntheses, properties and applications of fully conjugated ladder polymers are reviewed, together with an outlook to future opportunities and challenges.
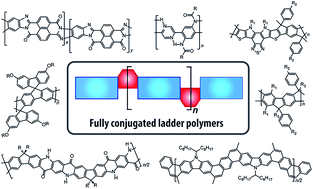
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 2503-2521
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC00154A
Block copolymers: controlling nanostructure to generate functional materials – synthesis, characterization, and engineering
In this perspective, we survey recent advances in the synthesis and characterization of block copolymers, discuss several key materials opportunities enabled by block copolymers, and highlight some of the challenges that currently limit further realization of block copolymers in promising nanoscale applications.
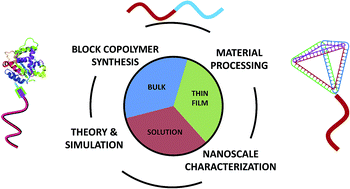
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 1674-1689
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03505H
Mechanochemistry of the mechanical bond
Strong and stable under tension?
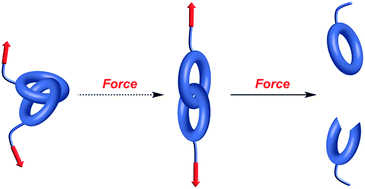
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 15-21
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04200K
Interfacing porphyrins and carbon nanotubes through mechanical links
U-shaped bisporphyrin molecules are clipped around SWCNTs using ring-closing metathesis yielding rotaxane-type derivatives, in which porphyrins and SWCNTs are connected through mechanical links.
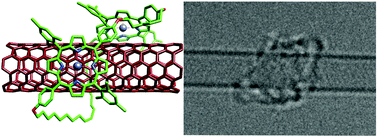
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 6779-6784
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC02492H
Reversibly tuning hydrogel stiffness through photocontrolled dynamic covalent crosslinks
By controlling the stability of dynamic covalent crosslinks with adjacent photoswitches, the stiffness of an adaptable hydrogel is tuned reversibly.
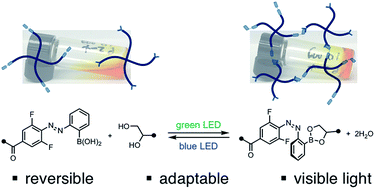
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5987-5993
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC02093K
White-light emission from a single organic compound with unique self-folded conformation and multistimuli responsiveness
White-light emission from a single molecule was realized and tuned via multistimuli including excitation, solvent polarity, temperature and host–guest interactions.
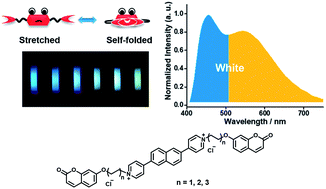
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5709-5715
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01915K
Pyrene hydrogel for promoting direct bioelectrochemistry: ATP-independent electroenzymatic reduction of N2
We demonstrate a novel hydrogel material to facilitate direct bioelectrochemistry of a wide range of redox proteins and enable ATP-independent electroenzymatic reduction of N2 by nitrogenase.
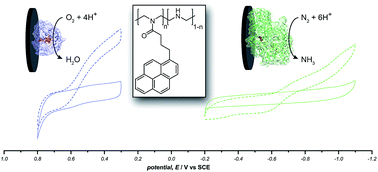
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5172-5177
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01638K
The chemical identity, state and structure of catalytically active centers during the electrochemical CO2 reduction on porous Fe–nitrogen–carbon (Fe–N–C) materials
We report novel structure–activity relationships and explore the chemical state and structure of catalytically active sites under operando conditions during the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) catalyzed by a series of porous iron–nitrogen–carbon (FeNC) catalysts.
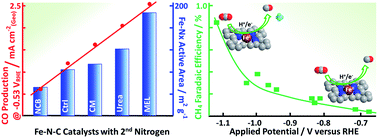
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 5064-5073
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00491A
Phase-segregated NiPx@FePyOz core@shell nanoparticles: ready-to-use nanocatalysts for electro- and photo-catalytic water oxidation through in situ activation by structural transformation and spontaneous ligand removal
The phase-segregated NiPx@FePyOz core@shell NPs act as a colloidally stable, ready-to-use, and excellent OER active transition metal phosphide-based catalyst.
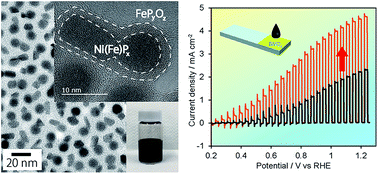
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 4830-4836
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC00420J
Self-assembled orthoester cryptands: orthoester scope, post-functionalization, kinetic locking and tunable degradation kinetics
Self-assembled orthoester cryptands offer appealing properties for applications in ion sensing and transport, such as convenient post-functionalization and tunable biodegradation.
