Themed collection Food & Function HOT Articles 2024

Correlation between vitamin D metabolic pathway-related gene polymorphisms and cardiovascular disease
Polymorphisms in key genes in the vitamin D metabolic pathway affect susceptibility to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and play potential roles in the pathogenesis of CVD.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 11342-11364
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO03234A
Advances in plant-derived extracellular vesicles: isolation, composition, and biological functions
Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) are nanoscale vesicles released from plant cells into the extracellular space.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 11319-11341
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO04321A
Beyond flavor: the versatile roles of eugenol in health and disease
Emerging evidence highlights that eugenol exhibits significant biological activities across various conditions, suggesting it is a promising nutritional supplement with both flavoring properties and therapeutic potential.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 10567-10581
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02428A
Effect of dietary fibre on cognitive function and mental health in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis
The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of dietary fibre on the mental health and cognitive function of children and adolescents.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 8618-8628
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02221A
Effects of quercetin on the DNA methylation pattern in tumor therapy: an updated review
Quercetin reverses the expression of abnormal genes by regulating DNA methylation, and is an important regulator of gene transcription in tumorigenesis. The use of nanoscale delivery of quercetin increases its bioavailability in cancer therapy.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 3897-3907
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03831A
Edible insects as a source of biopeptides and their role in immunonutrition
Edible insect species are attracting the attention of the food industry and consumers in Western societies due to their high content and quality of protein, which is starting to be evaluated as source of peptides with immunomodulatory properties.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 2789-2798
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03901C
Long-term fucoxanthin treatment prevents cognitive impairments and neuroinflammation via the inhibition of Nogo-A in APP/PS1 transgenic mice
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by neuroinflammation and cognitive impairments.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 3891-3903
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO05034G
Organic acids from ice wine ameliorate fructose-induced disorders of glycolipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice
Studies have confirmed that long-term consumption of ice wine does not induce disorders of glycolipid metabolism, and that the high content of malic and succinic acids in ice wine inhibits the negative effects of fructose to a certain extent.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 3296-3307
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO05580B
Alleviation effects of Lactobacillus plantarum in colitis aggravated by a high-salt diet depend on intestinal barrier protection, NF-κB pathway regulation, and oxidative stress improvement
A schematic of the potential mechanism of HGD228 supplementation in alleviating HSD-exacerbated UC.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 2718-2736
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO06377E
Improving dietary energy and antioxidative properties benefit early maternal BMI and further manage adverse pregnancy outcomes with better weight gain
The proportion of caloric intake derived from different macronutrients and the antioxidative properties of the diet are important factors in managing body weight gain-related gestational outcomes throughout pregnancy in China.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 2687-2702
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO06451H
Effect of long-term moderate red wine consumption in CD1 female mice
The controversial health effects of long-term moderate wine consumption have been evaluated in mice fed a standard or fat diet and supplied with water, or wine or alcohol diluted with water.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 2656-2668
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5FO00435G
Human milk oligosaccharides 2′-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose attenuate ovalbumin-induced food allergy through immunoregulation and gut microbiota modulation
2′-FL and 3-FL may modulate immunity by modulating the gut microbiota, increasing the content of short-chain fatty acids, and enhancing the intestinal barrier function, thus attenuating OVA-induced allergic symptoms.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 1267-1283
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO04638B
Oyster powder supplementation enhances immune function in mice partly through modulating the gut microbiota and arginine metabolism
Oysters are well-known for their health benefits such as immuno-modulatory functions.

Food Funct., 2025,16, 1254-1266
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO06068G
Milk fat globule membranes ameliorate diet-induced obesity in mice by modulating glucolipid metabolism, body inflammation, and oxidative stress
This study aimed to explore the lipid-lowering effect and the mechanism of action of the milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) in obese mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 11903-11917
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO04072D
Along the gut-bone marrow signaling pathway: use of longan polysaccharides to regenerate blood cells after chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression
TLPL promoted the production of Lactobacillus in myelosuppressed mice, and promoted the haematopoiesis of bone marrow cells via the gut-bone marrow axis.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 11888-11902
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO03758H
Allergenicity evaluation of an extensively hydrolyzed infant formula based on cow milk protein
We developed an extensively hydrolyzed infant formula (EHF) with a protein composition similar to breast milk (whey protein-to-casein ratio of 6 : 4) and evaluated its sensitization in vitro and in vivo.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 11036-11046
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO03582H
The influence of magnesium and manganese cations on the chemical and bioactive properties of purple and green basil
Effects of hydroponic cultivation with enriched concentrations of magnesium (+Mg), manganese (+Mn), combinations of +Mg and +Mn, or decreased concentrations of these minerals (control) on the chemical/bioactive attributes of basil, were investigated.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 10644-10662
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02820A
Degradation effects and mechanisms of Limosilactobacillus fermentum on ethanol
Limosilactobacillus fermentum DACN611 degraded ethanol through adaptive metabolic changes under ethanol stress conditions and by promoting alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase activities in gastric and hepatic tissues.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 10283-10299
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02918F
Green tea polyphenols alleviate TBBPA-induced gastric inflammation and apoptosis by modulating the ROS-PERK/IRE-1/ATF6 pathway in mouse models
Green tea polyphenols (GTP), an important phytochemical in the daily human diet, bind to various cellular receptors and exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 10179-10189
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO03012E
Lead toxicity mitigation effect of a Lactiplantibacillus plantarum–chondroitin sulfate complex revealed by microbiome and metabolomic analyses
A complex of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CCFM8661 and chondroitin sulfate alleviates lead toxicity in lead-exposed mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 10110-10120
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02815E
Differential effects of milk, yogurt, and cheese on energy homeostasis and brown adipose tissue phenotype in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
The effects of fat-free milk, fat-free yogurt, and reduced-fat cheese on brown adipose tissue (BAT) thermogenesis in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 9833-9848
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02201G
Proteomic profiles revealed enzymatic activities associated with the flavor formation of salted shrimp paste influenced by Bacillus subtilis K-C3 inoculation
Enzymatic proteomic profiles were examined to comprehend the predominant enzymes involved in the flavor development of salted shrimp paste influenced by Bacillus subtilis K-C3 inoculation (Inoc), compared to those without inoculation (CON).

Food Funct., 2024,15, 9100-9115
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02645D
Effects of konjac glucomannan intake patterns on glucose and lipid metabolism of obese mice induced by a high fat diet
Any type of KGM intake pattern could reduce body weight and fat mass in obese mice. However, KGM sol has the most significant effect on controlling blood glucose and blood lipid.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 9116-9135
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02442G
Construction of chlorogenic acid nanoparticles for effective alleviation of ulcerative colitis
The onset and progression of ulcerative colitis (UC) are intricately linked to the worsening of intestinal inflammation, an imbalance in oxidative stress, and impairment of the intestinal mucosal barrier.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 9085-9099
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02122C
Construction and characterization of stable multi-species biofilms formed by nine core gut bacteria on wheat fiber
Nine core gut bacteria (M9) can successfully form stable and complex multi-species biofilms on wheat fiber through a dynamic fermentation method.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 8674-8688
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO01294A
Improving insulin resistance by sulforaphane via activating the Bacteroides and Lactobacillus SCFAs–GPR–GLP1 signal axis
SFN alleviated IR via the Bacteroides and Lactobacillus-SCFAs–GPR41/43-GLP1 axis and protected the intestinal mucosal barrier, thereby, reducing the inflammatory response.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 8644-8660
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO01059K
N-Glycan profile of the cell membrane as a probe for lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial neuroinflammation uncovers the effects of common fatty acid supplementation
Aberrant glycosylation induced by LPS in the microglial glycocalyx can be restored by dietary and gut microbe-derived fatty acids highlighting their potential to relieve neuroinflammation.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 8258-8273
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO01598C
Circulating low-molecular-weight (poly)phenol metabolites in the brain: unveiling in vitro and in vivo blood–brain barrier transport
Circulating metabolites resulting from colonic metabolism of dietary (poly)phenols are highly abundant in the bloodstream, though still marginally explored, particularly concerning their brain accessibility.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 7812-7827