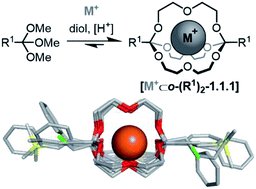
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 4785-4793
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC01750F
Redox and photocatalytic properties of a NiII complex with a macrocyclic biquinazoline (Mabiq) ligand
Upon irradiation with visible light, the NiII complex 1 is converted to the reduced form 2 in the presence of NEt3. The Ni-based photosensitizer catalyzes the cyclization of a bromoalkyl-substituted indole.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 3313-3317
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC05320G
ZnSe quantum dots modified with a Ni(cyclam) catalyst for efficient visible-light driven CO2 reduction in water
A robust precious metal-free photocatalyst system comprised of ligand-free ZnSe quantum dots and a phosphonic acid-functionalised Ni(cyclam) catalyst achieves efficient reduction of aqueous CO2 to CO.
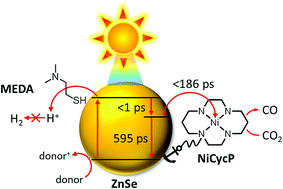
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 2501-2509
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04429A
Understanding light-driven H2 evolution through the electronic tuning of aminopyridine cobalt complexes
Electronic effects provide a general mechanistic scenario for rationalizing photocatalytic water reduction activity with aminopyridine cobalt complexes.
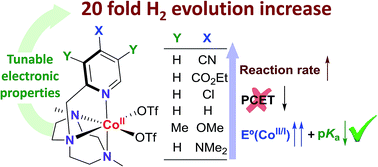
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 2609-2619
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04328G
Extraction of nickel from NiFe-LDH into Ni2P@NiFe hydroxide as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting
Ni2P@FePOx has been synthesized via extraction and selective phosphorization of nickel in NiFe-LDH, and then conversed to a new heterostructure of Ni2P@NiFe hydroxide (P-NiFe) during water splitting. P-NiFe can act as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting.
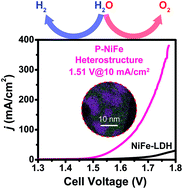
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 1375-1384
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04569G
A highly efficient double-hierarchical sulfur host for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries
A double-hierarchical sulfur host has been synthesized in which hierarchical carbon spheres, constructed from building blocks of hollow carbon nanobubbles used for loading sulfur, are sealed by a polar MoS2 coating that is composed of ultrathin nanosheets (MoS2@HCS composite).
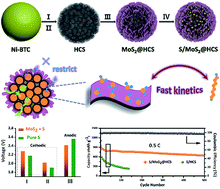
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 666-675
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03960C
Unveiling hole trapping and surface dynamics of NiO nanoparticles
Mesoporous NiO is used as p-type material in photoelectrochemical energy conversion devices. The presence of two kinds of hole traps can affect device performance. Here, after band-gap excitation, the relaxation of the hole into two different traps was observed and characterized.
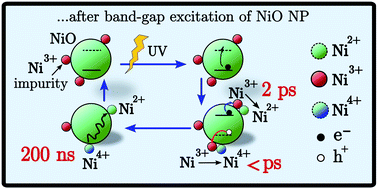
Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 223-230
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03442C
Variations in the fuel structure control the rate of the back and forth motions of a chemically fuelled molecular switch
Moderate variations in the fuel structure cause large changes in the rate of the back and forth motions experienced by a chemically fuelled catenane-based switch.

Chem. Sci., 2018,9, 181-188
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC04123C
Machine learning for quantum dynamics: deep learning of excitation energy transfer properties
Understanding the relationship between the structure of light-harvesting systems and their excitation energy transfer properties is of fundamental importance in many applications including the development of next generation photovoltaics.
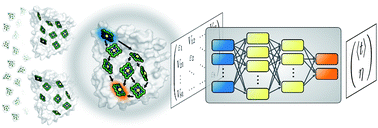
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 8419-8426
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03542J
Bond breakage under pressure in a metal organic framework
The internal free volume of porous materials diminishes upon mechanical compression, and such volume collapse can have chemical consequences.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 8004-8011
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC03786D
Hollowing out MOFs: hierarchical micro- and mesoporous MOFs with tailorable porosity via selective acid etching
We report a new strategy for the synthesis of robust hierarchical micro- and mesoporous MOFs from water stable MOFs via a selective acid etching process.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 6799-6803
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC02886E
Is iron unique in promoting electrical conductivity in MOFs?
Identifying the metal ions that optimize charge transport and charge density in metal–organic frameworks is critical for systematic improvements in the electrical conductivity in these materials.
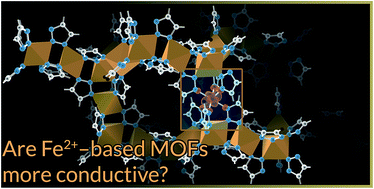
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 4450-4457
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC00647K
Functional metal–organic framework boosting lithium metal anode performance via chemical interactions
Stable-cycling Li metal anode is realized with a MOF layer regulating Li-ion transport and Li deposition via chemical interactions.
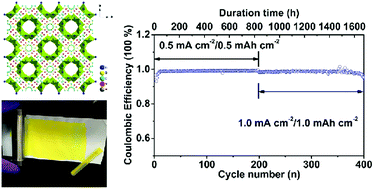
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 4285-4291
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7SC00668C
Effect of ring rotation upon gas adsorption in SIFSIX-3-M (M = Fe, Ni) pillared square grid networks
Dynamic and flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) that respond to external stimuli, such as stress, light, heat, and the presence of guest molecules, hold promise for applications in chemical sensing, drug delivery, gas separations, and catalysis.
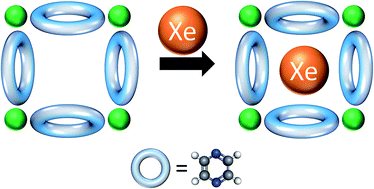
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 2373-2380
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC05012C
AIE-active theranostic system: selective staining and killing of cancer cells
A mitochondrion-specific AIEgen is a theranostic molecule, with the function of lighting up and killing cancer cells rather than normal cells.
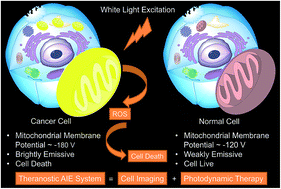
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 1822-1830
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC04947H
Activity modulation and allosteric control of a scaffolded DNAzyme using a dynamic DNA nanostructure
We report a DNA nanotechnology-enabled approach for the rational design of an allosteric deoxyribozyme by precisely and dynamically controlling the nanometer-scale interactions of two catalytic centers within a well-defined tetrahedral DNA scaffold.
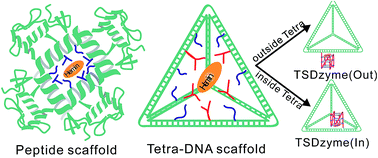
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 1200-1204
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03705K
An enantioselective artificial Suzukiase based on the biotin–streptavidin technology
Introduction of a biotinylated monophosphine palladium complex within streptavidin affords an enantioselective artificial Suzukiase. Site-directed mutagenesis allowed the optimization of the activity and the enantioselectivity of this artificial metalloenzyme. A variety of atropisomeric biaryls were produced in good yields and up to 90% ee.
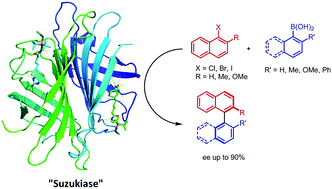
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 673-677
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03116H
Next-generation disulfide stapling: reduction and functional re-bridging all in one
A next-generation disulfide stapling reagent, incorporating both reducing and re-bridging functions, is shown to be successful across various proteins.
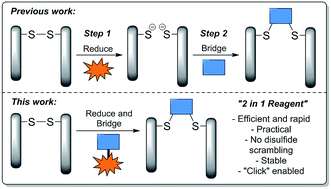
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 799-802
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02666K
Assembly line termination in cylindrocyclophane biosynthesis: discovery of an editing type II thioesterase domain in a type I polyketide synthase
Investigation of cylindrocyclophane biosynthesis reveals a C-terminal thioesterase domain involved in PKS assembly line editing, not termination.
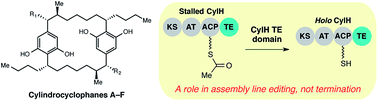
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 3816-3822
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03132F
Polymerization-induced thermal self-assembly (PITSA)
Polymerization-induced thermal self-assembly (PITSA) was conducted using thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) to result in micelle, worm, and vesicle polymeric morphologies.
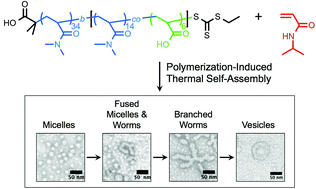
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 1230-1236
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03334E
About this collection
This collection of Chemical Science articles has been put together by a number of our Associate Editors, including Vincent Artero, Luis Campos, Michelle Chang, Mircea Dinca, Steve Goldup and Jihong Yu. These world-leading experts have selected the articles which inspire them, and as all articles in Chemical Science are open access, you can also discover and share the kind of high quality research that they’re passionate about.