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO01396D
Pomegranate supplementation alleviates dyslipidemia and the onset of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Wistar rats by shifting microbiota and producing urolithin-like microbial metabolites
Pomegranate supplemetation decreased fat depots, counteracted the dyslipidemia caused by fructose and improved markers of liver injury. Microbial metabolites from pomegranate may be responsible for these health benefits.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 7348-7363
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00688G
Mitigation of high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis by thyme (Thymus quinquecostatus Celak) polyphenol-rich extract (TPE): insights into gut microbiota modulation and bile acid metabolism
Thyme polyphenol-rich extract effectively mitigate HFD- induced NAFLD by modulating the gut-liver axis, specifically targeting the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 7333-7347
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05235D
Carboxymethylated Lycium barbarum seed dreg dietary fiber alleviates high fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in mice via intestinal regulation
The carboxymethylated Lycium barbarum seed dreg insoluble dietary fiber (IDFs) significantly alleviated HFD-induced dyslipidemia, inflammation and hepatocyte degeneration, and ameliorated gut dysbiosis and increased SCFAs levels in obese mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 6955-6965
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO02123A
Associations between dietary macronutrient quality and asthenozoospermia risk: a hospital-based case-control study
Dietary macronutrient quality and asthenozoospermia risk.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 6383-6394
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO01234H
Efficacy and safety of galacto-oligosaccharide in the treatment of functional constipation: randomized clinical trial
The efficacy and safety of galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) in treating functional constipation were evaluated in a four-week randomized, double-blind clinical trial on 63 patients who met Rome IV criteria (34 GOS, 29 placebo group).

Food Funct., 2024,15, 6374-6382
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00999A
Fucoxanthin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier injury in mice
Fx effectively prevents LPS-induced intestinal barrier injury via inhibiting intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 6359-6373
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00611A
Protection effect of lutein-loaded Pickering emulsion prepared via ultrasound-assisted Maillard reaction conjugates on dry age-related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a prominent cause of vision loss among the elderly, and the treatment options for dry AMD (dAMD) are severely limited.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 6347-6358
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00673A
Chronic consumption of a bergamot-based beverage does not affect glucose, lipid and inflammatory biomarkers of cardiometabolic risk in healthy subjects: a randomised controlled intervention study
A bergamot-based beverage does not affect glucose, lipid and inflammatory biomarkers of cardiometabolic risk in healthy subjects.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5842-5854
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00877D
A red-fleshed apple rich in anthocyanins improves endothelial function, reduces inflammation, and modulates the immune system in hypercholesterolemic subjects: the AppleCOR study
Red-fleshed apples (RFA), improve endothelial function and decrease inflammation. RFA induce more improvements in inflammation than aronia infusion (AI), whereas AI improves lipid profile. RFA, white-fleshed apples and AI modulate immune system.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5825-5841
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05114E
Heat-moisture and acid treatments can increase levels of resistant starch in arrowroot starch without adversely affecting its prebiotic activity in human colon microbiota
Carbohydrates are an important macronutrient whose processing and digestive fate can have numerous beneficial or adverse effects on consumer health.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5813-5824
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00711E
Efficient regioselective enzymatic acylation of troxerutin: difference characterization of in vitro cellular uptake and cytotoxicity
Multi-site acylation of troxerutin can solve the problems of cytotoxicity and rapid hydrolysis of ester bonds caused by mono-acylation and increase cellular uptake.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5785-5796
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00906A
Long-term administration of royal jelly regulates age-related disorders and improves gut function in naturally aging mice
A natural aging mouse model can exhibit physiological characteristics that closely resemble those of human aging.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5272-5286
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00781F
The dairy-derived peptide Miltin exerts anti-obesity effects by increasing adipocyte thermogenesis
Miltin, a dairy-derived peptide, activates the thermogenic programs in brown and white adipocytes by directly interacting with GADD45r.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5300-5314
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05704F
Bioactive components and mechanisms of Pu-erh tea in improving levodopa metabolism in rats through COMT inhibition
Pu-erh tea can enhance the efficacy of levodopa in treating Parkinson's disease by inhibiting COMT activity and improving levodopa's pharmacokinetic behavior in rats.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 5287-5299
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00538D
Litchi pulp-derived gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) extract counteracts liver inflammation induced by litchi thaumatin-like protein
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the predominant amino acid in litchi pulp, known for its neuroregulatory effects and anti-inflammatory properties.
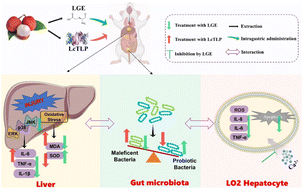
Food Funct., 2024,15, 4818-4831
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05463B
The synergism of Lactobacillaceae, inulin, polyglucose, and aerobic exercise ameliorates hyperglycemia by modulating the gut microbiota community and the metabolic profiles in db/db mice
This study aimed to assess the impact of Lactobacillaceae (L or H represents a low or high dose), inulin (I), and polydextrose (P) combined with aerobic exercise (A) on the composition of the gut microbiota and metabolic profiles in db/db mice.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4832-4851
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04642G
Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum NCU-08 ameliorated senescence via modulation of the AMPK/Sirt1 signaling pathway and gut microbiota in mice
Mechanisms of B. pseudocatenulatum NCU-08 in mitigating aging via the microbiota–gut–brain axis.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4095-4108
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO04575G
Nutritional profiling, fiber content and in vitro bioactivities of wheat-based biscuits formulated with novel ingredients
Designing a cereal-based product with added nutritional value and health-enhancing effects.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4051-4064
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00204K
Increased nitrate intake from beetroot juice over 4 weeks affects nitrate metabolism, but not vascular function or blood pressure in older adults with hypertension
In this randomized placebo-controlled crossover study, we evaluated whether previously reported cardiovascular benefits of plant-derived inorganic nitrate via NO translate into improved vascular function and blood pressure-lowering in middle-aged and older men and women with treated hypertension.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4065-4078
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03749E
Structure characteristics, protective effect and mechanisms of ethanol-fractional polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale on acute ethanol-induced gastritis
Gastritis is a common disease characterized by gastric ulcers and severe bleeding.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4079-4094
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05540J
Long-term intake of thermo-induced oxidized oil results in anxiety-like and depression-like behaviors: involvement of microglia and astrocytes
Frequent consumption of fried foods has been strongly associated with a higher risk of anxiety and depression, particularly among young individuals.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 4037-4050
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05302D
Dietary lipoic acid alleviates autism-like behavior induced by acrylamide in adolescent mice: the potential involvement of the gut–brain axis
Lipoic acid (LA) ameliorated acrylamide (ACR)-induced social impairment in adolescent mice. Lipoic acid (LA) reshaped gut microbiota and its metabolites. Lipoic acid (LA) regulated serum amino acid level.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 3395-3410
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05078E
Green tea polyphenols inhibit TBBPA-induced lung injury via enhancing antioxidant capacity and modulating the NF-κB pathway in mice
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a global pollutant. When TBBPA is absorbed by the body through various routes, it can have a wide range of harmful effects on the body.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 3411-3419
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FO00480A
Neuroprotective effects of probiotics on anxiety- and depression-like disorders in stressed mice by modulating tryptophan metabolism and the gut microbiota
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum D-9 shows neuroprotective effects on anxiety- and depression-like disorders in CUMS mice by modulating tryptophan metabolism and the gut microbiota.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 2895-2905
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03897A
Exploring novel Kokumi peptides in Agaricus bisporus: selection, identification, and tasting mechanism investigation through sensory evaluation and computer simulation analysis
Two novel Kokumi peptides, identified from Agaricus bisporus via sensory and computer analyses, potentially enhance umami taste and reduce salt intake.

Food Funct., 2024,15, 2879-2894
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO05406C
Association between adequate dietary protein and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with selective glomerular hypofiltration syndrome
We studied how protein intake and sources affect selective glomerular hypofiltration syndrome patients' mortality. More protein (mainly from non-red meat) lowered death risk by 40% (all-cause) and 88% (cardiovascular).

Food Funct., 2024,15, 2433-2442
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3FO03212D
About this collection
This themed collection features articles published in Food & Function marked as HOT by the handling editor or as recommended by referees. Congratulations to all the authors whose articles are featured.